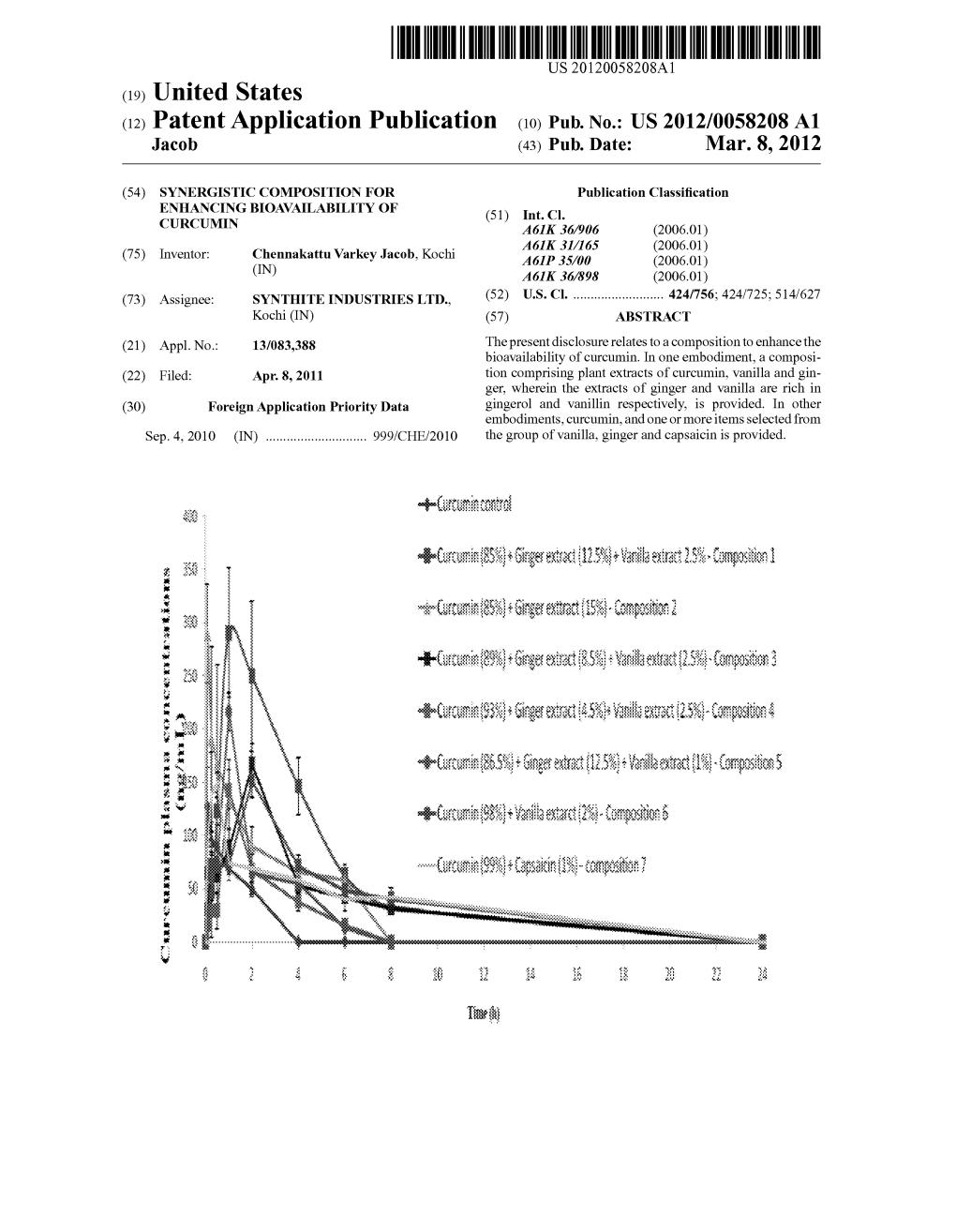
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0058208A1 Jacob (43) Pub
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-
![[6]-Gingerol in Db/Db Mice](https://docslib.b-cdn.net/cover/5809/6-gingerol-in-db-db-mice-495809.webp)
[6]-Gingerol in Db/Db Mice
International Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences. Vol. 1(12), pp. 536-544, December, 2009. Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ijmms ISSN 2006-9723 ©2009 Academic Journals Full Length Research Paper Anti-hyperglycaemic, lipid lowering and anti-oxidant properties of [6]-gingerol in db/db mice Amar Bahadur Singh1, Akanksha2, Nilendra Singh3, Rakesh Maurya2 and Arvind Kumar Srivastava1* 1Biochemistry Division, Central Drug Research Institute, Lucknow-226001, India. 2Medicinal and Process Chemistry Division, CDRI, Lucknow-226001, India. 3Pharmacology Division CDRI, Lucknow-226001, India. Accepted 3 August, 2009 In the present study, we investigated the blood glucose lowering, lipid lowering and antioxidant effect of [6]- gingerol in type 2 diabetic db/db mice. Treatment of db/db mice with [6]-gingerol (100 mg/kg bw) for 12 days significantly (p<0.05) lowered fasting blood glucose and improved the glucose tolerance in db/db mice. Oral administration of [6]-gingerol also significantly (p < 0.05) decreased plasma triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), free fatty acid (FFA), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and plasma insulin concentration. In addition, [6]-gingerol significantly (p < 0.05) reduces the content of hydrogen peroxide or suppresses the reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and restores the enzyme activity of catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GPx) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) in db/db mice. These findings suggest that [6]-gingerol exhibits a significant potential as an anti-hyperglycaemic, lipid lowering and anti- oxidant agent for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Key words: Antihyperglycaemic, antioxidant, antilipidemic, reactive oxygen species, db/db mice, [6]-gingerol. INTRODUCTION Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disease which stress, which is believed to be a pathogenetic factor in now afflicts approximately 3% of the world population. -

