MATH 180 PEDAGOGY & ASSESSMENT PLANS Rev: Winter 2007
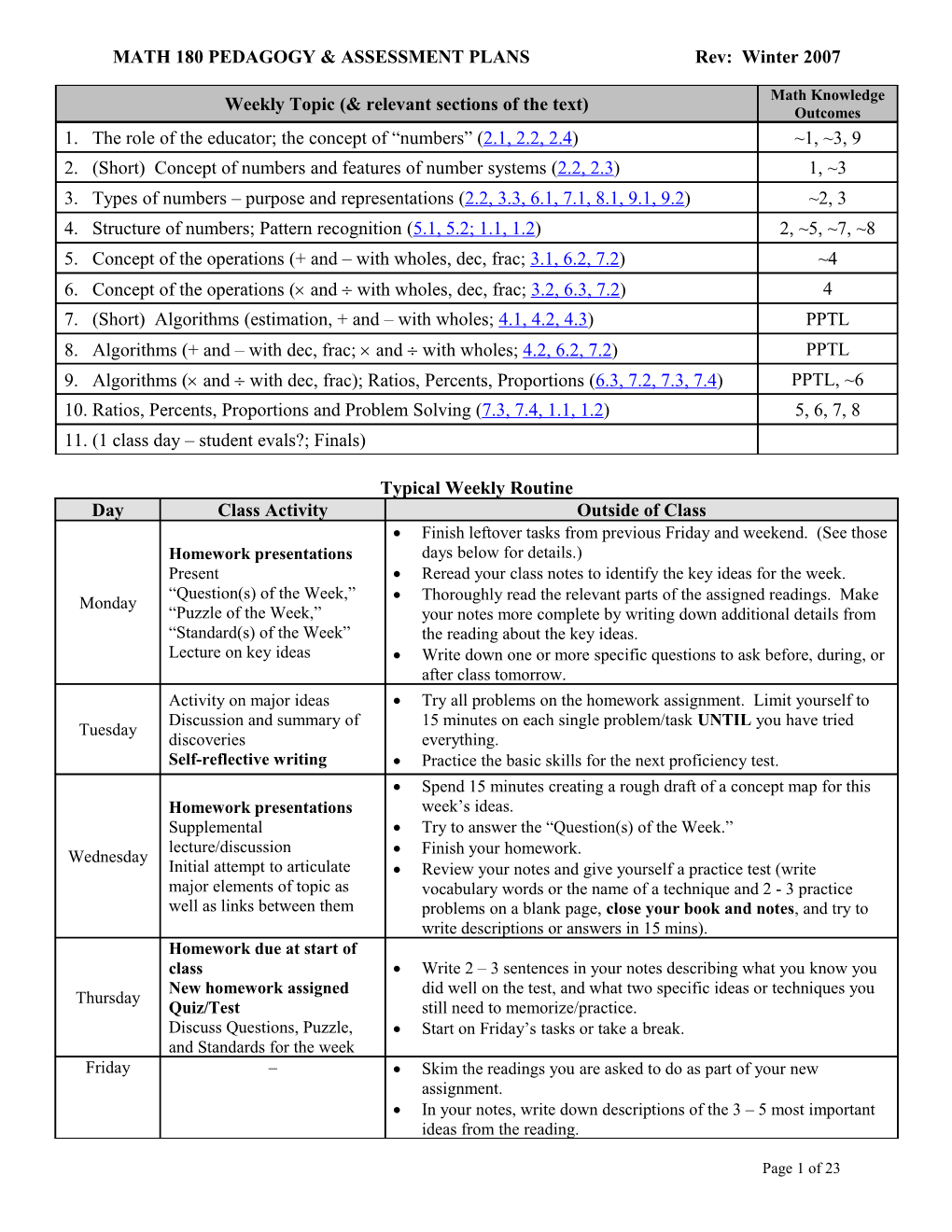
Math Knowledge Weekly Topic (& relevant sections of the text) Outcomes 1. The role of the educator; the concept of “numbers” (2.1, 2.2, 2.4) ~1, ~3, 9 2. (Short) Concept of numbers and features of number systems (2.2, 2.3) 1, ~3 3. Types of numbers – purpose and representations (2.2, 3.3, 6.1, 7.1, 8.1, 9.1, 9.2) ~2, 3 4. Structure of numbers; Pattern recognition (5.1, 5.2; 1.1, 1.2) 2, ~5, ~7, ~8 5. Concept of the operations (+ and – with wholes, dec, frac; 3.1, 6.2, 7.2) ~4 6. Concept of the operations ( and with wholes, dec, frac; 3.2, 6.3, 7.2) 4 7. (Short) Algorithms (estimation, + and – with wholes; 4.1, 4.2, 4.3) PPTL 8. Algorithms (+ and – with dec, frac; and with wholes; 4.2, 6.2, 7.2) PPTL 9. Algorithms ( and with dec, frac); Ratios, Percents, Proportions (6.3, 7.2, 7.3, 7.4) PPTL, ~6 10. Ratios, Percents, Proportions and Problem Solving (7.3, 7.4, 1.1, 1.2) 5, 6, 7, 8 11. (1 class day – student evals?; Finals)
Typical Weekly Routine Day Class Activity Outside of Class Finish leftover tasks from previous Friday and weekend. (See those Homework presentations days below for details.) Present Reread your class notes to identify the key ideas for the week. “Question(s) of the Week,” Monday Thoroughly read the relevant parts of the assigned readings. Make “Puzzle of the Week,” your notes more complete by writing down additional details from “Standard(s) of the Week” the reading about the key ideas. Lecture on key ideas Write down one or more specific questions to ask before, during, or after class tomorrow. Activity on major ideas Try all problems on the homework assignment. Limit yourself to Discussion and summary of 15 minutes on each single problem/task UNTIL you have tried Tuesday discoveries everything. Self-reflective writing Practice the basic skills for the next proficiency test. Spend 15 minutes creating a rough draft of a concept map for this Homework presentations week’s ideas. Supplemental Try to answer the “Question(s) of the Week.” lecture/discussion Wednesday Finish your homework. Initial attempt to articulate Review your notes and give yourself a practice test (write major elements of topic as vocabulary words or the name of a technique and 2 - 3 practice well as links between them