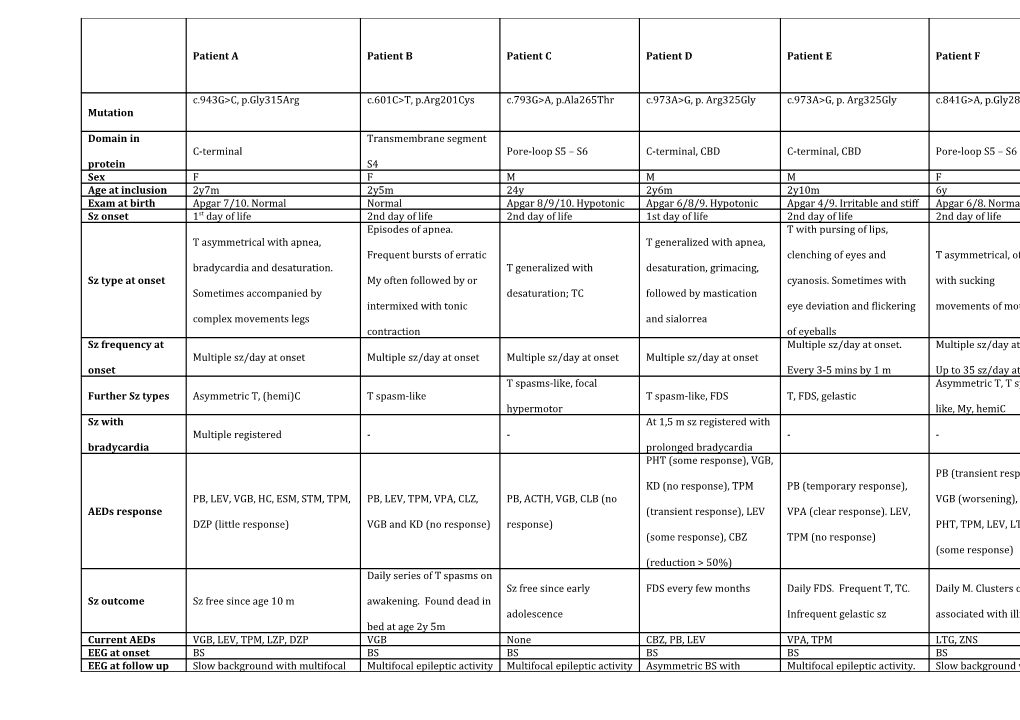
Patient A Patient B Patient C Patient D Patient E Patient F
c.943G>C, p.Gly315Arg c.601C>T, p.Arg201Cys c.793G>A, p.Ala265Thr c.973A>G, p. Arg325Gly c.973A>G, p. Arg325Gly c.841G>A, p.Gly281Arg Mutation
Domain in Transmembrane segment C-terminal Pore-loop S5 – S6 C-terminal, CBD C-terminal, CBD Pore-loop S5 – S6 protein S4 Sex F F M M M F Age at inclusion 2y7m 2y5m 24y 2y6m 2y10m 6y Exam at birth Apgar 7/10. Normal Normal Apgar 8/9/10. Hypotonic Apgar 6/8/9. Hypotonic Apgar 4/9. Irritable and stiff Apgar 6/8. Normal Sz onset 1st day of life 2nd day of life 2nd day of life 1st day of life 2nd day of life 2nd day of life Episodes of apnea. T with pursing of lips, T asymmetrical with apnea, T generalized with apnea, Frequent bursts of erratic clenching of eyes and T asymmetrical, often bradycardia and desaturation. T generalized with desaturation, grimacing, Sz type at onset My often followed by or cyanosis. Sometimes with with sucking Sometimes accompanied by desaturation; TC followed by mastication intermixed with tonic eye deviation and flickering movements of mouth complex movements legs and sialorrea contraction of eyeballs Sz frequency at Multiple sz/day at onset. Multiple sz/day at onset. Multiple sz/day at onset Multiple sz/day at onset Multiple sz/day at onset Multiple sz/day at onset onset Every 3-5 mins by 1 m Up to 35 sz/day at 1.5 m T spasms-like, focal Asymmetric T, T spasm- Further Sz types Asymmetric T, (hemi)C T spasm-like T spasm-like, FDS T, FDS, gelastic hypermotor like, My, hemiC Sz with At 1,5 m sz registered with Multiple registered - - - - bradycardia prolonged bradycardia PHT (some response), VGB, PB (transient response), KD (no response), TPM PB (temporary response), PB, LEV, VGB, HC, ESM, STM, TPM, PB, LEV, TPM, VPA, CLZ, PB, ACTH, VGB, CLB (no VGB (worsening), VPA, AEDs response (transient response), LEV VPA (clear response). LEV, DZP (little response) VGB and KD (no response) response) PHT, TPM, LEV, LTG, KD (some response), CBZ TPM (no response) (some response) (reduction > 50%) Daily series of T spasms on Sz free since early FDS every few months Daily FDS. Frequent T, TC. Daily M. Clusters of TC Sz outcome Sz free since age 10 m awakening. Found dead in adolescence Infrequent gelastic sz associated with illness bed at age 2y 5m Current AEDs VGB, LEV, TPM, LZP, DZP VGB None CBZ, PB, LEV VPA, TPM LTG, ZNS EEG at onset BS BS BS BS BS BS EEG at follow up Slow background with multifocal Multifocal epileptic activity Multifocal