Phase II Study of the Effects of Ginger Root Extract on Eicosanoids in Colon Mucosa in People at Normal Risk for Colorectal Cancer
Published OnlineFirst October 11, 2011; DOI: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-11-0224 Cancer Prevention Research Article Research Phase II Study of the Effects of Ginger Root Extract on Eicosanoids in Colon Mucosa in People at Normal Risk for Colorectal Cancer Suzanna M. Zick1, D. Kim Turgeon3, Shaiju K. Vareed6, Mack T. Ruffin1, Amie J. Litzinger1, Benjamin D. Wright1, Sara Alrawi1, Daniel P. Normolle2, Zora Djuric1, and Dean E. Brenner3,4,5 Abstract Inhibitors of COX indicate that upregulation of inflammatory eicosanoids produced by COX, and in particular prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), are early events in the development of colorectal cancer (CRC). Ginger has shown downregulation of COX in vitro and decreased incidence/multiplicity of adenomas in rats. This study was conducted to determine if 2.0 g/d of ginger could decrease the levels of PGE2, 13-hydroxy- octadecadienoic acids, and 5-, 12-, and 15-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (5-, 12-, and 15-HETE), in the colon mucosa of healthy volunteers. To investigate this aim, we randomized 30 subjects to 2.0 g/d ginger or placebo for 28 days. Flexible sigmoidoscopy at baseline and day 28 was used to obtain colon biopsies. A liquid chromatography mass spectrometry method was used to determine eicosanoid levels in the biopsies, and levels were expressed per protein or per free arachidonic acid. There were no significant differences in mean percent change between baseline and day 28 for any of the eicosanoids, when normalized to protein. There was a significant decrease in mean percent change in PGE2 (P ¼ 0.05) and 5-HETE (P ¼ 0.04), and a trend toward significant decreases in 12-HETE (P ¼ 0.09) and 15-HETE (P ¼ 0.06) normalized to free arachidonic acid. -

Dietary Compounds for Targeting Prostate Cancer
Review Dietary Compounds for Targeting Prostate Cancer Seungjin Noh 1, Eunseok Choi 1, Cho-Hyun Hwang 1, Ji Hoon Jung 2, Sung-Hoon Kim 2 and Bonglee Kim 1,2,* 1 College of Korean Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul 02453, Korea; [email protected] (S.N.); [email protected] (E.C.); [email protected] (C.-H.H.) 2 Department of Pathology, College of Korean Medicine, Graduate School, Kyung Hee University, Seoul 02453, Korea; [email protected] (J.H.J.); [email protected] (S.-H.K.) * Correspondence: [email protected]; Tel.: +82-2-961-9217 Received: 10 August 2019; Accepted: 17 September 2019; Published: 8 October 2019 Abstract: Prostate cancer is the third most common cancer worldwide, and the burden of the disease is increased. Although several chemotherapies have been used, concerns about the side effects have been raised, and development of alternative therapy is inevitable. The purpose of this study is to prove the efficacy of dietary substances as a source of anti-tumor drugs by identifying their carcinostatic activities in specific pathological mechanisms. According to numerous studies, dietary substances were effective through following five mechanisms; apoptosis, anti-angiogenesis, anti- metastasis, microRNA (miRNA) regulation, and anti-multi-drug-resistance (MDR). About seventy dietary substances showed the anti-prostate cancer activities. Most of the substances induced the apoptosis, especially acting on the mechanism of caspase and poly adenosine diphosphate ribose polymerase (PARP) cleavage. These findings support that dietary compounds have potential to be used as anticancer agents as both food supplements and direct clinical drugs. -

