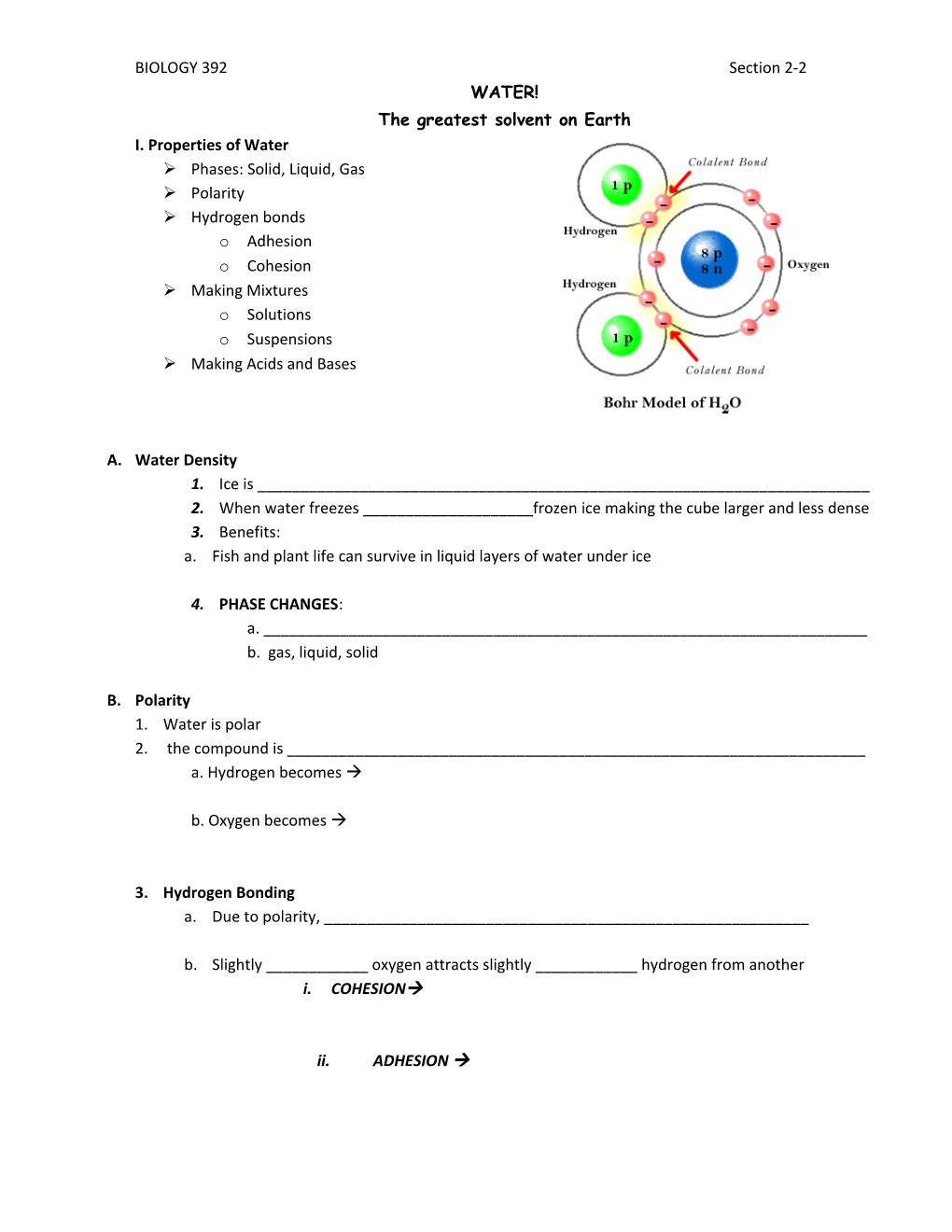
BIOLOGY 392 Section 2-2 WATER! The greatest solvent on Earth I. Properties of Water Phases: Solid, Liquid, Gas Polarity Hydrogen bonds o Adhesion o Cohesion Making Mixtures o Solutions o Suspensions Making Acids and Bases
A. Water Density 1. Ice is ______2. When water freezes ______frozen ice making the cube larger and less dense 3. Benefits: a. Fish and plant life can survive in liquid layers of water under ice
4. PHASE CHANGES: a. ______b. gas, liquid, solid
B. Polarity 1. Water is polar 2. the compound is ______a. Hydrogen becomes
b. Oxygen becomes
3. Hydrogen Bonding a. Due to polarity, ______
b. Slightly ______oxygen attracts slightly ______hydrogen from another i. COHESION
ii. ADHESION
C. Mixtures 1. The greatest solvent on Earth! 2. Water’s polarity allows it to
3. Definition 4. Types of Mixtures
a. SOLUTIONS
i. Distributes evenly ii. “Like dissolves Like” iii. Ex: b. SUSPENSIONS
i. Example:
RECAP 1. Why does ice float on a lake?
2. Explain the polarity of water – how are the charges distributed?
3. What is the difference between adhesion and cohesion?
4. Explain the difference between a solution and a suspension
D. Water Dissociation 1. Water can break apart on its own into 2 charged ions a.
II. ACIDS & BASES 1. Water can react to form individual ions: 2. In pure water this occurs naturally
3. H+ is always ______OH- so water remains ______
A. pH scale: “the power of Hydrogen”
1. Some solutions made with water become acidic or basic. 2. This is determined by ______3. pH = - log [H+] a. Example: [H+] = 1 x 10 -5 à pH = 5 (acid) = [H+] = 1 x 10 -9 à pH = 9 (base) = B. Acids 1 pH range ______2 Definition:______3 H+ ions ____ OH- ions 4 The closer ______the more acidic the solution 5 Examples: ______
C. Bases (Alkaline) 1. pH ranges ______2. Definition ______3. OH- ions ______H+ ions 4. The closer ______the more basic the solution 5. Examples: ______
D. pH and Living Things 1. pH values in living cells ______a. Optimal pH for chemical reactions to take place in the body b. Any switch in pH could cause serious/fatal problems E. Buffers 1. Definition ______2. Function ______3. There are natural buffers in your blood that keep the pH ______
RECAP 1. What makes a solution acidic or basic?
2. How is acidity measured?
3. A solution with pH 8.5 is considered….