Name Per
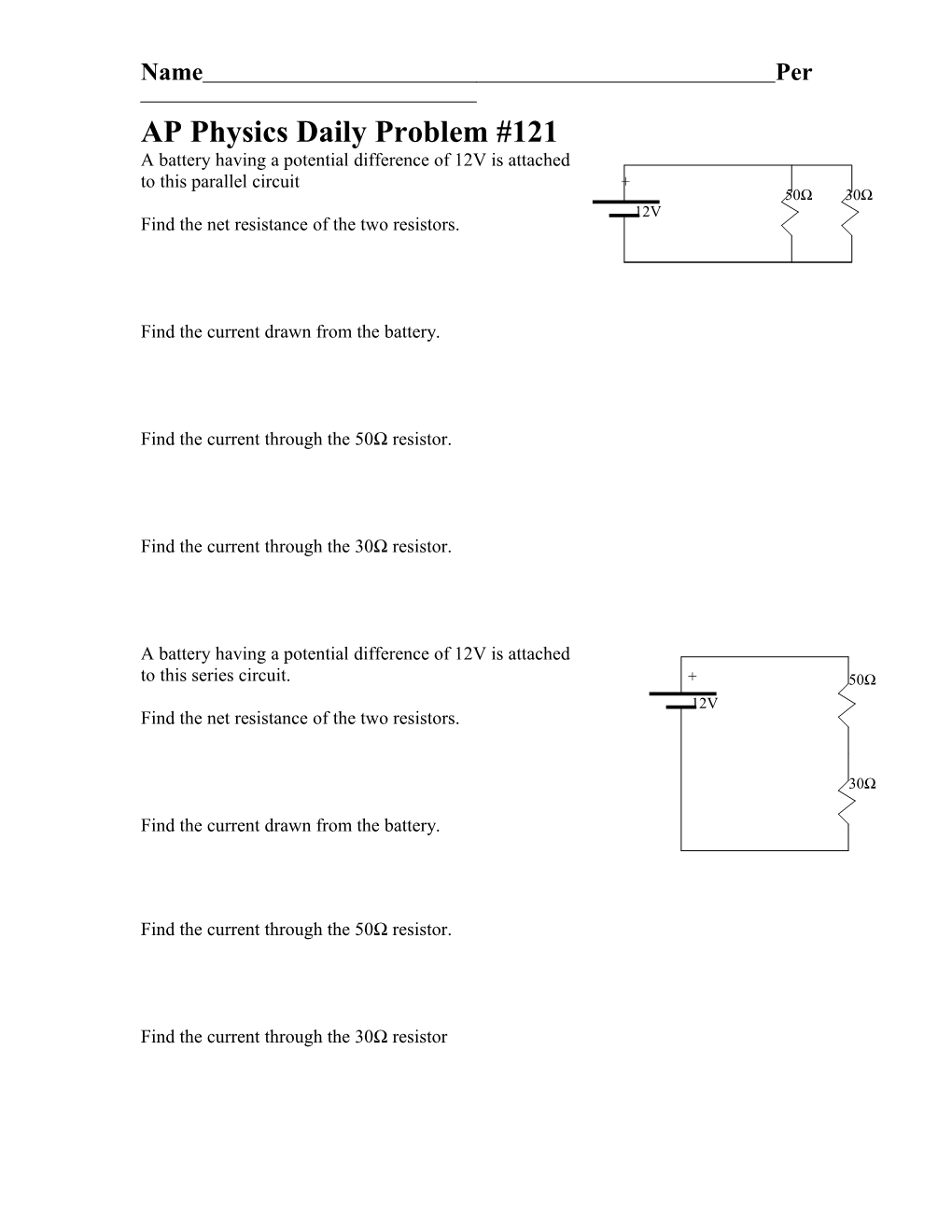
AP Physics Daily Problem #121 A battery having a potential difference of 12V is attached to this parallel circuit + 50Ω 30Ω 12V Find the net resistance of the two resistors.
Find the current drawn from the battery.