Transient Receptor Potential Channels and Metabolism
Molecules and Cells Minireview Transient Receptor Potential Channels and Metabolism Subash Dhakal and Youngseok Lee* Department of Bio and Fermentation Convergence Technology, Kookmin University, BK21 PLUS Project, Seoul 02707, Korea *Correspondence: [email protected] https://doi.org/10.14348/molcells.2019.0007 www.molcells.org Transient receptor potential (TRP) channels are nonselective Montell, 2007). These cationic channels were first charac- cationic channels, conserved among flies to humans. Most terized in the vinegar fly, Drosophila melanogaster. While TRP channels have well known functions in chemosensation, a visual mechanism using forward genetic screening was thermosensation, and mechanosensation. In addition to being studied, a mutant fly showed a transient response to being sensing environmental changes, many TRP channels constant light instead of the continuous electroretinogram are also internal sensors that help maintain homeostasis. response recorded in the wild type (Cosens and Manning, Recent improvements to analytical methods for genomics 1969). Therefore, the mutant was named as transient recep- and metabolomics allow us to investigate these channels tor potential (trp). In the beginning, researchers had spent in both mutant animals and humans. In this review, we two decades discovering the trp locus with the germ-line discuss three aspects of TRP channels, which are their role transformation of the genomic region (Montell and Rubin, in metabolism, their functional characteristics, and their 1989). Using a detailed structural permeation property anal- role in metabolic syndrome. First, we introduce each TRP ysis in light-induced current, the TRP channel was confirmed channel superfamily and their particular roles in metabolism. as a six transmembrane domain protein, bearing a structural Second, we provide evidence for which metabolites TRP resemblance to a calcium-permeable cation channel (Mon- channels affect, such as lipids or glucose. -

Ginger Between 10-Gingerol and the Second Prominent Band DEFINITION Corresponding to 6-Shogaol in Standard Solution A
Printed on: Tue Dec 22 2020, 02:55:47 AM Official Status: Currently Official on 22-Dec-2020 DocId: 1_GUID-4E7E04A2-8C5A-4586-A11D-B67425D4CA8D_2_en-US (EST) Printed by: Jinjiang Yang Official Date: Official as of 01-Aug-2016 Document Type: DIETARY SUPPLEMENTS @2020 USPC 1 variable number of low-intensity dark-gray bands appear Ginger between 10-gingerol and the second prominent band DEFINITION corresponding to 6-shogaol in Standard solution A. In the Ginger is the dried rhizome of Zingiber officinale Roscoe (Fam. distal part of the chromatogram, a dark-purple Zingiberaceae), scraped, partially scraped, or unscraped. It is somewhat diffuse band is observed. Under long-wave known in commerce as unbleached ginger. UV (365 nm), the chromatograms of the Standard solutions exhibit patterns similar to those observed under IDENTIFICATION white light. The bands due to gingerols and shogaols are · A. bright orange; the bands between the origin and the Analysis: Pulverize 5 g of Ginger. To 1 g of the pulverized 6-gingerol band are dark-red to brown, somewhat less Ginger add 5 mL of dilute acetic acid, prepared by diluting prominent than when observed in white light. The 1 part of glacial acetic acid with 1 part of water, and shake bands between 10-gingerol and 6-shogaol are variably for 15 min. Filter, and add a few drops of ammonium colored; frequently, a light-gray band appears halfway oxalate TS to the filtrate. between them, with a light-purple diffuse band between Acceptance criteria: NMT a slight turbidity is produced. it and the orange band due to 6-shogaol. -

