Interventions for Students At-Risk of Dropping Out of School
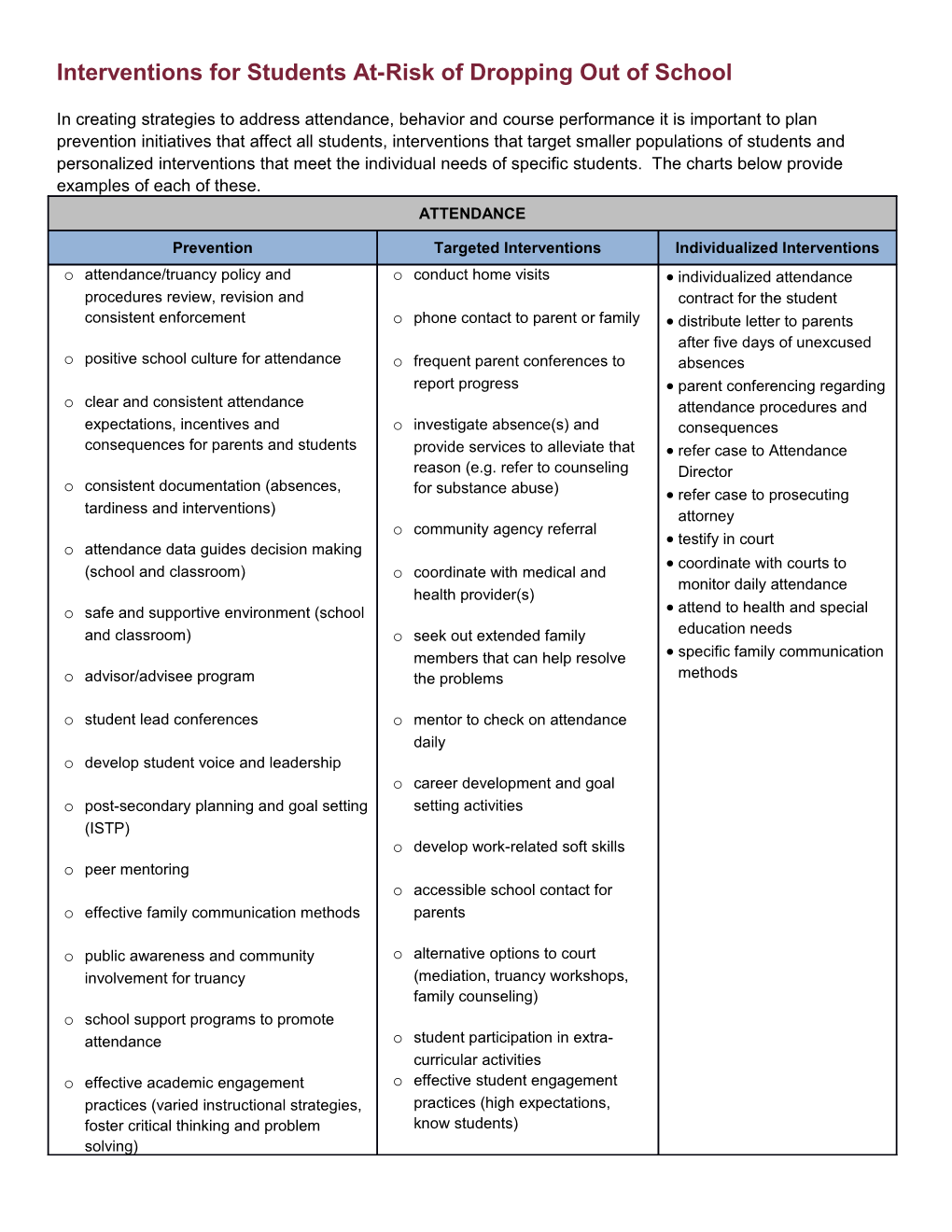
In creating strategies to address attendance, behavior and course performance it is important to plan prevention initiatives that affect all students, interventions that target smaller populations of students and personalized interventions that meet the individual needs of specific students. The charts below provide examples of each of these. ATTENDANCE
Prevention Targeted Interventions Individualized Interventions o attendance/truancy policy and o conduct home visits individualized attendance procedures review, revision and contract for the student consistent enforcement o phone contact to parent or family distribute letter to parents after five days of unexcused o positive school culture for attendance o frequent parent conferences to absences report progress parent conferencing regarding o clear and consistent attendance attendance procedures and expectations, incentives and o investigate absence(s) and consequences consequences for parents and students provide services to alleviate that refer case to Attendance reason (e.g. refer to counseling Director consistent documentation (absences, o for substance abuse) refer case to prosecuting tardiness and interventions) attorney o community agency referral testify in court o attendance data guides decision making coordinate with courts to (school and classroom) o coordinate with medical and monitor daily attendance health provider(s) o safe and supportive environment (school attend to health and special and classroom) o seek out extended family education needs members that can help resolve specific family communication o advisor/advisee program the problems methods
o student lead conferences o mentor to check on attendance daily o develop student voice and leadership o career development and goal o post-secondary planning and goal setting setting activities (ISTP) o develop work-related soft skills o peer mentoring o accessible school contact for o effective family communication methods parents
o public awareness and community o alternative options to court involvement for truancy (mediation, truancy workshops, family counseling) o school support programs to promote attendance o student participation in extra- curricular activities o effective academic engagement o effective student engagement practices (varied instructional strategies, practices (high expectations, foster critical thinking and problem know students) solving) BEHAVIOR Prevention Targeted Interventions Individualized Interventions review and adjust discipline positive behavior intervention individualized positive policies strategies and supports behavior intervention and effective classroom pre-planned intervention support plan management skills and strategies functional behavior practices clear expectations and assessment predictable learning procedures for non-classroom SAT referral environment settings behavior contract with home clear administrative data based decision making involvement procedures for responding (ongoing data collection and mental health counseling to office discipline referrals use to design behavior alternative instruction teach and model desired interventions) opportunities (e.g. virtual social behaviors classroom behavior checklist course, distance learning, clear behavior expectations parent communication journal academies) positive school climate (daily/weekly) individual school