Find the current through the 50Ω resistor.
Find the current through the 30Ω resistor.
A battery having a potential difference of 12V is attached to this series circuit. + 50Ω 12V Find the net resistance of the two resistors.
30Ω
Find the current drawn from the battery.
Find the current through the 50Ω resistor.
Find the current through the 30Ω resistor Name Per
AP Physics Daily Problem #122 Label each resistor in the circuit below with its voltage drop, current, and power used. Calculate the current and power drawn from the battery. At the bottom of this page, list the steps you used in solving this problem, including the law (loop rule, junctions rule, Ohm’s law) used.
50Ω 30Ω
20Ω + 120V
Steps used in solving circuit: Name Per
AP Physics Daily Problem #123 (1984 #3) A heating coil is placed in a thermally isolated tank of negligible heat capacity. The tank contains 0.1kg of water and 0.01kg of ice, both initially at a temperature of 0C. The resistance of the coil is 25Ω, independent of temperature and there is a current of 2.0A in the coil. Calculate each of the following quantities:
(a) The heat transferred to the water and ice in time t.
(b) The time t1 necessary to melt all the ice (the latent heat of fusion of ice is 3.34x105joules per kilogram.)
(c) The additional time t2 necessary to bring the water to a boil (the specific heat of water is 4.19x103 Joules per kilogram • Kelvin.) Name Per
AP Physics Daily Problem #124 The circuit below has a battery with an internal resistance of 1.0Ω.
5.0Ω 3.0Ω
2.0Ω + 12V
What is the overall resistance of the circuit (including the battery’s internal resistance)
How much current is drawn from the battery?
How much power is drawn from the battery?
What is the current through the 5.0Ω and 3.0Ω resistors?
What is the total power dissipated by the three resistors?
Why is the amount of power dissipated by the three resistors different from the amount of power produced by the battery? Name Per
AP Physics Daily Problem #125
The battery in this circuit has no internal resistance.
2.0Ω 4.0V R1 R2
3.5A + R3 12V
What is the overall resistance of the circuit?
Find the voltage drop of R3.
Find the resistance of R3.
Find the current through R1.
Find the current through R2
Find the resistance of R2. Name Per
AP Physics Daily Problem #126
The battery in this circuit has an internal resistance of 2Ω.
R R 1 5 12V 3.0A R 2 2.0V 2.0A R 6 R R R 3 4 7 + 12Ω 5.0A 8.0V 48V
Make a table showing the resistance, current, and voltage drop for each resistor. Be sure to include the internal resistance in your table! Name Per
AP Physics Daily Problem #127
20F
10F 50F
+ 10V
What is the net capacitance of the 10F and 50F capacitors in parallel?
What is the net capacitance of the complete circuit?
How much charge is stored in the circuit?
How much charge is stored in the 20F capacitor?
What is the voltage drop across the 20F capacitor?
What is the voltage drop across the 10F capacitor?
How much charge is stored in the 10F capacitor?
How much charge is stored in the 50F capacitor? Name Per
AP Physics Daily Problem #128 (1995 #2)
A certain light bulb is designed to dissipate 6 watts when it is connected to a 12V source. (a) Calculate the resistance of the light bulb
(b) If the light bulb functions as designed and is continuously lit for 30 days, how much energy is used? Be sure to indicate the units in your answer.
The 6-watt, 12-volt bulb is connected in a circuit with a 1500-watt 120-volt toaster, an adjustable resistor, and a 120-volt power supply. The circuit is designed such that the bulb and the toaster operate at the given values and, if the light bulb fails, the toaster will still function at these values. (c) On the diagram below, draw in wires connecting the components shown to make a complete circuit that will function as described above.
120-Volt Supply
12-Volt Adjustable 120-Volt Bulb Resistor Toaster
(d) Determine the value of the adjustable resistor that must be used in order for the circuit to work as designed.
(e) If the resistance of the adjustable resistor is increased, what will happen to the following? The brightness of the bulb. Briefly explain your reasoning
The power dissipated by the toaster. Briefly explain your reasoning Name Per
AP Physics Daily Problem #129 (Read Chapter 20 before doing this problem!)
