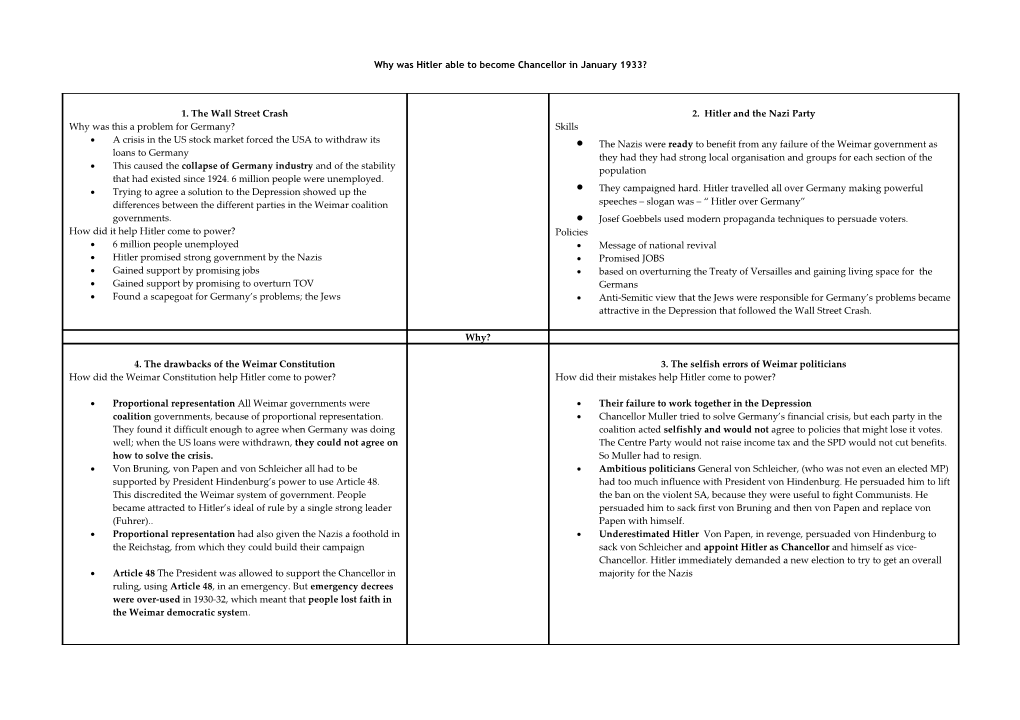
Why was Hitler able to become Chancellor in January 1933?
1. The Wall Street Crash 2. Hitler and the Nazi Party Why was this a problem for Germany? Skills A crisis in the US stock market forced the USA to withdraw its The Nazis were ready to benefit from any failure of the Weimar government as loans to Germany they had they had strong local organisation and groups for each section of the This caused the collapse of Germany industry and of the stability population that had existed since 1924. 6 million people were unemployed. Trying to agree a solution to the Depression showed up the They campaigned hard. Hitler travelled all over Germany making powerful differences between the different parties in the Weimar coalition speeches – slogan was – “ Hitler over Germany” governments. Josef Goebbels used modern propaganda techniques to persuade voters. How did it help Hitler come to power? Policies 6 million people unemployed Message of national revival Hitler promised strong government by the Nazis Promised JOBS Gained support by promising jobs based on overturning the Treaty of Versailles and gaining living space for the Gained support by promising to overturn TOV Germans Found a scapegoat for Germany’s problems; the Jews Anti-Semitic view that the Jews were responsible for Germany’s problems became attractive in the Depression that followed the Wall Street Crash.
Why?
4. The drawbacks of the Weimar Constitution 3. The selfish errors of Weimar politicians How did the Weimar Constitution help Hitler come to power? How did their mistakes help Hitler come to power?
Proportional representation All Weimar governments were Their failure to work together in the Depression coalition governments, because of proportional representation. Chancellor Muller tried to solve Germany’s financial crisis, but each party in the They found it difficult enough to agree when Germany was doing coalition acted selfishly and would not agree to policies that might lose it votes. well; when the US loans were withdrawn, they could not agree on The Centre Party would not raise income tax and the SPD would not cut benefits. how to solve the crisis. So Muller had to resign. Von Bruning, von Papen and von Schleicher all had to be Ambitious politicians General von Schleicher, (who was not even an elected MP) supported by President Hindenburg’s power to use Article 48. had too much influence with President von Hindenburg. He persuaded him to lift This discredited the Weimar system of government. People the ban on the violent SA, because they were useful to fight Communists. He became attracted to Hitler’s ideal of rule by a single strong leader persuaded him to sack first von Bruning and then von Papen and replace von (Fuhrer).. Papen with himself. Proportional representation had also given the Nazis a foothold in Underestimated Hitler Von Papen, in revenge, persuaded von Hindenburg to the Reichstag, from which they could build their campaign sack von Schleicher and appoint Hitler as Chancellor and himself as vice- Chancellor. Hitler immediately demanded a new election to try to get an overall Article 48 The President was allowed to support the Chancellor in majority for the Nazis ruling, using Article 48, in an emergency. But emergency decrees were over-used in 1930-32, which meant that people lost faith in the Weimar democratic system.