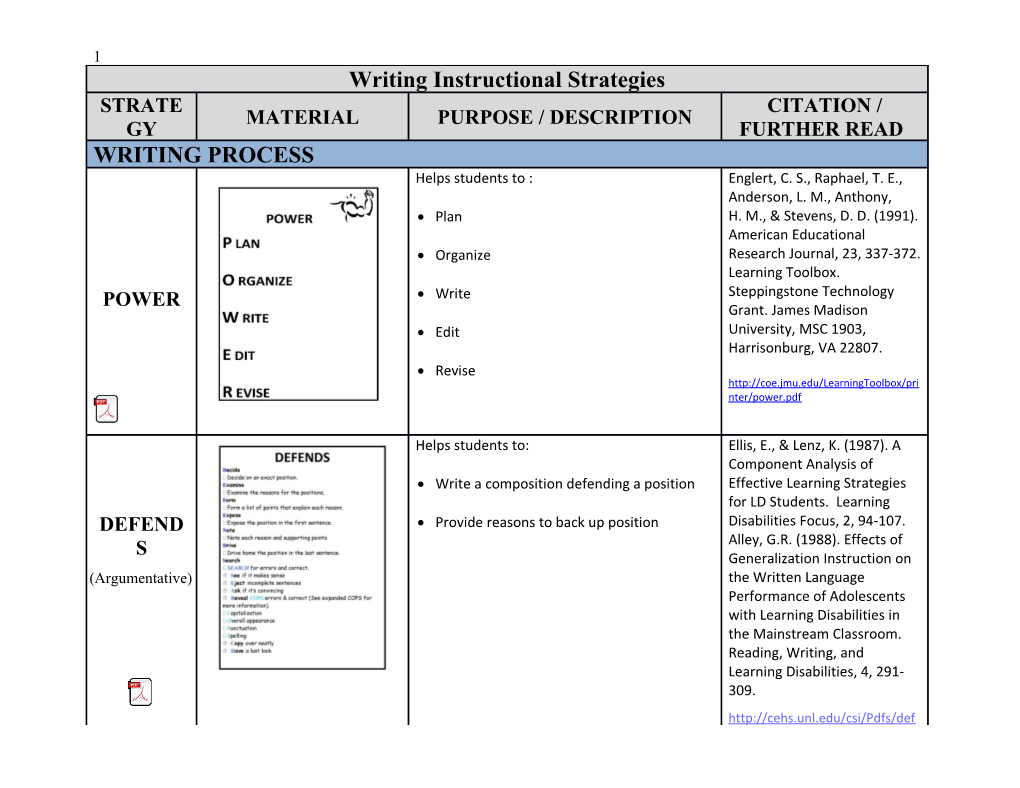
1 Writing Instructional Strategies STRATE CITATION / MATERIAL PURPOSE / DESCRIPTION GY FURTHER READ WRITING PROCESS Helps students to : Englert, C. S., Raphael, T. E., Anderson, L. M., Anthony, Plan H. M., & Stevens, D. D. (1991). American Educational Organize Research Journal, 23, 337-372. Learning Toolbox. POWER Write Steppingstone Technology Grant. James Madison Edit University, MSC 1903, Harrisonburg, VA 22807.
Revise http://coe.jmu.edu/LearningToolbox/pri nter/power.pdf
Helps students to: Ellis, E., & Lenz, K. (1987). A Component Analysis of Write a composition defending a position Effective Learning Strategies for LD Students. Learning DEFEND Provide reasons to back up position Disabilities Focus, 2, 94-107. S Alley, G.R. (1988). Effects of Generalization Instruction on (Argumentative) the Written Language Performance of Adolescents with Learning Disabilities in the Mainstream Classroom. Reading, Writing, and Learning Disabilities, 4, 291- 309. http://cehs.unl.edu/csi/Pdfs/def 2 Writing Instructional Strategies STRATE CITATION / MATERIAL PURPOSE / DESCRIPTION GY FURTHER READ WRITING PROCESS Helps students to : Englert, C. S., Raphael, T. E., Anderson, L. M., Anthony, Plan H. M., & Stevens, D. D. (1991). American Educational Organize Research Journal, 23, 337-372. Learning Toolbox. POWER Write Steppingstone Technology Grant. James Madison Edit University, MSC 1903, Harrisonburg, VA 22807.