counseling peer mediation program mentor (peer or adult) daily conferencing school wide positive respite or time out area reinforce expected behaviors behavior intervention and small group counseling explicit social skills support plan, including (anger management, grief, instruction incentives for desired substance abuse social skills) teach replacement behaviors behaviors Pro Officer to monitor student fading plan for behavioral discipline data analysis behaviors supports (school and classroom) explore real world behavior self-determination and self- advisor/advisee program consequences (e.g. visits to advocacy development conflict resolution and jails, drug rehab centers, self-monitoring and deterrence (e.g. Pro mortuaries and courts) correction strategies Officers on campus) alternative instruction positive student-teacher opportunities (e.g. virtual relationships course, distance learning, extra-curricular and co- academies) curricular opportunities juvenile justice collaboration club or activity day model/practice expected structured developmental behaviors guidance program explicit social skills instruction effective student develop student voice engagement, family engagement and instructional practices
COURSE PERFORMANCE Prevention Targeted Interventions Individualized Interventions research-based instructional extra help options in the daily Individualized Education strategies and practices to schedule Program (IEP) or Section 504 promote student learning blocked academic support support plan and engagement courses (math and individualized tutoring professional development English/Language Arts) referral for special education targeted to improve effective small class size eligibility instructional practices flexibility in student’s instructional accommodations integration of career skills schedule specific skills based instruction Individualized Student credit recovery opportunities classroom flexibility to Transition Planning before, during and after maximize learning AP/Honors courses school credit recovery opportunities embedded credits in career virtual learning before, during and after technical or other programs school dual credit courses small group tutoring pre-teaching opportunities student lead conferences career mentors explicit basic skills instruction academies peer mentors (literacy and math) virtual learning GED Option virtual learning college and career middle college program strategic skill instruction readiness standards and summer school (academic vocabulary) skills development (rigor pre-teaching strategies know student learning styles and relevance) support instruction and vary instruction to well-developed use of coordination and integration increase student engagement differentiated instruction of post-secondary planning responsive instructional (ISTP and special education) family engagement practices (modeling, guided practices pre-teaching opportunities practice, feedback) monitor student progress remediation and re-teach corrective reading and adjust instruction opportunities cueing experiential learning explicit basic skills instruction scaffold instruction opportunities (literacy and math) learning strategies and skills build classroom flexible grouping strategies relationships co-teaching strategies before/after school options learning strategies and skills work-related skills (soft skills) community partnerships know student learning styles and vary instruction to increase student engagement