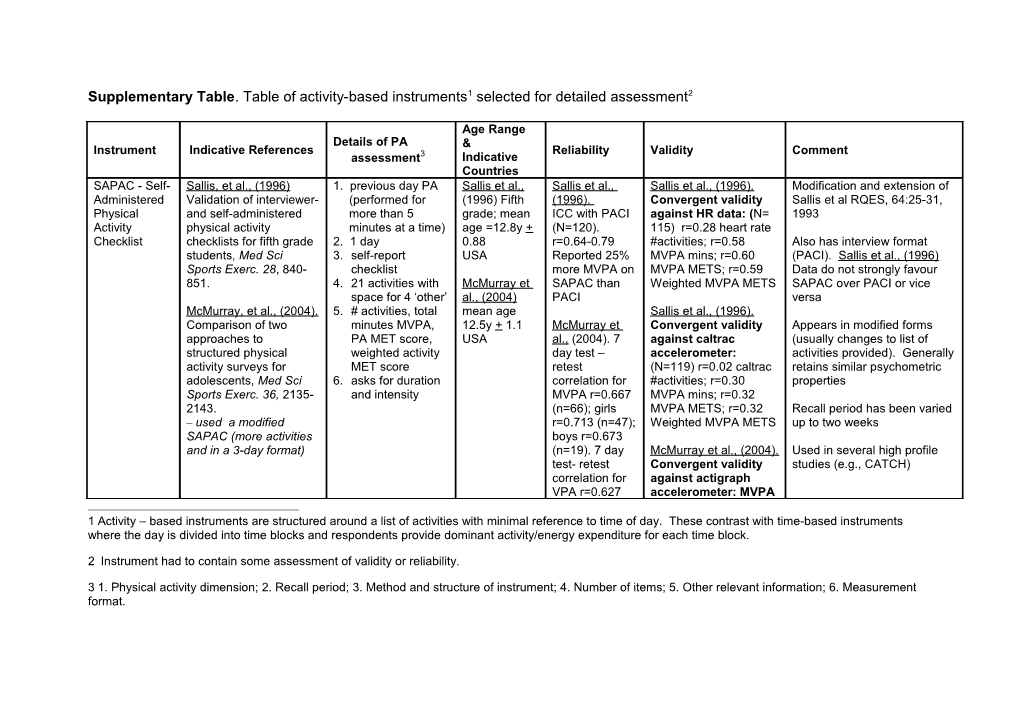
Supplementary Table. Table of activity-based instruments1 selected for detailed assessment2
Age Range Details of PA & Instrument Indicative References Reliability Validity Comment assessment3 Indicative Countries SAPAC - Self- Sallis, et al., (1996) 1. previous day PA Sallis et al., Sallis et al., Sallis et al., (1996). Modification and extension of Administered Validation of interviewer- (performed for (1996) Fifth (1996). Convergent validity Sallis et al RQES, 64:25-31, Physical and self-administered more than 5 grade; mean ICC with PACI against HR data: (N= 1993 Activity physical activity minutes at a time) age =12.8y + (N=120). 115) r=0.28 heart rate Checklist checklists for fifth grade 2. 1 day 0.88 r=0.64-0.79 #activities; r=0.58 Also has interview format students, Med Sci 3. self-report USA Reported 25% MVPA mins; r=0.60 (PACI). Sallis et al., (1996) Sports Exerc. 28, 840- checklist more MVPA on MVPA METS; r=0.59 Data do not strongly favour 851. 4. 21 activities with McMurray et SAPAC than Weighted MVPA METS SAPAC over PACI or vice space for 4 ‘other’ al., (2004) PACI versa McMurray, et al., (2004). 5. # activities, total mean age Sallis et al., (1996). Comparison of two minutes MVPA, 12.5y + 1.1 McMurray et Convergent validity Appears in modified forms approaches to PA MET score, USA al., (2004). 7 against caltrac (usually changes to list of structured physical weighted activity day test – accelerometer: activities provided). Generally activity surveys for MET score retest (N=119) r=0.02 caltrac retains similar psychometric adolescents, Med Sci 6. asks for duration correlation for #activities; r=0.30 properties Sports Exerc. 36, 2135- and intensity MVPA r=0.667 MVPA mins; r=0.32 2143. (n=66); girls MVPA METS; r=0.32 Recall period has been varied – used a modified r=0.713 (n=47); Weighted MVPA METS up to two weeks SAPAC (more activities boys r=0.673 and in a 3-day format) (n=19). 7 day McMurray et al., (2004). Used in several high profile test- retest Convergent validity studies (e.g., CATCH) correlation for against actigraph VPA r=0.627 accelerometer: MVPA
1 Activity – based instruments are structured around a list of activities with minimal reference to time of day. These contrast with time-based instruments where the day is divided into time blocks and respondents provide dominant activity/energy expenditure for each time block.