problems on a blank page, close your book and notes, and try to write descriptions or answers in 15 mins). Homework due at start of class Write 2 – 3 sentences in your notes describing what you know you New homework assigned did well on the test, and what two specific ideas or techniques you Thursday Quiz/Test still need to memorize/practice. Discuss Questions, Puzzle, Start on Friday’s tasks or take a break. and Standards for the week Friday – Skim the readings you are asked to do as part of your new assignment. In your notes, write down descriptions of the 3 – 5 most important ideas from the reading.
Page 1 of 23 MATH 180 PEDAGOGY & ASSESSMENT PLANS Rev: Winter 2007
In either a separate section, or after your descriptions of ideas, write up to 10 key words and definitions that appeared in the reading. Circle or star definitions you don’t understand. Practice the basic skills for the next proficiency test. Take a break, then try at least three problems from the homework to be ready for presenting on Monday. Weekend – In your notes, write down one or more specific questions you still have about the words, skills, or concepts you’re studying. Do any of the tasks you did not do earlier in the week.
Learning Objectives Procedural Proficiency at the Elementary Student Level Able to accurately and efficiently perform computations and tasks expected of students in grades K-8 without the use of a calculator or notes. Procedural Proficiency at the Elementary Teacher Level Able to accurately explain and use alternative strategies to perform computations or other tasks expected of students in grades K-8. (Some strategies will make use of a calculator.) Robust Understanding of Core Concepts Depth of understanding at highest levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy: Able to analyze mathematical techniques or student work to describe core assumptions and ideas being used. Able to synthesize a variety of ideas into concept maps showing the relationships between mathematical concepts and techniques. Able to evaluate and articulate one’s own understanding and uncertainty of mathematical ideas. Increased Awareness of Own Attitudes and Behaviors About Mathematics and Learning Able to describe one’s own attitudes and behaviors, along with how they change and their consequences for one’s future students.
