Name: ______Date: ______Per. ______
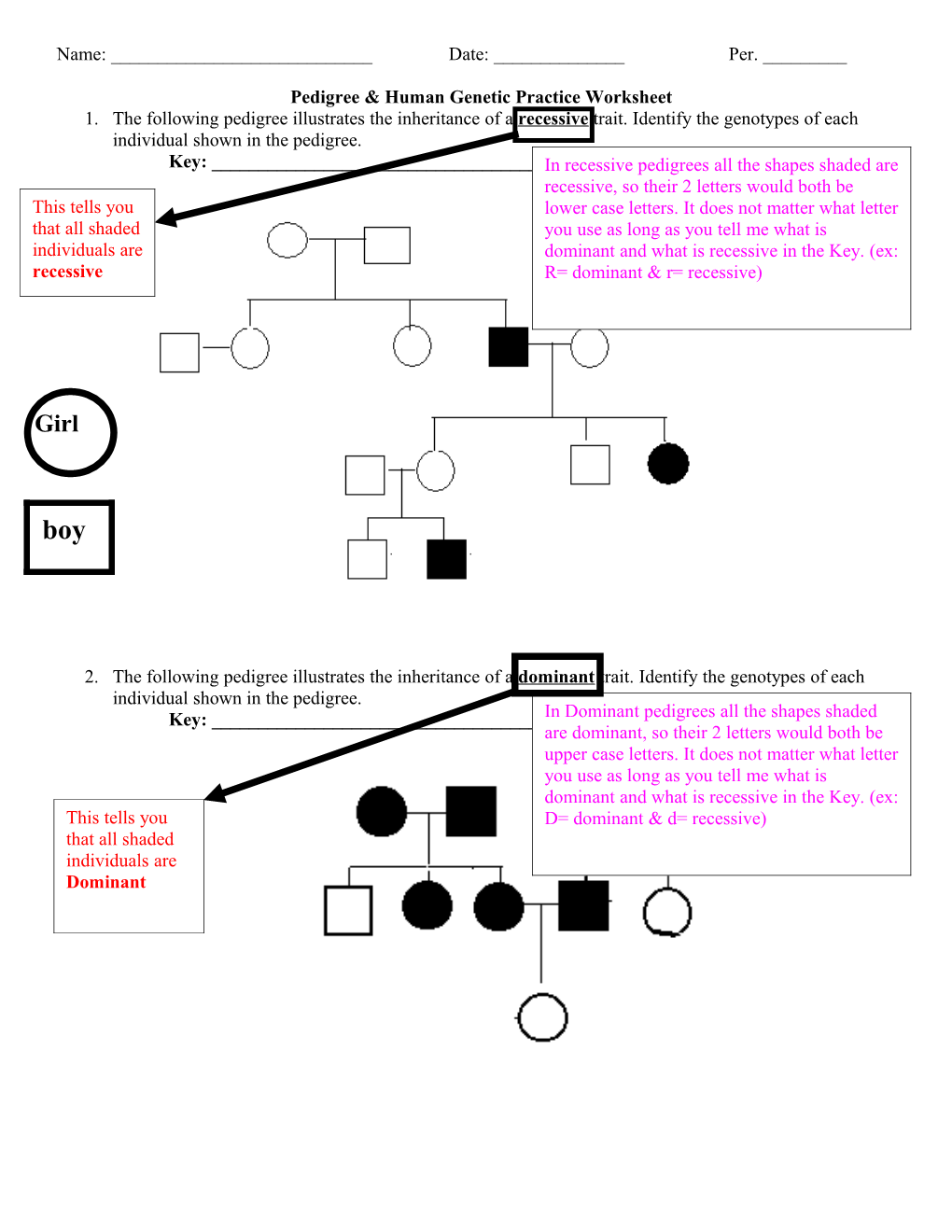
Pedigree & Human Genetic Practice Worksheet 1. The following pedigree illustrates the inheritance of a recessive trait. Identify the genotypes of each individual shown in the pedigree. Key: ______In recessive pedigrees all the shapes shaded are recessive, so their 2 letters would both be This tells you lower case letters. It does not matter what letter that all shaded you use as long as you tell me what is individuals are dominant and what is recessive in the Key. (ex: recessive R= dominant & r= recessive)
Girl
boy
2. The following pedigree illustrates the inheritance of a dominant trait. Identify the genotypes of each individual shown in the pedigree. Key: ______In Dominant pedigrees all the shapes shaded are dominant, so their 2 letters would both be upper case letters. It does not matter what letter you use as long as you tell me what is dominant and what is recessive in the Key. (ex: This tells you D= dominant & d= recessive) that all shaded individuals are Dominant 3. Examine the pedigree below showing the inheritance of albinism. Identify the genotypes of all individuals Being albino is a recessive trait. Use A= normal & a= albino
a. Key: ______
b. If individual E marries a man with albinism, what is the probability they would have a child with the disorder? Cross: ______
c. If this same couple (E x albino male) has a child with normal pigmentation, what is the probability their child is a carrier for albinism? ______
4. Two couples, the Pages and the Bakers, had baby boys in the same hospital at the same time. There was mix up in the nursery. Do Punnett squares to determine the biological parents of the babies. Us the information given below to help you.