2 Instrument had to contain some assessment of validity or reliability.
3 1. Physical activity dimension; 2. Recall period; 3. Method and structure of instrument; 4. Number of items; 5. Other relevant information; 6. Measurement format. Age Range Details of PA & Instrument Indicative References Reliability Validity Comment assessment Indicative Countries (n=66); girls counts r=0.239 r=0.642 (n=47); (n=107); girls r=0.265 boys r=0.811 (n=75); boys r=0.340 (n=19) (n=32); VPA counts r=0.281 (n=107); girls r=0.312 (n=75); boys r=0.289 (n=32)
Adolescent Booth et al., (2002). 1. organised sport, Booth et al., Booth et al., Booth et al (2002). 20 mins to complete Physical The reliability and non-organised (2002) 13 & (2002) N=226, N=2026, 44 high Activity Recall validity of the adolescent sport 15y Australia 7 high schools schools Used in SPANS (Schools Questionnaire physical activity recall 2. normal week in Test-retest (2 Convergent validity: Physical Activity and Nutrition (A-PARQ) questionnaire. Med Sci school year, Li, et al., weeks) EE total (organised Survey) Sports Exerc, 34, 1986- recalled (2006). 11- Weighted and non-organised 1995. separately for 17y kappa: activities) against Li et al., (2006) adapted for summer and China 3 Category laps on multi-stage Chinese adolescents to Booth, et al., (2005). winter terms. outcome fitness test: include popular Chinese Methods of the NSW 3. SR ranged 0.33- Spearman’s rho=0.147 activities such as jumping schools physical activity 4. 4 grids (activity 0.71 and 0.39- and 0.208 for grade 8 rope and parcel shooting, and and nutrition survey category by 0.71 for girls and boys; activities such as cricket and (SPANS). J Sci Med winter/summer) summer and Spearman’s rho=0.139 squash were deleted. Sport, 8(3), 284-293. 5. categorical winter. and 0.391 for grade 10 outcome: vig (vig 2 Category girls and boys. Li, et al., (2006). Factors PA 3x week for outcome associated with 20min), mod ranged 0.34- Booth et al. (2005) and adolescents' physical (3.5hrs 0.74 and 0.25- Li et al. (2006) cite inactivity in Xi'an City, MPA/week over 5 0.68 for Booth et al. (2002) China,' Med Sci Sports sessions), summer and when describing the A- Exerc, 39, 2075-2085. inactive (not in winter. PARQ. other 2 categories), Continuous sometimes vig outcome: and mod are Total EE range combined. Summer ICC Continuous = .30-.86; Age Range Details of PA & Instrument Indicative References Reliability Validity Comment assessment Indicative Countries outcome: EE Winter ICC = . from METS for 36-.91 organised and Summer non-organised Spearmans rho activities. = .64-.81; 6. free-response Winter (although Spearmans rho common activities = .52-.74 are listed as prompts). Frequency and average duration of each activity is recorded. Durations of <10mins are excluded during processing. Winter and summer recalls are NOT combined.