Thorough Knowledge of Specific Mathematical Content At the end of this course, you should be able to: 1. explain the concept of “number” along with the key features of enumeration using systems other than base-10, 2. describe the structure of and types of numbers in the real number system, 3. represent numbers in a variety of ways, 4. describe the central idea(s) underlying each of the basic operations, 5. use the understanding of the role of each operation and the different types of numbers to correctly set up and solve problems presented in words, 6. explain how ratios, proportions, and percentages describe relationships between quantities, 7. describe differences between genuine problem solving situations and routine exercises, 8. describe problem solving strategies (like Polya’s 4-step process) and apply them to a wide variety of problems, and 9. name the primary national and state standards governing K-8 mathematics teaching, and summarize several major learning outcomes.
Page 2 of 23 MATH 180 PEDAGOGY & ASSESSMENT PLANS Rev: Winter 2007
Details on Class Activities
Lecture – This is an opportunity for me to highlight major concepts and provide additional explanation of ideas presented in your book or other materials.
In-Class Exploration – Each week you will spend class time working on activities that will help you deepen your understanding of the ideas. As a potential teacher, it is not enough for you to simply mimic what someone else tells you to do; you MUST be in the habit of actively developing your own understanding of the “whys” and “hows” of new ideas and techniques. Working with others in groups can assist you with this, but be careful not to rely on others to get you unstuck.
Weekly Assignments and Presentations – You will have a formal assignment including problems from the book on a weekly basis. This will help you practice techniques and answer questions that highlight some of the main ideas. Members of the class will be asked to present their reasoning and methods on some of these problems in class each week.
Concept Maps – These are a standard type of diagram used to show relationships between major ideas. It will be one of the ways I help you develop, and also measure your ability to synthesize the concepts and techniques.
Self-Reflective Writing – The best teachers and students engage in metacognition, meaning “thinking about how they think.” It provides us with an opportunity to understand why we do or don’t grasp an idea, which offers suggestions for how to adjust our learning. I will ask you to do this in small amounts on a weekly basis, and use it as a window into your understanding of the course material during your midterm and final self-evaluations.
Student Proficiency Tests – You will have four, 10-minute proficiency tests on basic knowledge expected of the students you may teach. They will cover decimal arithmetic, fraction arithmetic, ratios/percents/proportions, and equation solving/graphing – topics included in the WEST-B screening exam that must be passed by all preservice K-8 teachers. You MUST pass each of these tests with an 80% or higher average in order to pass this class REGARDLESS of your other work in this course. You will have an opportunity to retake each of these tests at least once during the quarter.
Teacher Proficiency Tests – These will be regular quizzes on the new ideas presented in this class. Unlike the student proficiency tests, these are NOT “high stakes” tests that by themselves can determine whether you pass the class. As a result, they also cannot be retaken to improve your score.
Page 3 of 23 MATH 180 PEDAGOGY & ASSESSMENT PLANS Rev: Winter 2007
Topics, Outcomes, Week Daily Plan & Sections of Text 1 Introductions Monday 1/8 Have them read cover page of syllabus, write into info as I Establishing process take roll. Summ Write introductory info to share with groups (& hand in?): The Role of an Educator o Name, where you are from. The Concept of “Number” o [Why do you want to teach?] (2.1, 2.2, 2.4) o What level do you want to teach, and why? o What’s your experience with children (age, setting)? Math Knowledge Outcomes: o What’s your definition of a very smart (or “gifted”) [MK~1] explain the concept of o child? “number” along with the key What are the core differences in the mission of elementary features of enumeration using teachers compared to day care providers? systems other than base-10 Assign: Write about the following for in-class discussion. Teaching – What is the purpose of a “standard” like the [MK~3] represent numbers in a o Essential Academic Learning Requirements (EALRs) or variety of ways Grade Level Expectations (GLEs)? (Compare w/ syllabus learning objectives & course components) [MK 9] name the primary o Math – What is a “number”? For example, “eight” is more national and state standards than just a word or symbol. governing K-8 mathematics Write two questions you have about the learning objectives teaching, and summarize and course components. several major learning outcomes Tuesday [Standards, 2.1, 2.2] Group creation. Procedural Proficiency (Student) Student Proficiency Test #1 Hand out HW assignment with QotW, PotW, SotW on
Standard(s) of the Week: Wednesday [2.1, 2.2, 2.4] GLE 1.1.1, Grade 2: List following key terms related to “number” “Represent a number to at least o Set, subset, element 1000 in different ways, o Relation, function, one-to-one correspondence including numerals, words, o Ordinal, cardinal numbers pictures, and physical models; Activity: Distribute chips, place 4 dots on board, ask translate between students to show me how many using their chips.