Revise http://coe.jmu.edu/LearningToolbox/pri nter/power.pdf
Helps students to: Ellis, E., & Lenz, K. (1987). A Component Analysis of Write a composition defending a position Effective Learning Strategies for LD Students. Learning DEFEND Provide reasons to back up position Disabilities Focus, 2, 94-107. S Alley, G.R. (1988). Effects of Generalization Instruction on (Argumentative) the Written Language Performance of Adolescents with Learning Disabilities in the Mainstream Classroom. Reading, Writing, and Learning Disabilities, 4, 291- 309. http://cehs.unl.edu/csi/Pdfs/def 3 Writing Instructional Strategies STRATE CITATION / MATERIAL PURPOSE / DESCRIPTION GY FURTHER READ WRITING PROCESS Helps students to : Englert, C. S., Raphael, T. E., Anderson, L. M., Anthony, Plan H. M., & Stevens, D. D. (1991). American Educational Organize Research Journal, 23, 337-372. Learning Toolbox. POWER Write Steppingstone Technology Grant. James Madison Edit University, MSC 1903, Harrisonburg, VA 22807.
Revise http://coe.jmu.edu/LearningToolbox/pri nter/power.pdf
Helps students to: Ellis, E., & Lenz, K. (1987). A Component Analysis of Write a composition defending a position Effective Learning Strategies for LD Students. Learning DEFEND Provide reasons to back up position Disabilities Focus, 2, 94-107. S Alley, G.R. (1988). Effects of Generalization Instruction on (Argumentative) the Written Language Performance of Adolescents with Learning Disabilities in the Mainstream Classroom. Reading, Writing, and Learning Disabilities, 4, 291- 309. http://cehs.unl.edu/csi/Pdfs/def 4 Writing Instructional Strategies STRATE CITATION / MATERIAL PURPOSE / DESCRIPTION GY FURTHER READ WRITING PROCESS Helps students to : Englert, C. S., Raphael, T. E., Anderson, L. M., Anthony, Plan H. M., & Stevens, D. D. (1991). American Educational Organize Research Journal, 23, 337-372. Learning Toolbox. POWER Write Steppingstone Technology Grant. James Madison Edit University, MSC 1903, Harrisonburg, VA 22807.
Revise http://coe.jmu.edu/LearningToolbox/pri nter/power.pdf
Helps students to: Ellis, E., & Lenz, K. (1987). A Component Analysis of Write a composition defending a position Effective Learning Strategies for LD Students. Learning DEFEND Provide reasons to back up position Disabilities Focus, 2, 94-107. S Alley, G.R. (1988). Effects of Generalization Instruction on (Argumentative) the Written Language Performance of Adolescents with Learning Disabilities in the Mainstream Classroom. Reading, Writing, and Learning Disabilities, 4, 291- 309. http://cehs.unl.edu/csi/Pdfs/def 5 Writing Instructional Strategies STRATE CITATION / MATERIAL PURPOSE / DESCRIPTION GY FURTHER READ WRITING PROCESS Helps students to : Englert, C. S., Raphael, T. E., Anderson, L. M., Anthony, Plan H. M., & Stevens, D. D. (1991). American Educational Organize Research Journal, 23, 337-372. Learning Toolbox. POWER Write Steppingstone Technology Grant. James Madison Edit University, MSC 1903, Harrisonburg, VA 22807.