Swedish Ekelund., et al (2006) 1. school, transport Ekelund, et al Not reported Ekelund et al (2006). Adolescent The criterion validity of a & leisure time PA (2006) Convergent validity Physical last 7-day physical plus sitting time mean age (criterion): (N=49) Activity activity questionnaire 2. last 7 days 16.8y + 0.4 Correlations between Questionnaire (SAPAQ) for use in 3. self-report total volume of self- (SwAPAQ) adolescents with a wide 4. 25 Sweden reported PA (total MET- variation in body fat: The 5. frequency, minutes) and MTI Stockholm Weight duration and Corder et al. accelerometer Development Study, Int intensity used to (2009) assessed variables of J Obes, 39, 1019-1021. generate British 16-17y PA. Adjusted for outcomes gender: against time Questionnaire available 6. response format UK spent sedentary (min Age Range Details of PA & Instrument Indicative References Reliability Validity Comment assessment Indicative Countries for download at unclear; broad day) r= -0.44; against www.mrc- categories offered time spent in PA (min epid.ac.cam.uk day) r=0.51; against total counts per day Corder, et al. (2009). Is r=0.48; against total it possible to assess counts per minute per free-living physical day r=0.44 activity and energy expenditure in young Corder et al (2009) people by self-report? Convergent validity Am J Clin Nutr, 89, 1-9. (criterion): (N=24) Spearman rho: SwAPAQ MVPA v accelerometer MVPA = 0.23; SwAPAQ PAEE v DLW-EE = 0.40. Physical Crocker, et al., (1997). 1. Moderate to PAQ-C PAQ-C: PAQ-C PAQ-A is the same as PAQ-C Activity Measuring general vigorous PA 8-13y; Crocker et al., Kowalski et al., but doesn’t include a question Questionnaire levels of physical levels during the (1997). (1997a). (N=89). about morning recess for Older activity: Preliminary school year PAQ-A: (N=215) Test- Convergent validity: Children evidence for the 2. 7-day recall 14-18y retest (1-week): Relationships for PAQ- Both designed to be used (PAQ-C) Physical Activity 3. Self-report r=0.75 (males) C and activity rating during the school year and not Questionnaire for Older 4. 9 items Canada, USA r=0.82 question, a teacher's during vacation periods Physical Children. Med Sci 5. Outcome (females) rating of physical Activity Sports Exerc, 29, 1344- measure: activity, and moderate Questionnaire 1349. composite PA; Internal to vigorous PA for LMVPA (longer- reliability >0.80. assessed by a separate Adolescents Crocker, et al., (2000) than-10mins- inventory (r=0.45 to (PAQ-A) Children's physical MVPA) PAQ-C & PAQ- r=0.63). Construct activity and physical 6. 5-point rating A: Janz et al validity: positive self-perceptions. J scale (2008) (N=210) relationship with Sports Sci, 18, 383-394. Internal perceived competence consistency; (r=0.48) Divergent Kowalski, et al., (1997a). standardised validity: no Validation of the Cronbach relationship with Age Range Details of PA & Instrument Indicative References Reliability Validity Comment assessment Indicative Countries Physical Activity alphas ranged behavioural conduct Questionnaire for Older from 0.72 to (r=0.16). Children. Pediatr Exerc 0.88. Sci, 9, 174-186. Kowalski et al., (1997a). (N=97). Kowalski, et al., (1997b). Convergent validity: Convergent validity of r=0.39 caltrac; r=0.41- the Physical Activity 0.43 with other self- Questionnaire for reports - PAR interview Adolescents. Pediatr and leisure time Exerc Sci, 9, 342-352. exercise questionnaire; r=0.28 step test (fitness Janz, et al., (2008). test). Measuring Activity in Children and PAQ-A Adolescents Using Self- Kowalski et al., (1997b). Report: PAQ-C and (N=85) Convergent PAQ-A. Med Sci Sports validity: r=0.73 activity Exerc, 40, 