Page 4 of 23 MATH 180 PEDAGOGY & ASSESSMENT PLANS Rev: Winter 2007
representations.” o How did they know? o Associating “set” of dots with set of objects. (1-1 corresp.) If done by “counting,” they associated with what set? o What other sets are relevant? [Number the list] (Arabic #s – they must describe symbol to draw; other lang; other numerals; other collections of objects!) Complexity of what’s being asked of students – show number of links as number of different sets grows. Step back and highlight another layer of complexity: using chips in front of you, show me “two.” o Does “two” mean “two chips” or does it mean “chip two?” o Concept of showing an amount versus showing placement. (Cardinal vs. ordinal) Formal definition of terms: set, subset, element, cardinal #, ordinal #. Highlight signaling of cardinal number through use of number word as adjective, but we eventually drop the noun it modifies as part of the process of abstraction. Diagram ways of enumerating the set of four dots to arrive at conclusion it shows “four.” o Correct way: Map each dot to one word in counting chant (order of chant matters, assignment doesn’t!) o They propose incorrect ways (saying two names for one dot – double-counting dot – relation only; saying one name for two different dots – repeating oneself – function) Define relation, function, 1-1 correspondence Articulate benefits of realizing these elements of learning – constructivist approach of honoring logic of what individual is doing while honing in on erroneous assumptions. Finish with intro to different number systems.
Thursday [10 min] SPT #1 – Decimals 20 min HW, 10 on Presentations of 2.2 (p. 67) #2, 5, 9ac o #5: Circle subset, equiv to subset, position in counting chant Distribute new assignment. [15 min] General questions, “of the week” stuff [18 min] Chip abacus and different bases
Page 5 of 23 MATH 180 PEDAGOGY & ASSESSMENT PLANS Rev: Winter 2007
Topics, Outcomes, Week Daily Plan & Sections of Text 2 The Concept of “Numbers” Monday
Page 6 of 23 MATH 180 PEDAGOGY & ASSESSMENT PLANS Rev: Winter 2007
Wednesday [2.2, 2.3] [15 min] Groups discuss HW/post solution attempts Preferred: 2.2A #11 cdeil; 2.2B #15 – explain pattern, 52,603 2.3A 4 – 9
[15 min] Groups present their work, I grade, then comment Definitions of classification terms: o Positional – the physical location of a symbol affects the value of the overall number o Place valued – each location in the number system changes the meaning of all symbols placed there in a consistent way o Additive – the overall value of a set of symbols comes from adding the values associated with each symbol o Multiplicative – the value of a symbol sometimes represents a fixed multiple of that symbol (can be determined by place value or accents) o Subtractive – the overall value of a set of symbols comes from subtracting the values associated with each symbol o Has zero – There is a symbol which represents “none” of a particular amount. I present a number system: “Celeste” o Up to 4 ticks (s, st, sta, star) at compass points, then cap for crosshairs with concatenation of name o 8 is a ring (mun), add a new tick for each 8 (muna, muni, muno, munae) up to 40. Two of these is a double-ring, called “sol.” o Analyze this system, then ask students to present their own.