Growth Stimulation of Bifidobacterium from Human Colon Using
www.nature.com/scientificreports OPEN Growth stimulation of Bifdobacterium from human colon using daikenchuto in an in vitro model of human intestinal microbiota Kengo Sasaki1*, Daisuke Sasaki1, Katsunori Sasaki2, Yuto Nishidono3, Akihiro Yamamori2, Ken Tanaka3 & Akihiko Kondo1,4 Daikenchuto (DKT) is a Japanese traditional herbal (Kampo) medicine containing ginseng, processed ginger, and Japanese or Chinese pepper. We aimed to determine how DKT afects human colonic microbiota. An in vitro microbiota model was established using fecal inocula collected from nine healthy volunteers, and each model was found to retain operational taxonomic units similar to the ones in the original human fecal samples. DKT was added to the in vitro microbiota model culture at a concentration of 0.5% by weight. Next-generation sequencing of bacterial 16S rRNA gene revealed a signifcant increase in the relative abundance of bacteria related to the Bifdobacterium genus in the model after incubation with DKT. In pure cultures, DKT signifcantly promoted the growth of Bifdobacterium adolescentis, but not that of Fusobacterium nucleatum or Escherichia coli. Additionally, in pure cultures, B. adolescentis transformed ginsenoside Rc to Rd, which was then probably utilized for its growth. Our study reveals the in vitro bifdogenic efect of DKT that likely contributes to its benefcial efects on the human colon. Daikenchuto (DKT) is a traditional herbal (Kampo) medicine in Japan that comprises three medicinal herbs: gin- seng (Panax ginseng), Japanese pepper (Zanthoxylum piperitum) or Chinese pepper (Zanthoxylum bungeanum), and processed ginger (Zingiber ofcinale)1. DKT is prepared by mixing the herbs, followed by extraction using hot water and fnally converting the extract into a powder or sof form 1. -

Balancing Heat and Flavor
[Seasonings & Spices] Vol. 21 No. 1 January 2011 ww Balancing Heat and Flavor By Joseph Antonio, Contributing Editor During a recent culinary visit to Oaxaca, Mexico, I experienced a part of Mexican culture and cuisine that helped me gain a deeper understanding of how distinct ingredients, particularly chiles, help define a region’s food culture. Just seeing the plethora of chiles that go into the many different moles, for example, was awe- inspiring from a chef’s perspective. Each of those chiles has characteristics that can add layers of complexity to a dish. Chiles, as well as other pungent ingredients like ginger, horseradish, wasabi, mustard and peppercorns, can either play the leading role in a food’s performance or serve an important part of the supporting cast. Certain chemical compounds in chile peppers, peppercorns, ginger, galangal, wasabi, horseradish and mustard seeds, such as capsaicin, piperine, gingerol and allyl isothiocyanate, affect the senses to give the characteristic “spice" or “heat." Those trigeminal flavors can be accentuated by adding other strong, complementary flavor profiles, or subdued by contrasting, elements. Balancing those heat-imbuing components with other flavors, such as those from fruits, nuts, spices and seasonings, and other vegetables, can lead to some truly inspired creations. Chile connections Chiles are used in many cuisines from Southeast Asia to Latin America to Europe. Chiles’ placental walls contain capsaicin, which contributes the burning sensation. Each chile, whether fresh or dried, also contributes its own distinct flavor. There are chile peppers of all shapes, sizes and forms. They come in all heat levels, from a mild bell pepper to a fiery bhut jolokia, or “ghost chile." Chiles come in many forms the chef and product developer can use: fresh, dried, pickled and fermented, to name a few. -