767-772. rating; r=0.57 Leisure Time Exercise Moore., et al. (2007) Questionnaire; r=0.33 Validation of the Caltrac; r=0.59 7-day Physical Activity physical activity recall Questionnaire for Older interview. Children in children of different races. Pediatr Janz et al., (2008). Exerc Sci, 19:6–19. (N=49) Convergent validity. Rho=0.47 for total activity and actigraph; rho=0.49 for MVPA and actigraph. Rho improved to.56 and .63 when questions about PA and lunch activity were removed. Age Range Details of PA & Instrument Indicative References Reliability Validity Comment assessment Indicative Countries
Youth Risk Brener, et al., (2002). 1. school and leisure Brener et al., Brener et al., Troped et al (2007). ‘Physical activity’ items Behaviour Reliability of the 1999 time PA; 2002. (2002). Convergent validity. include measures of Survey Youth Risk Behaviour vigorous, mixed race (N=4619) (N=128) sedentary behaviour and (YRBS) Survey Questionnaire. moderate, high school PA behaviours Concordance between injury. J Adolesc Health, 31, strength students 13- assessed, on YRBS and Actigraph 336-342. exercises, sport 18y. average 15 moderate physical 2. past week and days apart. activity measures was Brener, et al., (1995). past year Brener et al. Kappa highest using Reliability of the Youth 3. self-report 1995. grades statistics: accumulated Risk Behaviour Survey 4. 5 PA items 7-12. 41.1-84.8%. accelerometer minutes. Questionnaire, Am J 5. Physical activity Kappas did not Sensitivity of the Epi, 141, 575-580. behaviours Troped et al. differ by moderate YRBS item defined as: watch 2007. 12.7y gender, grade, ranged from 0.19 to Troped, et al., (2007). 2 hours or more +0.6 race/ethnicity. 0.23 for four Reliability and validity of of television on an comparisons, and YRBS Physical Activity average school Brener et al. specificity was 0.74- Items among Middle day; attend USA, (1995) 0.92. School Students,' Med physical Philippines, (N=1679) PA For vigorous activity: Sci Sports Exerc, 39, education class 1 Canada behaviours sensitivity was high 416-425. or more days a assessed, 2- (0.75-0.92) compared week; exercise weeks apart with the four actigraph Survey available: more than 20 Kappa measures. Specificity www.drjamessallis.sdsu. minutes during statistics: was low (0.23-0.26) edu/measures/html physical 64.2-91.1% education class; played on 1 or Troped et al more sports team (2007). during the past 12 Moderate and months; injured vigorous during physical physical activity activity 1 or more assessed by Age Range Details of PA & Instrument Indicative References Reliability Validity Comment assessment Indicative Countries times during the YRBS between past 12 months 1-40 days apart 6. frequency of Test-retest participation ICC for moderate physical activity items: 0.51 (0.59 for girls and 0.37 for boys)
ICC for vigorous physical activity items: 0.46 (0.47 for girls and 0.42 for boys). Health Booth, et al., (2001). 1. out-of-school 11-16y Booth et al Booth et al (2001). Behaviour in The reliability and moderate-to- (2001). N=121 N=1072 year 8 School Aged validity of the physical vigorous PA (“.. >30 countries year 8 students students and N=954 Children activity questions in the out of breath or in network and N=105 year 10 students (HBSC) WHO health behaviour sweat”) (mainly year 10 Convergent validity: in schoolchildren 2. “usually” European). students. Higher fitness scores (HBSC) survey: a 3. self-report Scale 2-week test- for those with higher population study, Brit J 4. 2 PA items; 2 established in retest: Kappa self-reported PA. Sports Med, 35,263-267 sedentary 1983/84 in statistics: 67- behaviour items Austria, 85% England, Samdal, et al., (2006). 