Revise http://coe.jmu.edu/LearningToolbox/pri nter/power.pdf
Helps students to: Ellis, E., & Lenz, K. (1987). A Component Analysis of Write a composition defending a position Effective Learning Strategies for LD Students. Learning DEFEND Provide reasons to back up position Disabilities Focus, 2, 94-107. S Alley, G.R. (1988). Effects of Generalization Instruction on (Argumentative) the Written Language Performance of Adolescents with Learning Disabilities in the Mainstream Classroom. Reading, Writing, and Learning Disabilities, 4, 291- 309. http://cehs.unl.edu/csi/Pdfs/def 6 Writing Instructional Strategies STRATE CITATION / MATERIAL PURPOSE / DESCRIPTION GY FURTHER READ WRITING PROCESS Helps students to : Englert, C. S., Raphael, T. E., Anderson, L. M., Anthony, Plan H. M., & Stevens, D. D. (1991). American Educational Organize Research Journal, 23, 337-372. Learning Toolbox. POWER Write Steppingstone Technology Grant. James Madison Edit University, MSC 1903, Harrisonburg, VA 22807.
Revise http://coe.jmu.edu/LearningToolbox/pri nter/power.pdf
Helps students to: Ellis, E., & Lenz, K. (1987). A Component Analysis of Write a composition defending a position Effective Learning Strategies for LD Students. Learning DEFEND Provide reasons to back up position Disabilities Focus, 2, 94-107. S Alley, G.R. (1988). Effects of Generalization Instruction on (Argumentative) the Written Language Performance of Adolescents with Learning Disabilities in the Mainstream Classroom. Reading, Writing, and Learning Disabilities, 4, 291- 309. http://cehs.unl.edu/csi/Pdfs/def 7 Writing Instructional Strategies STRATE CITATION / MATERIAL PURPOSE / DESCRIPTION GY FURTHER READ WRITING PROCESS Helps students to : Englert, C. S., Raphael, T. E., Anderson, L. M., Anthony, Plan H. M., & Stevens, D. D. (1991). American Educational Organize Research Journal, 23, 337-372. Learning Toolbox. POWER Write Steppingstone Technology Grant. James Madison Edit University, MSC 1903, Harrisonburg, VA 22807.
Revise http://coe.jmu.edu/LearningToolbox/pri nter/power.pdf
Helps students to: Ellis, E., & Lenz, K. (1987). A Component Analysis of Write a composition defending a position Effective Learning Strategies for LD Students. Learning DEFEND Provide reasons to back up position Disabilities Focus, 2, 94-107. S Alley, G.R. (1988). Effects of Generalization Instruction on (Argumentative) the Written Language Performance of Adolescents with Learning Disabilities in the Mainstream Classroom. Reading, Writing, and Learning Disabilities, 4, 291- 309. http://cehs.unl.edu/csi/Pdfs/def 8 Writing Instructional Strategies STRATE CITATION / MATERIAL PURPOSE / DESCRIPTION GY FURTHER READ WRITING PROCESS Helps students to : Englert, C. S., Raphael, T. E., Anderson, L. M., Anthony, Plan H. M., & Stevens, D. D. (1991). American Educational Organize Research Journal, 23, 337-372. Learning Toolbox. POWER Write Steppingstone Technology Grant. James Madison Edit University, MSC 1903, Harrisonburg, VA 22807.
Revise http://coe.jmu.edu/LearningToolbox/pri nter/power.pdf
Helps students to: Ellis, E., & Lenz, K. (1987). A Component Analysis of Write a composition defending a position Effective Learning Strategies for LD Students. Learning DEFEND Provide reasons to back up position Disabilities Focus, 2, 94-107. S Alley, G.R. (1988). Effects of Generalization Instruction on (Argumentative) the Written Language Performance of Adolescents with Learning Disabilities in the Mainstream Classroom. Reading, Writing, and Learning Disabilities, 4, 291- 309. http://cehs.unl.edu/csi/Pdfs/def 9 Writing Instructional Strategies STRATE CITATION / MATERIAL PURPOSE / DESCRIPTION GY FURTHER READ WRITING PROCESS Helps students to : Englert, C. S., Raphael, T. E., Anderson, L. M., Anthony, Plan H. M., & Stevens, D. D. (1991). American Educational Organize Research Journal, 23, 337-372. Learning Toolbox. POWER Write Steppingstone Technology Grant. James Madison Edit University, MSC 1903, Harrisonburg, VA 22807.