(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0285919 A1 Alberte Et Al
US 20090285919A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0285919 A1 Alberte et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2009 (54) RCE BRAN EXTRACTS FOR filed on Sep. 30, 2008, provisional application No. NFLAMMATION AND METHODS OF USE 61/147,305, filed on Jan. 26, 2009. THEREOF Publication Classification (76) Inventors: Randall S. Alberte, Estero, FL (51) Int. Cl. (US); William P. Roschek, JR., A 6LX 36/899 (2006.01) Naples, FL (US) A2.3L I/28 (2006.01) Correspondence Address: A6IP 29/00 (2006.01) FOLEY HOAG, LLP A6IP 25/00 (2006.01) PATENT GROUP, WORLD TRADE CENTER A6IP35/00 (2006.01) WEST (52) U.S. Cl. ......................................... 424/750; 426/655 155 SEAPORT BLVD BOSTON, MA 02110 (US) (57) ABSTRACT The present invention relates in part to stabilized rice bran (21) Appl. No.: 12/467,835 extracts enriched in compounds that have inhibitory activity against certain anti-inflammatory therapeutic endpoints, such (22) Filed: May 18, 2009 as the COX-1, COX-2 and 5-LOX enzymes. Another aspect of the invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions com Related U.S. Application Data prising the extracts and to methods of treating inflammatory (60) Provisional application No. 61/054,151, filed on May diseases comprising administering the aforementioned 18, 2008, provisional application No. 61/101.475, eXtractS. Patent Application Publication Nov. 19, 2009 Sheet 1 of 6 US 2009/0285919 A1 Figure l Arachidonic Acid NSAIDs inhibition Prostaglandins PRO-NFLAMMATORY Arthritis (OA & RA) Patent Application Publication Nov. 19, 2009 Sheet 2 of 6 US 2009/0285919 A1 S.---------------Sssssssssss &s asy xxx s -Yvxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxx-xxxxxxxxxx:x O SSSSS i Patent Application Publication Nov. -

Isolation and Characterization of Natural
ABSTRACT OF THE DISSERTATION ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF NATURAL PRODUCTS FROM GINGER AND ALLIUM URSINUM BY HOU WU Dissertation Director: Dr. Chi-Tang Ho Phenolic compounds from natural sources are receiving increasing attention recent years since they were reported to have a remarkable spectrum of biological activities including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-carcinogenic activities. They may have many health benefits and can be considered possible chemo- preventive agents against cancer. In this research, we attempted to isolate and characterize phenolic compounds from two food sources: ginger and Allium ursinum. Solvent extraction and a series of column chromatography methods were used for isolation of compounds, while structures were elucidated by integration of data from MS, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, HMBC and HMQC. Antioxidant activities were evaluated by DPPH method and anti- inflammatory activities were assessed by nitric oxide production model. Ginger is one of most widely used spices. It has a long history of medicinal use dating back 2500 years. Although there have been many reports concerning ii chemical constituents and some biological activities of ginger, most works used ginger extracts or focused on gingerols to study the biological activities of ginger. We suggest that the bioactivities of shogaols are also very important since shogaols are more stable than gingerols and a considerable amount of gingerols will be converted to shogaols in ginger products. In present work, eight phenolic compounds were isolated and identified from ginger extract. They included 6-gingerol, 8-gingerol, 10- gingerol, 6-shogaol, 8—shogaols, 10-shogaol, 6-paradol and 1-dehydro-6-gingerdione. DPPH study showed that 6-shogaol had a comparable antioxidant activity compared with 6-gingerol, the 50% DPPH scavenge concentrations of both compounds were 21 µM. -

6-Shogaol Protects Human Melanocytes Against Oxidative Stress Through Activation of the Nrf2-Antioxidant Response Element Signaling Pathway
International Journal of Molecular Sciences Article 6-Shogaol Protects Human Melanocytes against Oxidative Stress through Activation of the Nrf2-Antioxidant Response Element Signaling Pathway Lingli Yang 1,2,*, Fei Yang 2, Lanting Teng 2 and Ichiro Katayama 1,2 1 Department of Pigmentation Research and Therapeutics, Graduate School of Medicine, Osaka City University, Osaka 545-0041, Japan; [email protected] 2 Department of Dermatology, Course of Integrated Medicine, Graduate School of Medicine, Osaka University, Osaka 565-0871, Japan; [email protected] (F.Y.); [email protected] (L.T.) * Correspondence: [email protected]; Tel.: +81-6-6556-7618; Fax: +81-6-6556-7618 Received: 1 April 2020; Accepted: 14 May 2020; Published: 16 May 2020 Abstract: Skin is a major target of oxidative stress. Increasing evidence suggests that oxidative stress is the cause of melanocyte disappearance in vitiligo, which is an acquired pigmentary skin disorder characterized by patches of skin that have lost pigmentation. New herbal extracts with antioxidant activity are therefore being studied. 6-Shogaol (6-SG), an active compound from ginger, is capable of attenuating oxidative stress-induced ageing and neurotoxicity. Subsequently, to investigate whether 6-SG could protect melanocytes from oxidative stress, cultured human primary epidermal melanocytes (HEMn-MPs) were treated with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in the presence or absence of 6-SG. The 6-SG exhibited protective effects against H2O2-induced cell death by reducing oxidative stress. In addition, the 6-SG treatment activated the Nrf2-antioxidant response element signaling pathway by upregulating the mRNA expression of the antioxidant enzyme heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1), and protein expression of Nrf2, NAD(P)H: quinine oxidoreductase 1 (Nqo1), and HO-1. -