Thursday [2.1-2.4] HW #2 turned in; #3 assigned Begin discussion of concept map – refer back to GLE. o Brainstorm key terms, skills, concepts o Group similar ones o Create networks of ideas Explain “Standard of the Week” in your own words Question/Puzzle of the Week [10 min] TPT #1 – Number systems/Numeration o ID errors in counting patterns o Compare/contrast a child’s number system to the Hindu-Arabic base-10 system, highlighting features the child’s system shares. (Constructivist POV)
Page 7 of 23 MATH 180 PEDAGOGY & ASSESSMENT PLANS Rev: Winter 2007
Topics, Outcomes, Week Daily Plan & Sections of Text 3 Types of Numbers – Purpose and Monday [2.2] 1/22 Representations Return/discuss TPT #1 (2.2, 3.3, 6.1, 7.1, 8.1, 9.1, 9.2) [15 min] Groups discuss HW/post solution attempts Preferred: Summ Math Knowledge Outcomes: o [MK~2] describe the structure [15 min] Groups present their work, I grade, then of and types of numbers in comment the real number system, Guided discussion – begin by brainstorming on: o [MK3] represent numbers in a o What are numbers for? variety of ways o Why do we have numbers, and not just stop at describing quantity with “none,” “one,” “two,” Procedural Proficiency (Student) “some,” and “many?” Student Proficiency Test #2 o Examining above questions leads to understanding
Page 8 of 23 MATH 180 PEDAGOGY & ASSESSMENT PLANS Rev: Winter 2007
Wednesday [3.3, 8.1, 9.1?] SPT #2 tomorrow – fraction arithmetic (includes mixed numbers), reducing [15 min] Groups discuss HW/post solution attempts Preferred: 6.1A #2c, 3, 4d, 18ab (&cd?); 7.1A#2b, 7c
[15 min] Groups present their work, I grade, then comment Discussion of concept map Guided discussion – begin by brainstorming on: o What is the purpose of exponents – why do they exist? How does multiplication itself serve a related purpose? [Increasing shorthand/compression of +] o What is a negative number? Can you touch one? Where/why do they come up? . “Does color have a negative?” Same meaning? . Take away too much and want to record that amount – words (debt, loss) vs. symbol; Notion of opposites; only exist in opposition to something else – need a reference direction o Brainstorm quantities, determine if there is a “negative” of it and what conveys direction . Ground level; possession/debtedness o Annihilation concept – Papy minicomputer & chips . Significant understanding of world – application to electricity; weather (pressure); “nature abhors a vacuum”
Thursday [8.1, 9.1, 9.2] HW #3 turned in; #4 assigned [concept map for number systems/preliminary self-eval?] More on annihilation w/ minicomputer Guided discussion – begin by brainstorming on: o What is a rational number? What numbers do you personally use that are NOT rational numbers? o Level of completeness of number system – closure of operations. o Other types of numbers and their reason for existence/purpose. Explain “Standard of the Week” in your own words Question/Puzzle of the Week [10 min] SPT #2 – Fraction arithmetic [10 min] SPT #1 (for those who hadn’t yet)
Page 9 of 23 MATH 180 PEDAGOGY & ASSESSMENT PLANS Rev: Winter 2007
Topics, Outcomes, Week Daily Plan & Sections of Text 4 Pattern Recognition; Monday [1.1, 5.1] 1/29 Structure of Numbers [10 min] Groups discuss HW/post solution attempts (1.1, 1.2; 5.1, 5.2) Preferred: 1.1 A #4, 6/9, 10, 13/19
Summ Math Knowledge Outcomes: [15 min] Groups present their work, I grade, then o [MK2] describe the structure comment of and types of numbers in the [15 min] “Problem Solving” real number system o Is being a “good problem solver” an asset? Why or o [MK~5] use understanding of why not? the role of each operation and . Does the answer depend on the problems being the different types of numbers “math” or “real life?” How are these different? to correctly set up and solve [Definition of “classroom math” vs. data analy.] problems presented in words o What are the attributes of a “good problem solver?” o [MK~7] describe differences . Persistent, patient, creative, resourceful, willing between genuine problem to take risks/try, observant of patterns, adaptable, solving situations and routine self-reflective, organized(?) exercises o Where are we taught this – both informally and o [MK~8] describe problem formally? solving strategies (like Polya’s . Why in math class? [Logos training – context- 4-step process) and apply them independent strategies for data-gathering and to a wide variety of problems reasoning] . Why use seemingly irrelevant number and shape Procedural Proficiency (Teacher) puzzles rather than real-world stuff like reducing Teacher Proficiency Test #2 littering/the amount of garbage we produce;
Standard(s) of the Week: [30 min] Patterns in numbers – divisibility GLE 2.1.1, Grade 4 evidence of o What does it mean for something to be divisible by learning: “Generate questions something else? (Can’t everything be divided?) that would need to be answered o Draw a picture strategy: Arrays to visualize numbers in order to solve the problem.” and ID groupings (both sums and products) GLE 2.2.3, most grades: o Model situation with symbols: From dots to factor “Apply a variety of strategies to trees construct solutions.” o Systematic exploration/recognizing patterns: Sieve of Erathostenes; Uniqueness of prime factorization
Page 10 of 23 MATH 180 PEDAGOGY & ASSESSMENT PLANS Rev: Winter 2007
[F.Thm. of Arith.]