Revise http://coe.jmu.edu/LearningToolbox/pri nter/power.pdf
Helps students to: Ellis, E., & Lenz, K. (1987). A Component Analysis of Write a composition defending a position Effective Learning Strategies for LD Students. Learning DEFEND Provide reasons to back up position Disabilities Focus, 2, 94-107. S Alley, G.R. (1988). Effects of Generalization Instruction on (Argumentative) the Written Language Performance of Adolescents with Learning Disabilities in the Mainstream Classroom. Reading, Writing, and Learning Disabilities, 4, 291- 309. http://cehs.unl.edu/csi/Pdfs/def 10 11 Writing Instructional Strategies STRATEG CITATION / MATERIAL PURPOSE / DESCRIPTION Y FURTHER READ DRAFTING Helps students to develop: IES Practice Guide: Teaching Elementary School Students to • Topic – Write a topic sentence expressing an Be Effective Writers, U.S. opinion. Department of Education, TREE June 2012. (p.26) (Opinion) • Reason – Give at least 3 reasons to support the topic sentence. https://earlychildhoodeducation. • Explanation – Explain your reasons. usu.edu/files/uploads/UTah_Stat e_SRSD.pptx.pdf • Ending – Formulate a statement to summarize the topic sentence. http://kc.vanderbilt.edu/casl/po wtree.html Helps students to identify the parts of a good National Center on story: Accelerating Student Learning, U.S. Department of W- who WWW Education’s Office of Special Education Programs (OSEP), What=2 W- when Teachers College of Columbia How=2 W-where University and Vanderbilt (Narrative) University. W- What do the characters do?
W- What happens then?
H-How does the story end? http://kc.vanderbilt.edu/casl/srsd.html 12 Writing Instructional Strategies STRATEG CITATION / MATERIAL PURPOSE / DESCRIPTION Y FURTHER READ DRAFTING H-How does the main character (and other characters) feel? Helps students to: This link provides a power point that explains SRSD and Work from plan to develop thesis STOP, DARE, PLAN, TREE, POW, and WRITE. Remember writing goals Information about teaching the WRITE self-regulating strategies for student materials and links to Include transition words Peabody/Vanderbilt interactive tutorials are provided. Try to use different kinds of sentences
use Exciting words https://earlychildhoodeducation. usu.edu/files/uploads/UTah_Stat e_SRSD.pptx.pdf Helps students to: IES Practice Guide: Teaching Elementary School Students to Say Sentences orally Be Effective Writers, U.S. Department of Education, June 2012. (p.16) SSS Select the best sentence SENTENCE Structure sentences using transition GENERATI words ON By using this strategy, students learn to select a sentence, paragraph, or text excerpt and imitate the author’s form. They learn to try out sentences orally before writing them on paper. http://ies.ed.gov/ncee/wwc/pdf/ 13 Writing Instructional Strategies STRATEG CITATION / MATERIAL PURPOSE / DESCRIPTION Y FURTHER READ DRAFTING They learn to try multiple sentences and practice_guides/writing_pg_062 choose the best one. They learn to use 612.pdf transition words to develop different sentence structures and to practice writing good topic sentences. Helps students to: IES Practice Guide: Teaching elaborate Elementary School Students to describe Be Effective Writers, U.S. increase sentence structure variety Department of Education, June To implement the activity: 2012. (p.31) 1. Introduce a short sentence. SENTENCE 2. Model how to add to the sentence using different parts EXPANDIN of speech, demonstrate appropriate capitalization and G punctuation as the sentence is expanded. 3. Have students provide suggestions for different parts of speech (e.g., subjects and predicates) to add to the short sentences. 4. Have students work independently or in pairs to http://ies.ed.gov/ncee/wwc/pdf/ expand a sentence. practice_guides/writing_pg_062 5. Encourage students to share their expanded sentences 612.pdf in small groups, providing feedback to their peers. 14 Writing Instructional Strategies STRATEG CITATION / MATERIAL PURPOSE / DESCRIPTION Y FURTHER READ DRAFTING Helps students to: IES Practice Guide: Teaching write complex yet concise sentences Elementary School Students to express important points and ideas Be Effective Writers, U.S. express ideas in an interesting way Department of Education, June SENTENCE To implement the activity: 2012. (p.31) COMBININ 1. Choose sentences for combining. 