5. frequency and Finland, Trends in vigorous duration Norway. 35 Samdal et al physical activity and TV 6. tick boxes countries from (2006) cite an watching of adolescents 2001/02. unpublished from 1986 to 2002 in report by seven European Torsheim et al Countries, Eur J Pub 1995 - Age Range Details of PA & Instrument Indicative References Reliability Validity Comment assessment Indicative Countries Health, 17, 242-248. Intraclass correlation Janssen, et al., (2005). coefficient Comparison of (ICC) = 0.74 overweight and obesity prevalence in school- aged youth from 34 countries and their relationships with physical activity and dietary patterns. Obes Rev, 6, 123-132
Children's Telford, et al., (2004). 1. physical activity 5-6 y, 10-12y Telford et al Telford et al (2004). Leisure Reliability & validity of 2. ‘typical week’ (2004): (n=56, Convergent validity: Activities physical activity 3. self-report (SR) Australia 5-6 year olds Individual item Study Survey questionnaire for for 10-12y olds; and their agreement between SR (CLASS) children: The Children's parental proxy parents; n=111 and PP was good. Leisure Activities Study (PP) for 5-6y and 10-12 year olds Moderate, vigorous and Survey, Ped Exerc Sci, 10-12y olds and their total PA scores were 16, 64-78. 4. checklist of parents) lowly correlated. activities 5. frequency and 2-week test- Telford et al (2004). duration retest reliability Criterion-related 6. tick boxes (% agreement) validity: for individual Low correlations activities = 62- between CLASS and 94% (SR & accelerometer scores PP); judged for both SR and PP ‘moderate to instruments for both substantial’. age groups.
ICC for SR & Telford et al (2005). PP varied for Criterion-related different validity: Age Range Details of PA & Instrument Indicative References Reliability Validity Comment assessment Indicative Countries intensity levels, Zero-to-low correlations parental between PP measure education, and and accelerometers. child gender (ICC = 0.15 to 0.89).
Godin Leisure- Godin & Shephard, 1. strenuous, From 9y Sallis et al., Gao et al., (2006). Time Exercise (1985). A simple method moderate and (1993) Criterion-related Questionnaire to assess exercise mild exercise for Canada, UK, Test-retest (2- validity (N=114): (LTEQ) behaviour in the more than 15mins USA wk) of total Number of days per community. Canadian J 2. “A 7-day period” score: 11y week of participation by Appl Sport Sci, 10, 141- 3. self-report r=0.69, 13/14y LTEQ v. accelerometer 146. 4. 4 items r=0.80, 16y data: strenuous r=0.23; 5. Strenuous score x r=0.96. moderate r=0.13. Sallis, et al., (1993). 9, moderate x 5, Seven-day recall and light x 3. “Weekly Gao et al., Scerpella et al., (2002). other physical activity leisure activity” is (2006). Criterion-related self-reports in children product of above. Test-retest (1 validity: Relationship and adolescents, Med “Total leisure wk): between total LTEQ Sci Sports Exerc, 25, activity” includes Ages 12-14y score and other activity 99-108. frequency (e.g., (N=250) measures in 7-11y girls strenuous = 9 x r=0.48-0.68 (N=61): Fulkerson, et al., (2004). frequency). Activity Rating Scale Depressive symptoms 6. Write in frequency (PACI) r=0.25; caltrac and adolescent eating estimates accelerometer r=0.10; and health behaviours: a self-reported organised multifaceted view in a activity (hrs/wk) r=0.30; population-based combined (above) sample, Prev Med, 38, r=0.38. 