Wednesday [1.2, 5.1, 5.2] TPT #2 tomorrow – WASL problems + analysis [15 min] Groups discuss HW/post solution attempts Preferred:
[15 min] Groups present their work, I grade, then comment Discussion o Inductive vs. deductive reasoning – pros and cons . Inductive: Child needs to touch burner to know it’s painful . Deductive: Child sees burner make hot food, knows hot food sometimes burns, concludes burner is unpleasantly hot o Power of deductive reasoning: demonstrating certainty of that which cannot be shown through experiment . p. 221’s proof that the number of primes is infinite o Demonstrating deductive nature of argument proving divisibility rules
Thursday [5.2] HW #4 turned in; #5 assigned [self-eval] Discussion: o What is the value of factoring? . Uniqueness of representation o Greatest common factor/Least common multiple – which is larger than the numbers you start from? (Linguistic confusion) o Algorithms for GCF, LCM
Explain “Standard of the Week” in your own words Question/Puzzle of the Week [20 min] TPT #2 – WASL problems + analysis
Page 11 of 23 MATH 180 PEDAGOGY & ASSESSMENT PLANS Rev: Winter 2007
Topics, Outcomes, Week Daily Plan & Sections of Text 5 Concept of the operations of + Monday [3.1] 2/5 and – with whole numbers, [10 min] Groups discuss HW/post solution attempts decimals, and fractions Preferred: (3.1, 6.2, 7.2) Summ [15 min] Groups present their work, I grade, then Math Knowledge Outcomes: comment o [MK~4] describe the central Collect HW idea(s) underlying each of the [20 min] TPT #2 – WASL problems + analysis basic operations [15 min] Lecture/Discussion:
to be redefined to understand 2 - 5?
Wednesday [3.1, 6.2, 7.2] SPT Retake tomorrow [15 min] Groups discuss HW/post solution attempts Preferred:
[15 min] Groups present their work, I grade, then comment Lecture/Discussion:
Thursday [3.2] HW #5 book work turned in; #6 assigned Leftover discussion of previous days’ topics o Addition facts & strategies o Operations in other bases Explain “Standard of the Week” in your own words Question/Puzzle of the Week [10 min] SPT Retake
Page 13 of 23 MATH 180 PEDAGOGY & ASSESSMENT PLANS Rev: Winter 2007
Topics, Outcomes, Week Daily Plan & Sections of Text 6 Concept of the operations of Monday [3.2] 2/12 and ÷ with whole numbers, Collect Self-Evals decimals, and fractions [10 min] Groups discuss HW/post solution attempts (3.2, 6.3, 7.2) Preferred: 3.2 #4, 5dg, 6cd, 9bc, 10ab, 14, 15; 3.2 B #13ab Summ 3.3 #8, 9, 11 Math Knowledge Outcomes: [15 min] Groups present their work, I grade, then o [MK4] describe the central comment idea(s) underlying each of the Lecture/Discussion:
division using words, pictures, . Set models: Partitioning – Partitive division is models, and/or numbers” when the number of partitions (groups) is known, but size of each is not; Measurement is Puzzles for later when the amount to be placed in each group is p.257 #26; Fibonacci; Pasc Tr. known, but the number of groups is not . Measurement models – Repeated subtraction & the division algorithm . Missing factor & the rules for zero o Note that addition and multiplication have one name for the components – addends or factors – while subtraction and division have two [reflects (non)commutativity]
Wednesday [3.2, 6.2, 7.2] TPT #3 tomorrow – meanings of operations [15 min] Groups discuss HW/post solution attempts Preferred:
[15 min] Groups present their work, I grade, then comment Lecture/Discussion: o Which of the whole number perspectives carry over to multiplication and division of decimals and fractions? . How can we represent it physically or visually? . What modifications are required? o Why is division by fractions so cognitively challenging? [Changing reference units] o Additional discussion of properties or representations.