A power line carrying 1000A of current is suspended 30m above ground level. The current is flowing from south to north.
Determine the direction and magnitude of the magnetic field at ground level.
An electric fence wire is located directly underneath and parallel to the power line. A 10A current flows through the wire northward. Determine the magnitude and direction of the force on 100m of this wire due to the magnetic field of the power line. Name Per
AP Physics Daily Problem #130
A 1g particle containing 50C is fired at 100m/s southward into an upwardly directed magnetic field of 5.0T
Determine the force exerted on the particle (magnitude and direction)
Determine the acceleration of the particle (magnitude and direction)
Describe the path of the particle as it remains in the field. You may find a diagram to be helpful in your description
Name Per
AP Physics Daily Problem #131
A particle containing 20C of charge is fired northward at 10m/s into a region occupied by a 2T magnetic field directed downward. You may neglect gravity.
Determine the force exerted on the particle (magnitude and direction)
Determine the magnitude and direction of an electric field that could be created in the same region to cause the particle to continue in a straight line. Name Per
AP Physics Daily Problem #132 (1977 #3)
P1 P2 x x x x x x
x x x x x x B x x x x x x Electron x x x x x x
x x x x x x
x x x x x x
x x x x x x
An electron is accelerated from rest through a potential difference of magnitude V between infinite parallel plates P1 and P2. The electron then passes into a region of uniform magnetic field strength B which exists everywhere to the right of plate P2. The magnetic field is directed into the page.
(a) On the diagram above, clearly indicate the direction of the electric field between the plates. (b) In terms of V and the electron’s mass and charge, determine the electron’s speed at plate P2.
(c) Describe in detail the motion of the electron through the magnetic field, and explain why the electron moves this way.
(d) In terms of V, B, and the electron’s mass and charge, determine the work done on the electron after it passes to the right of plate P2
(e) If the magnetic field remains unchanged, what could be done to cause the electron to follow the straight-line path to the right of P2? Be specific in your answer Name Per
AP Physics Daily Problem #133 (1994 #4) In a linear accelerator, protons are accelerated from rest through a potential difference to a speed of approximately 3.1 x 106 meters per second. The resulting proton beam produces a current of approximately 2 x 10-6ampere.
(a) Determine the potential difference through which the protons were accelerated.
(b) If the beam is stopped in a target, determine the amount of thermal energy that is produced in the target in one minute.
Region of Field B y Proton Beam
Electron x z (Positive z out of page)
The proton beam enters a region of uniform magnetic field B, as shown above, which causes the beam to follow a semicircular path.
(c) Determine the magnitude of the field that is required to cause an arc of radius 0.10 meters.
(d) What is the direction of the magnetic field relative to the axes shown on the right? Name Per
AP Physics Daily Problem #134
B
A square loop of wire, 30cm on each side, is free to rotate about the vertical axis shown. A current of 5.0A flows through the wire in a clockwise direction. The loop is in a uniform magnetic field of 2T directed from left to right. You may ignore the wires leading into the loop.
(a) Determine the force on the leftmost side of the loop (magnitude and direction).
(b) Determine the force on the rightmost side of the loop (magnitude and direction).
(c) Determine the force on the top side of the loop (magnitude and direction).
(d) Determine the torque about the vertical axis (magnitude and direction). Name Per
AP Physics Daily Problem #135
B N
wire
A horizontal wire is placed in a direction where it is perpendicular to the earth’s magnetic field (55x10-6T) at the equator of the earth.
(a) Derive an equation to determine the current I needed to precisely negate the earth’s magnetic field at a distance d above the wire.
(b) Using this equation, determine the current needed to negate the earth’s magnetic field at a distance of 2m above the wire.
(c) At this current, what would be the magnetic field strength and direction at a location 2m below the wire?