Name: Mrs. Page Mr. Page Mrs. Baker Mr. Baker Baby #1 Baby #2 Blood Type: B AB B A A O Blood type Punnett squares. Use your notes to help you. Remember, A can be heterozygous or homozygous. Same with B blood type.
Baby #1 Belongs to the ______Baby #2 Belongs to the ______
Sex-Linked In sex-linked you have to use X & Y’s along 5. A hemophiliac man marries a woman who is a carrier of the hemophiliacwith superscripts. condition. Hemophilia Draw a Punnett is a recessive square representing the offspring of this marriage. disorder. So H=normal h=hemophilia. a. What percentage of the offspring will be a hemophiliac?Women ______are XX and men are XY h h b. Is it possible for these parents to produce an offspring thatWoman is neither who a has hemophilia X X carrier Man who has hemophilia Xh Y nor a hemophiliac? ______Normal woman XH XH H c. If so, would this individual be male of female? ______Normal man X Y Carrier woman XH Xh (a woman can be a d. What would be the genotype of this individual? ______carrier because she has 2 X’s. Men only have e. Is it possible to have a female hemophiliac? ______1 X so they either have the trait or not 6. In the case of the sex-linked gene responsible for hemophilia, a hemophiliac father never transmits hemophilia to his son. Explain why: ______Think about whom does the boy get his Y from ______and who does the boy get his X from?
7. Red-green color blindness is also a sex-linked recessive trait in humans. Using B as the superscript for normal vision and b for color blindness, give the genotypes for the following: a. A normal female:______d. A normal male: ______b. A carrier female: ______Written just like thee. A color blind male: ______hemophilia one c. A color blind female: ______
8. In the following problems, draw Punnett squares to represent the crosses. Give the proportion (1/4, 2/4 ect.) of each phenotype listed. Note….. some phenotypes may not appear so you may leave those blank. a. A color blind male x a female carrier
Normal female (not carrier) ______Color blind female ______Carrier ______Normal male ______Color blind male ______
b. Normal vision male x color blind female:
Normal female (not carrier) ______Color blind female ______Carrier ______Normal male ______Color blind male ______
c. Color blind male x normal female (not a carrier):
Normal female (not carrier) ______Color blind female ______Carrier ______Normal male ______Color blind male ______9. Can a normal blood clotting man & a carrier female have a hemophilic son? ______10. Why? ______
Complete the following autosomal crosses: 11. Is Huntington’s dominant or recessive? ______
12. What is the probability of a male heterozygous for Huntington’s and a homozygous recessive female having a child with Huntington’s?
a. Phenotypic ratio: ______b. Genotypic ratio: ______
13. The following pedigree shows the path of inheritance of hemophilia through several generations. Identify the genotypes of each individual.
This is a sex-linked pedigree, so you have to write XX for girls and XY for boys. Fill in the boys first because they either have the disorder (Xh Y) or don’t (XH Y) then try to figure out the girls. If there is no way for you to know what the girl is you put XH X? a. Key: ______