Thursday [3.2, 6.2, 7.2, 8.2] HW #6 turned in; #7 assigned Leftover discussion of previous days’ topics (division by negatives?) Explain “Standard of the Week” in your own words Question/Puzzle of the Week [10 min] SPT Retake
Page 15 of 23 MATH 180 PEDAGOGY & ASSESSMENT PLANS Rev: Winter 2007
Topics, Outcomes, Week Daily Plan & Sections of Text 7 Algorithms for Computation: Monday [] – No class 2/20 Estimation, + and – with wholes (4.1, 4.2, 4.3) Tuesday [4.1] Lecture/Discussion: Short o Mental math techniques – clever uses of the Math Knowledge Outcomes: associative, commutative, and distributive properties [PPTL] … use alternative Summ o . Lists of summands & benefits of assoc/commut strategies to perform . Compensation (equal additions) for doing computations … subtraction . Multiplicative compensation and powers of 10 Procedural Proficiency (Student) o What is estimation, and why do we do it? Student Proficiency Test #3 . Is it important? When/where?
Thursday [4.3] [15 min] Groups discuss HW/post solution attempts Preferred: 4.1A#6c (iii, iv), 28; 4.2A#2, 4a, 5a; 4.3A#1d,2c,4b
Page 16 of 23 MATH 180 PEDAGOGY & ASSESSMENT PLANS Rev: Winter 2007
[15 min] Groups present their work, I grade, then comment HW #7 turned in; #8 assigned Lecture/Discussion: o Algorithms for + and – in base-5 . At what steps do we experience significant slowdown? What does this say about the building blocks for learning the base-10 algorith. o Tom Lehrer’s “New Math” song [10 min] SPT #3 – graphing and solving equations Explain “Standard of the Week” in your own words Question/Puzzle of the Week Alternative: Discuss the full spectrum of job duties of a faculty member o Teaching load o Official office hours + unofficial hours o Prep time + Grading o Phone + Email o Committees – hiring, textbook (& publishing cycle), curriculum devel, advising, letters of rec., student awards, grants/special projects, scheduling, tutor hiring/oversight, PT faculty hiring/oversight, student complaints o Amount of sleep, tradeoffs, enjoyment, compensation o Don’t expect much different in first couple of years of teaching (high attrition rate; student teachers taking TP with them)
Page 17 of 23 MATH 180 PEDAGOGY & ASSESSMENT PLANS Rev: Winter 2007
Topics, Outcomes, Week Daily Plan & Sections of Text 8 Algorithms for Computation: +,– Monday [4.2, 6.2, 7.2, 8.1] Lecture/Discussion:
Thursday [4.3] HW #8 turned in; #9 assigned [20 min] TPT #4 – Algorithms for Operations Leftover discussion of previous days’ topics, or multiplication and division in other bases Explain “Standard of the Week” in your own words Question/Puzzle of the Week
Page 19 of 23 MATH 180 PEDAGOGY & ASSESSMENT PLANS Rev: Winter 2007
Topics, Outcomes, Week Daily Plan & Sections of Text 9 Algorithms for Computation: ×,÷ Monday [6.3, 7.2] Lecture/Discussion: 3/5 w/ Dec., Frac.; Ratios, Percents, o How do the algorithms for and ÷ change for Proportions . Decimals – What changes in the algorithms? (6.3, 7.2, 7.3, 7.4) Alignment – why not important? Effect of Summ adding zeros? Quick fix for errors? Math Knowledge Outcomes: . Fractions o [PPTL] … use alternative Why don’t we need a common strategies to perform denominator? computations … Straight-across division strategy o [MK~6] explain how ratios, Developing trust in algorithm via patterns proportions, and percentages . Signed numbers – Failure of algorithm describe relationships between o Terminating/nonterminating decimals & the quantities relationship with fractions
Procedural Proficiency (Student) Tuesday [7.3] Lecture/Discussion:
Page 20 of 23 MATH 180 PEDAGOGY & ASSESSMENT PLANS Rev: Winter 2007
. “Want, Know, Relationship” strategy . Role of finding pairwise relationships between the known & unknown information . Using pairs to create proportion – one pair dictates a single fraction, and a second pair dictates placement of #s in second fraction o Judging equivalence of proportions ("Have I set it up right?") – identifying when proportions give the same or different answers (equality of diagonals; pairs) o “Cross multiply” vs. “Multiply across” vs. setting up the problem horizontally & vertically Wednesday [7.3]
[30 min] Groups present their work, I grade, then comment Lecture/Discussion: o Practice setting up ratios (rates) & proportions . [Fairness] In the 2001/2 academic year, Highline had 2,006 Asian/Pacific Islander students and 1,550 students of African American descent. If a single class had the same mix as the overall campus, how many Asian/PI students would be expected in a class with 5 AfrAm students? . [Scaling] On a map, the distance between two towns is 2¾ inches. The legend shows a half- inch represents 30 miles. How far apart are they? . [Sampling] Researchers at the Department of Fish and Wildlife decide they need to measure the fish population in a particular lake. They first go to the lake and catch 41 fish, which they tag and release back into the lake. One month later, the researchers return and catch 58 fish, of which 16 are tagged. How many fish might the researchers estimate are in the lake? Thursday [7.3/4] HW #9 turned in; #10 assigned o What is a percentage? How is it the same as, or different from a ratio? . Ratios – Comparison of two quantities measured in the same units; Compares part to part or part to whole; Clue word of “to”; Written as frac or : . Rates – Comparison of two quantities measured in different units (like distance, time, money, volume, etc.); Compares part to part; Clue word of “per”; Written as a frac or : . Percentages – Standardized comparison of two quantities in the same units; Compares part to whole; Clue word of “of”; Written frac/100 or % Explain “Standard of the Week” in your own words Question/Puzzle of the Week Page 21 of 23 MATH 180 PEDAGOGY & ASSESSMENT PLANS Rev: Winter 2007
[10 min] SPT #4 – Ratios, Percents, Proportions
Page 22 of 23 MATH 180 PEDAGOGY & ASSESSMENT PLANS Rev: Winter 2007
Topics, Outcomes, Week Daily Plan & Sections of Text 10 Ratios, Percents, Proportions Monday [7.4] Lecture/Discussion:
Robust Understanding: Tuesday [7.4] Group project work time [MK4] Creating lesson on o Check groups’ ideas algorithms for × (Anal) o Ask about components of project, division of labor o Their questions for me & hypothetical student Question+Puzzle of the Week: questions (Resolving confusion over describing parts using improper Wednesday [7.4, 1.1, 1.2] fractions or ratios) SPT #3 or 4 retake tomorrow Standard(s) of the Week: Hand out final self-assessment assignment GLE 1.1.4, Grade 6: [15 min] Groups discuss HW/post solution attempts “Understand the concepts of Preferred: ratio and percent.” GLE 1.1.4, Grade 6 evidence of [30 min] Groups present their work, I grade, then learning: “Write or show and comment explain ratios in part/part and Lecture/Discussion: part/whole relationships using o Practice with word problems words, objects, pictures, models, and/or symbols.” Thursday [] HW #10 turned in; reminder about project, self-eval [10 min] SPT #3 or 4 Retake Explain “Standard of the Week” in your own words Question/Puzzle of the Week
Page 23 of 23