2. Model how to combine the sentences using several G examples; with older students, introduce moving, deleting, and adding words or parts. 3. Have students rate the quality of the new sentence, provide alternatives to the new sentence, and discuss which sentences sound better and why. http://ies.ed.gov/ncee/wwc/pdf/ 4. Encourage students to work in pairs to combine practice_guides/writing_pg_062 sentences, creating several new possibilities and 612.pdf rating the quality of their new sentences. Helps student to develop sentence writing skills. IES Practice Guide: Teaching Elementary School Students to To implement the activity: Be Effective Writers, U.S. 1. Develop a sentence frame for students to use. Department of Education, June 2. Model the use of the sentence frame. 2012. (p.31) 3. Have students use the sentence frame to SENTENCE construct their own sentences. FRAMING 4. Have students share their sentences with peers and discuss their word choices. 5. Slowly fade the use of the sentence frame during instruction until students can write sentences independently. http://ies.ed.gov/ncee/wwc/pdf/ practice_guides/writing_pg_062 612.pdf 15 Writing Instructional Strategies STRATEG CITATION / MATERIAL PURPOSE / DESCRIPTION Y FURTHER READ DRAFTING Harris, K.R., & Graham, S. Helps students to make a writing plan by (1992). Helping young writers considering: master the craft: Strategy instruction and self-regulation Setting in the writing process. SPACE Cambridge, MA: Brookline (Narrative) Purpose Books, pg. 76.
Action
Conclusion
Emotions
This strategy is the second step of a three-step http://cehs.unl.edu/csi/Pdfs/spac writing strategy. It is designed to help students e.pdf make a writing plan and think about the details that should be included in stories. Models, demonstrations, and guided practice should be included when teaching student this strategy. 16 Writing Instructional Strategies STRATEG CITATION / MATERIAL PURPOSE / DESCRIPTION Y FURTHER READ REVISING & EDITING Helps students to: IES Practice Guide: Teaching Develop the thesis. Elementary School Students to Be Effective Writers, U.S. Department of Education, June 2012. Add ideas to support the thesis. This link provides a power point that explains SRSD and STOP, DARE, DARE Reject arguments on the other side. PLAN, TREE, POW, and WRITE. (Argumentative) Information about teaching the self- End with a strong conclusion. regulating strategies for student materials and links to Peabody/ Vanderbilt interactive tutorials are provided. https://earlychildhoodeducation.u su.edu/files/uploads/UTah_State_ SRSD.pptx.pdf Helps students to: IES Practice Guide: Teaching • Self-evaluate Elementary School Students to - Are the ideas clear? Be Effective Writers, U.S. CHECKLIS - Is there a clear beginning, middle, and Department of Education, June 2012. (p.16) T FOR end? WRITING - Does the writing connect with the reader? SELF- - Are sentence types varied? CHECK Self-monitor writing - Did I meet the goals I developed for my http://ies.ed.gov/ncee/wwc/pdf/ writing? If not, what changes should I practice_guides/writing_pg_062 612.pdf make to meet my goals? - Did I correctly use strategies that were appropriate for this task? If not, what should I change? 17 Writing Instructional Strategies STRATEG CITATION / MATERIAL PURPOSE / DESCRIPTION Y FURTHER READ REVISING & EDITING Helps students to edit through answering The Error Monitoring Strategy, questions: The University of Kansas Center for Research on • Did I Capitalize the first word in sentences Learning, http://www.kucrl.org/sim/strate and proper names? gies/error.shtml COPS • How is the Overall appearance of my paper? IES Practice Guide: Teaching Elementary School Students to • Did I use commas and end-of-sentence Be Effective Writers, U.S. punctuation? Department of Education, June 2012. (p.16) • Did I Spell each word correctly? http://ies.ed.gov/ncee/wwc/pdf/ practice_guides/writing_pg_062 612.pdf Helps students to edit using the steps: Schumaker, J.B., Nolan, S.M., & Deshler, D.D. (1985). The Write on every other line error monitoring strategy. In Ellis, E.S., & Lenz, B.K. (1987). A component analysis Read the paper for meaning WRITER of effective learning strategies for LD students. Learning Interrogate yourself using COPS Disabilities Focus, 2, 94-107.