865-875. Scerpella et al (2002). Gao, et al., (2006). Based on comparison Reliability and Validity of with multiple single day Age Range Details of PA & Instrument Indicative References Reliability Validity Comment assessment Indicative Countries a brief tool to measure measures of activity, children's physical the LTEQ did not activity, J Physical provide a good Activity Health, 3, 415- estimate of habitual 422 activity in preadolescent females Scerpella, et al., (2002) Validation of the Godin- Shephard questionnaire in prepubertal girls. Med Sci Sports Exerc, 34, 845-850. Seven-Day Sallis, et al., (1993). 1. very hard and 11-16y Sallis et al., Sallis et al., (1993). Physical Seven-day recall and moderate PA for (1993). Criterion validity Activity Recall other physical activity more than 15mins USA Test-retest (9 Relationship between (7D-PAR) self-reports in children 2. Previous 7 days Sweden weeks) for hours of recalled very and adolescents. Med 3. interview KKD: r=0.47 hard activity and heart Sci Sports Exerc, 25, administered (grade 5, rate monitoring time 99-108. 4. N/A N=36); r=0.59 periods >160beats/min 5. METs (grade 8, r= 0.29 (5th grade), Bratteby, et al., (1997). 6. Recall previous N=36); r=0.81 r=0.45 (8th grade), A 7-day activity diary for day then work (grade 11, r=0.72 (11th grade) assessment of daily back. N=30). energy expenditure For moderate validated by the doubly activity r=0.13 labelled water method in (grade 5, adolescents. Euro J Clin N=36); r=0.0.11 Nutr, 61, 585-591. (grade 8, N=36); r=0.0.75 (grade 11, N=30). Age Range Details of PA & Instrument Indicative References Reliability Validity Comment assessment Indicative Countries Teen Health Butcher, et al., (2008) 1. MVPA (≤3 14 - 17y Prochaska et Prochaska et al., 2001 Survey Correlates of Physical METS) al., 2001 Criterion Validity Activity Guideline 2. 7-d and USA (N=138) Survey vs. Compliance for typical week Test-retest accelerometer r=0.40. Adolescents in 100 U.S. from same day Stronger for boys self-report cities. J Adolesc Health, 3. to up to one (N=36): r=0.42 than for 42, 360-368 4. 2 month: ICC girls (N=63): r=0.32. 5. N/A controlled for Prochaska et al., 2001 A 6. free time to retest: Physical Activity response r=0.76, ICC = Screening Measure 0.88 for same for Use With day test- retest; Adolescents in Primary ICC = 0.53 for Care. Arch Pediatr one month test- Adolesc Med, 155, 554- retest 559. Cale, et al., (1997) The 1. PA at school, 11-18y Cale et al., Cale et al., (1997). Four by One- physical activity levels of sport at school, (1997). Criterion validity day Recall English adolescent leisure time PA, 4-week test- (N=20) Survey vs. HR Physical boys. Physical leisure time sport UK retest: (N=12), monitor r=0.61; vs. Activity Education & Sport 2. 24-h 11-14y r=0.62 observational method Questionnaire Pedagogy, 2, 74-82. r=0.79. 3. Self-report Khunti, et al., (2007) 4. 2 forms; Physical activity and weekday and a sedentary behaviours of weekend day. South Asian and white Form split into European children in parts: morning, inner city secondary afternoon and schools in the UK. evening Family Practice, 5. PA doi:10.1093/fampra/cm measured in m013. terms of intensity; MET values assigned to Age Range Details of PA & Instrument Indicative References Reliability Validity Comment assessment Indicative Countries activities 6. Tick boxes