Simultaneous Determination of 6-Shogaol and 6-Gingerol In
foods Article Simultaneous Determination of 6-Shogaol and 6-Gingerol in Various Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) Extracts and Commercial Formulations Using a Green RP-HPTLC-Densitometry Method Ahmed I. Foudah 1 , Faiyaz Shakeel 2 , Hasan S. Yusufoglu 1, Samir A. Ross 3,4 and Prawez Alam 1,* 1 Department of Pharmacognosy, College of Pharmacy, Prince Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University, Al-Kharj 11942, Saudi Arabia; [email protected] (A.I.F.); [email protected] (H.S.Y.) 2 Department of Pharmaceutics, College of Pharmacy, King Saud University, Riyadh 11451, Saudi Arabia; [email protected] 3 National Center for Natural Products Research, University of Mississippi, Oxford, MS 38677, USA; [email protected] 4 Department of Biomolecular Sciences, School of Pharmacy, University of Mississippi, Oxford, MS 38677, USA * Correspondence: [email protected] Received: 14 July 2020; Accepted: 11 August 2020; Published: 18 August 2020 Abstract: Various analytical methodologies have been reported for the determination of 6-shogaol (6-SHO) and 6-gingerol (6-GIN) in ginger extracts and commercial formulations. However, green analytical methods for the determination of 6-SHO and 6-GIN, either alone or in combination, have not yet been reported in literature. Hence, the present study was aimed to develop a rapid, simple, and cheaper green reversed phase high-performance thin-layer chromatography (RP-HPTLC) densitometry method for the simultaneous determination of 6-SHO and 6-GIN in the traditional and ultrasonication-assisted extracts of ginger rhizome, commercial ginger powder, commercial capsules, and commercial ginger teas. The simultaneous analysis of 6-SHO and 6-GIN was carried out via RP-18 silica gel 60 F254S HPTLC plates. -

Potential Inhibitor of COVID-19 Main Protease (Mpro) from Several Medicinal Plant Compounds by Molecular Docking Study
Preprints (www.preprints.org) | NOT PEER-REVIEWED | Posted: 13 March 2020 doi:10.20944/preprints202003.0226.v1 Article Potential Inhibitor of COVID-19 Main Protease (Mpro) from Several Medicinal Plant Compounds by Molecular Docking Study Siti Khaerunnisa 1,*, Hendra Kurniawan 2,3*, Rizki Awaluddin 4, Suhartati Suhartati5, Soetjipto Soetjipto 1,* 1 Departement of Medical Biochemistry, Faculty of Medicine, Airlangga University, Surabaya, East Java, Indonesia, 60132; [email protected]; [email protected] 2 Departement of Medical and Surgical Nursing, Faculty of Health Science, University of Muhammadiyah Jember, Jember, East Java, Indonesia, 68121; [email protected] 3 PhD Student, Tropical Disease Research Center, Faculty of Medicine. Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen, Thailand, 40002; [email protected] 4 Departement of Pharmacy, Faculty of Health Science, University of Darussalam Gontor, Ponorogo, East Java, Indonesia, 63471; [email protected] 5 Departement of Medical Biochemistry, Faculty of Medicine, University of Wijaya Kusuma Surabaya, East Java, Indonesia, 60225; [email protected] * Correspondence: [email protected] ; Tel.: +6281233118194 (S.K.); [email protected]; Tel.: +6281331340518 (S.S.); [email protected] ; Tel.: +628113572277 (H.K.) Abstract: COVID-19, a new strain of coronavirus (CoV), was identified in Wuhan, China, in 2019. No specific therapies are available and investigations regarding COVID-19 treatment are lacking. Liu et al. (2020) successfully crystallised the COVID-19 main protease (Mpro), which is a potential drug target. The present study aimed to assess bioactive compounds found in medicinal plants as potential COVID-19 Mpro inhibitors, using a molecular docking study.