Take the paper to someone to proofread
again http://cehs.unl.edu/csi/Pdfs/writ er.pdf Execute a final copy 18 Writing Instructional Strategies STRATEG CITATION / MATERIAL PURPOSE / DESCRIPTION Y FURTHER READ REVISING & EDITING Reread your paper a final time
Helps students to peer edit by: IES Practice Guide: Teaching Elementary School Students to Placing a question mark (?) by anything they Be Effective Writers, U.S. do not understand in their writing partner’s Department of Education, June paper. 2012. (p.16) PEER EDITING Placing a carat (^) anywhere it would be useful to have the author include more information. http://ies.ed.gov/ncee/wwc/pdf/ practice_guides/writing_pg_06 2612.pdf 19 Writing Instructional Strategies STRATEG CITATION / MATERIAL PURPOSE / DESCRIPTION Y FURTHER READ STRENGTHEN WRITING (SHARING WITH PEERS) Helps students provide appropriate verbal feedback to peers about their writing. IES Practice Guide: Teaching Elementary School Students to Be Effective Writers, U.S. Department of Education, June 2012. (p.38) (p.16) AUTHOR’S To implement the activity: CHAIR During the “Author’s Chair” activity, one student, sitting in a special chair, reads his or her work to peers as they sit on the rug. The teacher then models (using suggested “Author’s Chair”) and facilitates giving kind http://ies.ed.gov/ncee/wwc/pdf/ practice_guides/writing_pg_062 verbal comments. 612.pdf 20 Writing Instructional Strategies STRATEG CITATION / MATERIAL PURPOSE / DESCRIPTION Y FURTHER READ ADDITIONAL RESOURCES http://iris.peabody.vanderbilt.ed Improving This professional development module u/module/pow/ highlights the differences between students Writing who write well and those who struggle. Performance: Modules from IRIS website Elements of the writing process are discussed, A Strategy for as are the prerequisite skills students need to Writing write good papers. The module outlines and describes the process for teaching students the Persuasive POW+TREE strategy, a writing strategy to help Essays students produce better persuasive essays.
Adolescent Literacy.org is a resource for http://www.adlit.org/article/360 parents and educators, grades 4-12. Learn 70/%20-%20mnemonics/
Writing how to model a range of prewriting techniques Process Adolescent Literacy website and introduce several mnemonics to help students organize their writing.”A chart that lists the Planning Mnemonics, what they stand for, what type of writing and credits for RAFT, STOP, DARE, STOP, LIST, W4H2. Writing Center on Instruction This synopsis provides the findings reported in http://www.centeroninstruction. Next: website “Writing Next”; it identifies 11 instructional org/synopsis-of-writing-next- strategies, listed in decreasing order of effect effective-strategies-to-improve- Effective size. This resource can facilitate the writing-of-adolescents-in- Strategies to strengthening of writing instruction for middle--high-schools Improve implementation of the College & Career Ready Writing of Standards. Adolescents 21 Writing Instructional Strategies STRATEG CITATION / MATERIAL PURPOSE / DESCRIPTION Y FURTHER READ ADDITIONAL RESOURCES in Middle & High Schools
The Cognitive Strategy Instruction website http://cehs.unl.edu/csi/writing.s Cognitive contains a variety of writing strategies for html Strategy University of Nebraska- spelling, written composition, and Instruction: Lincoln Cognitive Strategy proofreading. Instruction website Writing