Computerised McMurray et al., (1998) 1. All PA and grades 6-8 McMurray et al McMurray et al (1998). Activity Recall Comparison of a sedentary behaviour (1998). (N=22) Criterion validity (CAR) computerised physical of at least 15m USA grade 6-8 CAR vs. Tritrac for total activity recall with a duration students. EE r=0.510. Kappa triaxial motion sensor in 2. Previous day 1-2 week test- statistic = 0.398 middle-school youth. 3. Self-report (via re-test ICC for indicating a low level of Med Sci Sports Exerc, computer) total EE= agreement between 30, 1238-1245. 4. Menu driven 0.947. methods. behaviour categories of over 200 behaviours 5. Time of day data also collected 6. Duration of behaviour Children’s Simons-Morton, et al., 1. All PA during Grades 3 & 5 Simons-Morton et al., Physical (1997) Physical activity waking hours (1994). Activity in a multiethnic 2. Previous day USA Pearson correlations Interview population of third recall between reported graders in four states. activity minutes and Am J Pub Health, 87, 3. Interview monitored minutes of 45-50. 4. Interview high intensity activity segmented into 5 (180% of resting HR): Simons-Morton, et al., time slots 3rd Grade (N=27) (1994). Validity of the 5. Filled in a r=0.57; 5th Grade Physical Activity Physical Activity (N=21) r=0.72 Interview with Record prior to preadolescent children. interview Research Quarterly for 6. Free Exercise and Sport, response directed 65(1), 84-88. by the interviewer Age Range Details of PA & Instrument Indicative References Reliability Validity Comment assessment Indicative Countries
Cardiovascula Telama, et al., (2000) 1. Leisure time 3, 6, 9, 12, 15 Telama et al ., Telama et al., (2005). r Risk in Decline of physical PA, sports & 18y (2000). Internal Criterion-related Young Finns activity from youth to club/competitions Finland consistency- validity: PAI scores young adulthood in 2. Habitual Cronbach correlated with Finland. Med Sci Sports activity (PA Index: alpha: 0.44 – measures of fitness: r = Exerc, 32, 1617-1622. PAI) 0.76 0.2 – 0.53. Self-report Telama, et al., (2005) 3. Physical Activity from 4. 5 items Childhood to Adulthood: 5. Frequency A 21-year tracking and intensity study. Am J Prev Med, 6. free 28, 267-273. response
Yang, et al., (2007) Testing a model of physical activity and obesity tracking from youth to adulthood: the cardiovascular risk in young Finns study. Int J Obesity, 31, 521-527. ACTIVITY Tremblay, et al., (2001) 1. School-day 3rd grade Tremblay et al (2001). video Preliminary evaluation of PA Criterion-related questionnaire a video questionnaire to 2. 1-d recall Canada validity: Pearson assess activity levels of correlations with children. Med Sci Sports 3. Self-report ACTIVITY score: Exerc, 33, 2139-2144 4. 10 items Accelerometer r=0.40, 5. n/a Heart rate r=0.50, 6. Checklists
Age Range Details of PA & Instrument Indicative References Reliability Validity Comment assessment Indicative Countries Youth Media Welk et al., (2007). 1. Out-of- 9 -13y Welk et al Welk et al (2007) . Reliability and validity Campaign Reliability and validity of school activities, (2007). Criterion-related coefficients were similar for Longitudinal questions on the Youth leisure time PA USA Test-Retest: validity: boys and girls, but older youth Survey Media Campaign 2. 7-d recall (1 week) Total weekly activity (11-13 years) had higher (YMCLS) Longitudinal Survey. and 1-d recall ICC= and accelerometer coefficients than younger Med Sci Sports Exerc, 0.78 (organised (r=0.24), activity log students (9-10 years) Structured 39, 612-621. 3. activity) 0.60 (r=0.46). phone interview (free-time Activity time and Heitzler et al., (2006). 4. ? activity) 0.60 sessions on previous Correlates of physical 5. n/a (total weekly day with accelerometer activity in a national 6. Free activity). (r=0.53 and 0.37) and sample of children aged response the activity log (r=0.37 9 to 13 years. Prev Med, and 0.47). Correlations 42, 253-260 between the YMCLS and the activity log were higher for organised activity (r=0.72) than for free- time activity (r=0.46). School Health Wong et al., (2006) 1. All PA grades 6 – 12 Wong et al Wong et al (2006). Action, Reliability and validity of 2. 