epileptic activity Asymmetric BS with Multifocal epileptic activity. Slow background with multifocal epileptic multifocal epileptic epileptic activity activity. EEG at 7 m: normal activity Later only BS during sleep Multifocal epileptic Frequent multifocal Nearly continuous Last EEG Slow background activity, Mild slow background activity activity, increasing with Slow background activity (poly)spike waves , nearly multifocal sharp waves multifocal epileptic activity sleep continuous at times and spikes Profound ID. Never normal.
Regression at 7-10 m Cognition Profound ID Profound ID Profound ID Profound ID Profound ID without evidence of sz , and
at ~2 y Severe axial hypotonia. Wheelchaired from Axial hypotonia, absent Axial hypotonia, sparse Axial hypotonia, limb No head control, no Axial hypotonia. No visual contact. childhood, axial hypotonia, speech, nystagmus. Limb Neurological spontaneous movements. spasticity. No grasping or fixation, no speech. Intermittently dystonic posture of pyramidal tetraparesis , hypertonia. Episodes of examination Does not sit, no visual eye reaching, poor head control, Incoordinated fingers poor speech with non-epileptic dystonic contact no fixing or following movements. Startle dysarthria, nystagmus opisthotonus response to noise Cleft soft palate. Recurrent Isolated COX deficiency
respiratory infections. (40% residual activity).
Gastro-intestinal tube. Mitochondrial DNA and Swallowing difficulties with Additional Respiratory impairment all known COX gastro-intestinal tube since age 6 features due to severe hypotonia deficiency genes normal. m with need of oxygen Secondary to frequent
supplementation sz?. Gastro-intestinal
tube
Table 1 continued Patient G Patient H Patient I Patient J Patient K
c.629G>A, p.Arg210His c.629G>A, p.Arg210His c.1655A>C, p.Lys552Thr c.1687G>A, p.Asp563Asn c.1666A>G, p.Lys556Glu Mutation
Domain in protein Transmembrane segment S4 Transmembrane segment S4 C-terminal, CBD C-terminal, CBD C-terminal, CBD Sex F M F F F 8y (limited clinical info on Age at inclusion 1y5m 1y7m 2y 14y first 4 y of life available) Born at 36.5 weeks. Apgar Exam at birth Normal Normal Normal Long partus, Apgar 6/8 9/9 Sz onset 1st day of life 1st day of life 3th day of life 1st day of life 2nd day of life On day 2 fed poorly,
difficult to rouse and
jaundiced; dusky episodes T asymmetrical with apnea and T asymmetrical with prolonged Sz type at onset T asymmetrical; hemiC T generalized witnessed. On day 3 cyanosis apnea, cyanosis apnoeic episodes.
