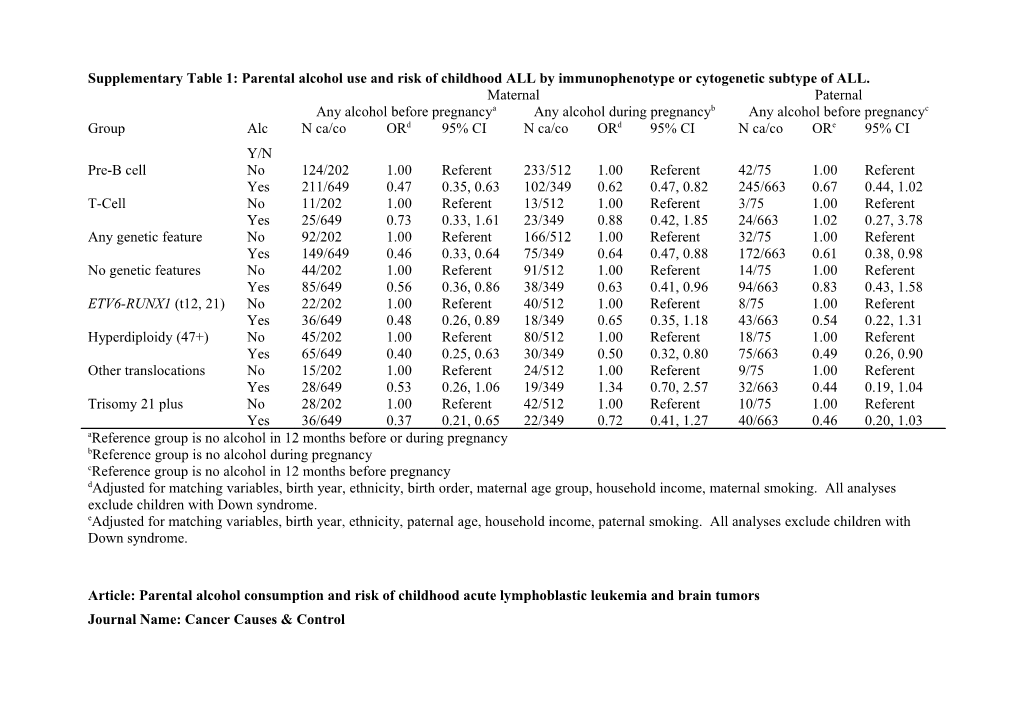
Supplementary Table 1: Parental alcohol use and risk of childhood ALL by immunophenotype or cytogenetic subtype of ALL. Maternal Paternal Any alcohol before pregnancya Any alcohol during pregnancyb Any alcohol before pregnancyc Group Alc N ca/co ORd 95% CI N ca/co ORd 95% CI N ca/co ORe 95% CI Y/N Pre-B cell No 124/202 1.00 Referent 233/512 1.00 Referent 42/75 1.00 Referent Yes 211/649 0.47 0.35, 0.63 102/349 0.62 0.47, 0.82 245/663 0.67 0.44, 1.02 T-Cell No 11/202 1.00 Referent 13/512 1.00 Referent 3/75 1.00 Referent Yes 25/649 0.73 0.33, 1.61 23/349 0.88 0.42, 1.85 24/663 1.02 0.27, 3.78 Any genetic feature No 92/202 1.00 Referent 166/512 1.00 Referent 32/75 1.00 Referent Yes 149/649 0.46 0.33, 0.64 75/349 0.64 0.47, 0.88 172/663 0.61 0.38, 0.98 No genetic features No 44/202 1.00 Referent 91/512 1.00 Referent 14/75 1.00 Referent Yes 85/649 0.56 0.36, 0.86 38/349 0.63 0.41, 0.96 94/663 0.83 0.43, 1.58 ETV6-RUNX1 (t12, 21) No 22/202 1.00 Referent 40/512 1.00 Referent 8/75 1.00 Referent Yes 36/649 0.48 0.26, 0.89 18/349 0.65 0.35, 1.18 43/663 0.54 0.22, 1.31 Hyperdiploidy (47+) No 45/202 1.00 Referent 80/512 1.00 Referent 18/75 1.00 Referent Yes 65/649 0.40 0.25, 0.63 30/349 0.50 0.32, 0.80 75/663 0.49 0.26, 0.90 Other translocations No 15/202 1.00 Referent 24/512 1.00 Referent 9/75 1.00 Referent Yes 28/649 0.53 0.26, 1.06 19/349 1.34 0.70, 2.57 32/663 0.44 0.19, 1.04 Trisomy 21 plus No 28/202 1.00 Referent 42/512 1.00 Referent 10/75 1.00 Referent Yes 36/649 0.37 0.21, 0.65 22/349 0.72 0.41, 1.27 40/663 0.46 0.20, 1.03 aReference group is no alcohol in 12 months before or during pregnancy bReference group is no alcohol during pregnancy cReference group is no alcohol in 12 months before pregnancy dAdjusted for matching variables, birth year, ethnicity, birth order, maternal age group, household income, maternal smoking. All analyses exclude children with Down syndrome. eAdjusted for matching variables, birth year, ethnicity, paternal age, household income, paternal smoking. All analyses exclude children with Down syndrome.
Article: Parental alcohol consumption and risk of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia and brain tumors Journal Name: Cancer Causes & Control Authors: Elizabeth Milne1, Kathryn R. Greenop1, Rodney J. Scott2, 3, Nicholas H. de Klerk1, Carol Bower1, Lesley J. Ashton4, John A. Heath5, 6, Bruce K. Armstrong7. 1Telethon Institute for Child Health Research, Centre for Child Health Research, University of Western Australia, Perth, Western Australia, Australia. 2 Hunter Medical Research Institute, School of Biomedical Sciences, Faculty of Health, University of Newcastle, New South Wales, Australia. 3 Hunter Area Pathology Service, HNEHealth, Newcastle, New South Wales, Australia. 4 Children’s Cancer Institute Australia for Medical Research, Lowy Cancer Research Centre, University of New South Wales, Sydney, NSW, Australia. 5 Children’s Cancer Centre, Royal Children’s Hospital, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. 6Department of Paediatrics, University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia. 7 Sydney School of Public Health, University of Sydney, Sydney, New South Wales, Australia
Author for correspondence:
Elizabeth Milne, Email: [email protected]