Page 1
HIGH LIMIT CONTROL SAFETY SWITCH
PURPOSE;
The high limit control protects the gas furnace from overheating.The contacts in the limit control will open to shut down the gas valve when over limit temperatures exist. This control is an auto reset device that will close the contacts when the furnace cools down.
TYPES OF HIGH LIMIT CONTROLS
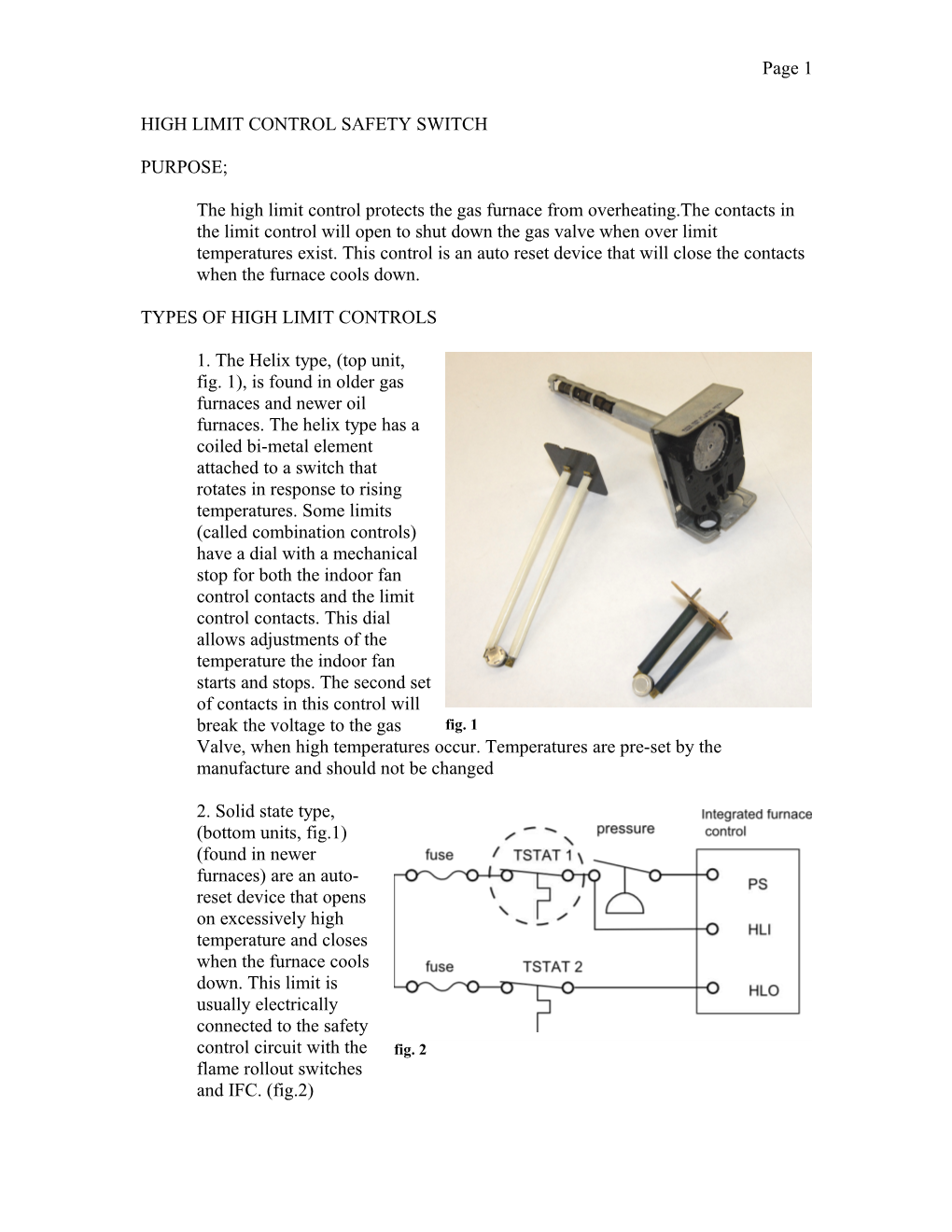
1. The Helix type, (top unit, fig. 1), is found in older gas furnaces and newer oil furnaces. The helix type has a coiled bi-metal element attached to a switch that rotates in response to rising temperatures. Some limits (called combination controls) have a dial with a mechanical stop for both the indoor fan control contacts and the limit control contacts. This dial allows adjustments of the temperature the indoor fan starts and stops. The second set of contacts in this control will break the voltage to the gas fig. 1 Valve, when high temperatures occur. Temperatures are pre-set by the manufacture and should not be changed
2. Solid state type, (bottom units, fig.1) (found in newer furnaces) are an auto- reset device that opens on excessively high temperature and closes when the furnace cools down. This limit is usually electrically connected to the safety control circuit with the fig. 2 flame rollout switches and IFC. (fig.2) Page 2
If a limit opens, the IFC will de-energize the gas valve, BUT will keep the indoor blower and induced draft blower running until the furnace cools and the switch resets and will call for heat. When a high limit opens, the cause must be determined.
PROCEDURE FOR CHECKING THE HIGH LIMIT CONTROL:
TOOLS NEEDED; Multimeter.
1. Disconnect power and turn off the gas to the furnace. 2. Remove the wires from the limit terminals.
3. Turn the meter to Ohms. Place one meter lead to one limit terminal and the other meter lead to the other limit terminal, measure for resistance between the two terminals, (fig. 3,4), if no resistance is measured, the switch is open and should have reclosed. So the switch must be replaced with one of equal value. 5. Check gas pressure, and air volume, correct any that are incorrect. 6. Cycle the unit through its sequence of events for correct operation.
fig. 3 fig. 4