7-d recall (2006). Criterion-related Planning and a school-based physical Canada (N=2812) validity: (N=67) Evaluation activity questionnaire. 3. Self-report 1 week test- Spearman’s correlation System Med Sci Sports Exerc, 4. 45 items retest: with MTI accelerometer (SHAPES) 38, 1593-1600. (multiple choice) Kappa/weighte r=0.44. Physical 5. Responses d kappa Activity are provided by coefficient = Questionnaire indicating the 0.57±0.24 number of hours and 15-min increments that each type of PA was performed for each day of the previous week. Age Range Details of PA & Instrument Indicative References Reliability Validity Comment assessment Indicative Countries 6. Tick boxes/multiple choice Finnish Twin Aarnio, et al., (2002a) Aarnio, et al., 16 - 18y Aarnio et al Aarnio et al (2002a). Cohort Study Stability of leisure-time (2002a) Finland (1997). Criterion-related physical activity during 1. Leisure time Test-Retest: (1 validity: (N=32) adolescence - a PA; frequency of month): questionnaire-reported longitudinal study leisure time PA Self-reported fitness and VO2max among 16-, 17- and 18- outside of school, fitness: rho= 0.47, interview- year old Finnish youth. perception of Boys: r= 0.76 based intense physical Scan J Med Sci Sports, physical fitness Girls: r=0.80 activity and VO2max 12, 179-185. and intensity of Self-reported rho = 0.61, PA Intensity: questionnaire-reported Aarnio, et al., (2002b) 2. Habitual PA Boys: r=0.79 frequency of activity Associations of health Girls: r=0.75 and VO2max rho=0.45. related behaviour, social 3. self-report relationships, and health 4. 2 items The correlation of status with persistent 5. interview-based intense physical activity and 6. Scale (1-6) physical activity with inactivity: a study of Aarnio, et al., questionnaire fitness Finnish adolescent (2002b) was r=0.62 and with twins. Brit J Sports Med, questionnaire 1. Sport 36,360-364. frequency r=0.52. 2. Habitual Aarnio, et al., (1997) sporting activity Associations of health 3. self-report related behaviour, social 4. 19 items relationships, and health 5. Report any status to physical activity sport they had among 16 year old boys participated in; and girls. Scand J Soc groups were then Med, 3, 156-167. divided into ‘aerobic’, ‘power’ and ‘other’, also Age Range Details of PA & Instrument Indicative References Reliability Validity Comment assessment Indicative Countries organised and non-organised sport was assessed 6. Check list Physical Argiropoulou et al., 1. Leisure time Mean age Argiropoulou et Argiropoulou et al Activity and (2004) Validity and PA 13.73y (SD al (2004). (2004). Lifestyle reliability of physical 2. 7-day and 0.8) (N=40) Criterion-related Questionnaire activity measures in habitual PALQ 2 week validity: (N=40) (PALQ) Greek high school age Greece test-retest accelerometer and children. J Sports Sci 3. Self-report ICC=0.52 PALQ r=0.53 Med, 3, 147-159. 4. 27 activities 5. 6. Combination of free response and tick boxes Physical Schmidt et al., (1998). 1. Usual PA 6-18y Schmidt et al., (1998). Activity and The Singapore Youth 2. Habitual Criterion-related Exercise Coronary Risk and Singapore validity: (N=24) PAEQ Self-report Questionnaire Physical Activity Study. 3. v heart rate r=0.67. (PAEQ) Med Sci Sports Exerc, 4. Choose 1 Construct validity: 30(1), 105-113. from 4 categories (N=745) PAEQ v total 5. PA described cholesterol r=0.35, high Chia, et al., (2002). in terms of density lipoprotein r=- Relationships between intensity; very 0.38, and triglycerides hours of computer use, light, light PA, r=-.027 physical activity and moderate PA & physical fitness among VPA children and 6. Tick boxes adolescents. Euro J Physical Educ, 7, 136- 155