(d) At this current, what would be the magnetic field strength and direction at a location 2m north of the wire? Name Per
AP Physics Daily Problem #136 x x x x x x A circular coil of wire, 30cm in diameter and containing 100 turns is placed in a magnetic field of 2T. The field is x x x x x x decreased to a value of 1T over a time period of 5s. B x x x x x x
(a) If the leads were connected, which way would current flow inx the loop?x x x x x
x x x x x x
x x x x x x
x x x x x x
(b) What is the voltage between the leads?
(c) If a resistance of 4Ω is placed between the leads, what is the current that would flow in the loop?
(d) If this process were repeated for an hour, how much energy would be dissipated by the resistor? Name Per
AP Physics Daily Problem #137 (1986 #4)
x x x x x x X x x x x x x 3m/s B=0.5T 2m 5Ω x x x x x x
x x x x x x Y x x x x x x
4m A wire loop, 2meters by 4 meters, of negligible resistance is in the plane of the page with its left end in a uniform 0.5-tesla magnetic field directed into the page, as shown above. A 5-ohm resistor is connected between points X and Y. The field is zero outside the region enclosed by the dashed lines. The loop is pulled to the right with a constant velocity of 3 meters per second. Make all determinations for the time that the left end of the loop is still in the field, and points X and Y are not in the field.
(a) Determine the potential difference induced between points X and Y.
(b) On the figure above, show the direction of the current induced in the resistor.
(c) Determine the force required to keep the loop moving at 3 meters per second
(d) Determine the rate at which work must be done to keep the loop moving at 3 meters per second. Name Per
AP Physics Daily Problem #138 (1994 #6) Rail
F l R v B (out of paper)
Rail Rod A force F is applied to a conducting rod so that the rod slides with constant speed v over a frictionless pair of parallel conducting rails that are separated by a distance l. The rod and rails have negligible resistance, but the rails are connected by a resistance R, as shown above. There is a uniform magnetic field B perpendicular to and directed out of the plane of the paper.
(a) What is the direction of the induced current through the resistor?
Determine expressions for the following in terms of v, B, l, and R (b) The induced emf in the rod.
(c) The electric field in the rod
(d) The magnitude of the induced current in the resistor R
(e) The power dissipated in the resistor as the rod moves in the magnetic field
(f) The magnitude of the external force F applied to the rod to keep it moving with constant speed v. Name Per
AP Physics Daily Problem #139
200m/s
60m
An airplane is flying directly over the magnetic south pole of the earth. It has a speed of 200m/s and a wingspan of 60m. The earth’s magnetic field is about 55x10-6T
(a) What is the rate at which the aircraft cuts the magnetic flux?
(b) What is the induced emf from one wingtip to the other?
(c) Which wingtip (right or left as you face forward in the airplane) will be positive? Explain your reasoning. Name Per
AP Physics Daily Problem #140
1/4λ
a. The optimum length for one type of receiving antenna is ¼ wavelength long. How long would this antenna be to receive a radio station on a frequency of 97.1MHz?
b. How long would the antenna be to receive an AM radio station on a frequency of 1070kHz?
c. How long would the antenna be to receive a cellular phone transmission on a frequency of 2.4GHz? Name Per
AP Physics Daily Problem #141
a. The speed of light in a vacuum is 3.0x108m/s in a vacuum. What is the speed of light in water (n=1.33) and diamond (n=2.42)?
b. If the light has a wavelength of 600nm in vaccum, what is its wavelength in water and diamond?
c. If the light has a frequency of 5.0x1014Hz in vacuum, what is its frequency in water and diamond? Name Per
AP Physics Daily Problem #142
a. If you are 5 feet tall, how tall of a plane mirror will you need to view yourself full length? Show your answer below in an accurately-drawn ray diagram:
b. Would the mirror required be larger or smaller if you were to move closer to it? Draw an accurate ray diagram to see!
c. What is the definition of electric potential energy? Yes, you need to remember this stuff! Name Per
AP Physics Daily Problem #143
a. An object 2cm tall is located 7.5cm from a concave mirror of radius 10cm. Where will the image be located? Will the image be real or virtual? Calculate the answer and show your answer below in an accurately-drawn ray diagram:
b. An object 2cm tall is located 2.5cm from a concave mirror of radius 10cm. Where will the image be located? Will the image be real or virtual? Calculate the answer and show your answer below in an accurately-drawn ray diagram:
c. Qualitatively, what happens to the size of the image as the object is moved closer to the focal point?