Asymmetric T on d3, d8,
d10 and d17 Multiple sz/day, from w2 nearly Multiple sz/day, at d5 leading to Little info available. Sz frequency at onset Multiple sz/day at onset Seizures at d2 and d10 continuous sz for several days intubation and transfer to IC Probably < daily Further sz types T, (hemi)C Asymmetric T, T-vibratory Asymmetric T, (hemi)C T, T spasm-like, TC T, TC, FDS Sz with bradycardia - Two sz registered - - - PB (no response). CBZ since age PB (sedating), CBZ (little 10d: rare T sz (2m, 9m, 10m). At PB, LEV, VGB: sz free between 1-4 response). Sz every 3 10m change to VPA. Exacerbation PB, MDZ (no response), PHT PB (no response), PHT m. Then re-occurrence of sz. Start months on PHT and B6 of sz at 1y, controlled with VGB AEDs response (temporarily response), CBZ (temporarily response), CBZ CBZ at age 8m. At age 11 m (after after age 3m. Sz recurrence and CLZ. Again exacerbation at 2y (seizure free) (seizure free) increasing dose CBZ?) strong when AED ceased at 5y. with then multiple sz/day for decrease in sz Commenced on VPA and some months. Controlled by LMT. CLB, then LEV and VPA Occasional sz since then Sz outcome Sz free since age 4 months Sz free since age 2 months Sz free since age 1 y 8 m Sz free since age 7 y Infrequent TC and FDS Current AEDs CBZ CBZ CBZ VPA, LTG VPA, LEV Focal spikes evolving into Multifocal epileptic activity, Multifocal epileptic activity and EEG at onset multifocal epileptic activity and Focal spike waves Bilateral spikes evolving into BS pattern BS pattern during sleep BS pattern during sleep Normal between 2m-1y. At age 1y Slow background and multifocal Slow background with multifocal EEG at follow up Slow background and multifocal hypsarrhythmia. At 2y slow Multifocal epileptic activity. epileptic activity with minimal paroxysmal anomalies and paroxysmal anomalies background with multifocal Normal from age 3y 10m residual BS pattern residual BS pattern epileptic activity Mild slow background activity; Mild slow background; multifocal Last EEG rare focal sharp-waves or spike Mild slow background activity epileptic activity increasing in Normal Normal
waves during sleep sleep Severe ID. Normal early Moderate ID. Never normal
Mild to moderate ID. Worst motor Mild to moderate ID. Worst motor Mild to moderate ID. Worst motor development. Regression during and regression with sz Cognition skills and better relational skills skills and better relational skills skills and better relational skills sz exacerbation at 1y and at 2y. exacerbation. Autism and
Autistic features behavioral problems Axial hypotonia with
Neurological Generalized hypotona. Sits hyperreflexia. Social smile Walks on toes. Stereotypic Severe hypotonia No abnormalities examination independently, does not stand. present. Does not sit alone. Hand movements. No speech
stereotypies Mild dysmorphic facial features
with prominent forehead.
Additional features Marcrocrania (+2SD).
Hydrosyringomyelia and
diastematomyelia type II
Abbreviations: BS: burst suppression; C: clonic seizures; CBD: Calmodulin Binding Domain; CBZ: carbamazepine; CLB: clobazam; CLZ: clonazepam; d: days; DZP: diazepam; ESM: ethosuximide; F: female; FDS: focal dyscognitive seizures; HC: hydrocortisone; ID: intensive care; ID: intellectual disability; KD: ketogenic diet; LEV: levetiracetam; LTG: lamotrigine;
LZP: lorazepam; M: Male; m: months; MDZ: midazolam; My: myoclonic seizures; PB: phenobarbital; PHT: phenytoine; sz: seizures; STM: sulthiame; T: tonic seizures; TC: tonic clonic seizures; TPM: topiramate; VPA: valproic acid; VGB: vigabatrine; y: years; ZNS: zonisamide