Name Per
AP Physics Daily Problem #144
An object 2.0cm tall is located 7.0cm from a convex lens of focal length 4 cm. Where will the image be located? Will the image be real or virtual? Calculate the answer and show your answer below in an accurately-drawn ray diagram: Name Per
AP Physics Daily Problem #145
An object 5.0cm tall is located 7.0cm from a concave lens of focal length –4.0 cm. Where will the image be located? Will the image be real or virtual? Calculate the answer and show your answer below in an accurately-drawn ray diagram: Name Per
AP Physics Daily Problem #146 (1987 #5)
Θ 2 Air (n=1.0)
Glass (n=1.6)
Θ1 Θ3
14 Light of frequency 6.0 x 10 Hz strikes a glass-air boundary at an angle of incidence θ1. The ray is partially reflected and partially refracted at the boundary as shown above. The index of refraction of this glass is 1.6 for light of this frequency.
(a) Determine the value of θ3 if θ1 is 30
(b) Determine the value of θ2 if θ1 is 30
(c) Determine the speed of light in this glass
(d) Determine the wavelength of light in this glass
(e) What is the largest value of θ1 that will result in a refracted ray? Name Per
AP Physics Daily Problem #147
grating screen
630nm
5.0m
Laser light of wavelength 630nm passes through a diffraction grating of spacing 100 lines per millimeter. A screen is placed 5 meters away from the grating.
(a) Determine the angle of diffraction of the first order fringe
(b) Determine the location of the third order fringe on the screen, relative to the central maximum
(c) Another laser is installed. If the fringes are spaced 20cm apart, determine the frequency of the light of this laser. Name Per
AP Physics Daily Problem #148
illumination
gasoline
water
A thin film of gasoline (n=1.5) is spread on the surface of a puddle of water (n=1.33). It is illuminated from directly above.
(a) State the condition required to induce a 1/2λ phase change during a reflection
(b) Do any phase changes occur in the example above? If so, on what surface(s)?
(c) When viewed from above, the reflected light appears red, with the strongest light received at a wavelength of 600nm. What is the minimum thickness of the gasoline film? Name Per
AP Physics Daily Problem #149 (1986 #6) An object is placed 3 centimeters to the left of a convex (converging) lens of focal length F=2 centimeters, as shown below: F = +2 cm
0 1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 (cm)
(a) Sketch a ray diagram on the figure above to construct the image. (b) Determine the ratio of image size to object size
The converging lens is removed and a concave (diverging) lens of focal length f=-3 centimeters is placed as shown below. F = -3cm
0 1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 (cm)
(c) Sketch a ray diagram on the figure above to construct the image (d) Calculate the distance of this image from the lens
(e) State whether the image is real or virtual.
The two lenses and the object are placed as shown below. F = +2 cm F = -3 cm
0 1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 (cm)
(f) Construct a complete ray diagram to show the final position of the image produced by the two lens system Name Per
AP Physics Daily Problem #150
1. A battery produces a current of 20A at 12V for one hour Using the principle of mass-energy equivalence, determine the mass lost by the battery in the process.
2. A metal surface is illuminated by a beam of light. The work function (w0) of the metal is 2.9eV. a. If the beam of light has an wavelength of 400nm, determine the energy of a photon, whether an electron will be ejected, and the kinetic energy of the ejected electron.
b. If the beam of light has an wavelength of 600nm, determine the energy of a photon, whether an electron will be ejected, and the kinetic energy of the ejected electron.
3. In the space below, draw a qualitative graph of kinetic energy of the ejected electron versus wavelength. Indicate the work function on your graph.
KE
λ