JOINT DISORDERS/ ARTHRITIS
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
At the end of lecture the student should be able to know about:
• Joint disorders • Definition of arthritis • history ,examination aspect of arthritis • Different types of arthritis • Investigations required for diagnosing different types of arthritis
JOINT DISORDERS/ ARTHRITIS
1. SURGICAL CONDITIONS . Dislocation . Fractures . Joint sprain
2. MEDICAL CONDITIONS . Arthritis . Enthesitis
RHEUMATOLOGY
Rheumatology is the sub-specialty of medicine that deals with clinical problems of joint, soft tissues and other connective tissues
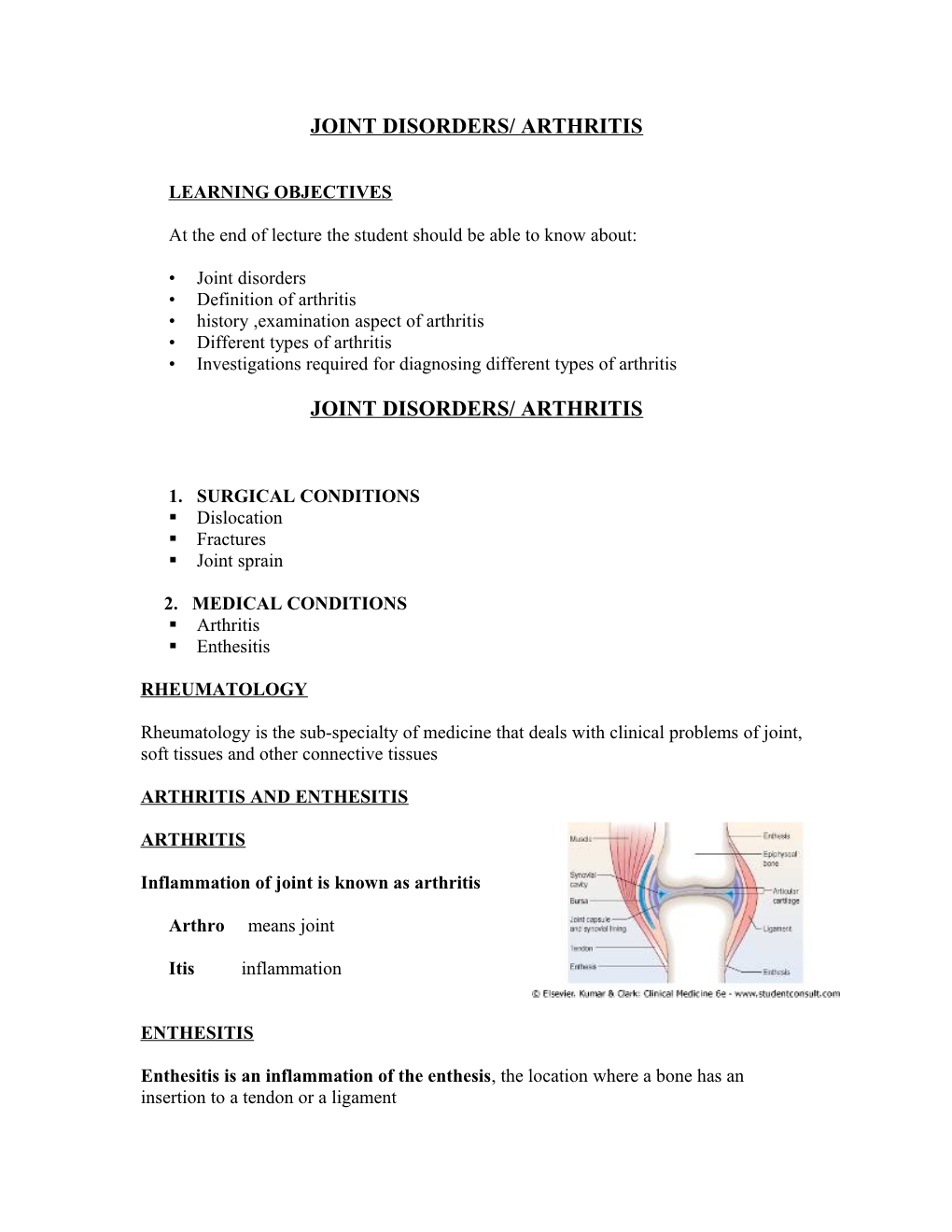
ARTHRITIS AND ENTHESITIS
ARTHRITIS
Inflammation of joint is known as arthritis
Arthro means joint
Itis inflammation
ENTHESITIS
Enthesitis is an inflammation of the enthesis, the location where a bone has an insertion to a tendon or a ligament INFLAMATION
A protective neuro vascular response to any type of injury in tissue known as Inflammation characterized by
• Pain (Dolor) • Heat (Calor) • Redness (Rubor) • Tumor (Swelling) • Loss of function (functio laesea)
CAUSES OF ARTHRITIS
• Degenerative • Infections • Trauma • Crystal induced • Autoimmune
HISTORY
Ask few questions
How long the symptoms are there? How many joints are involved? Is there any history of stiffness? Is there any history of systemic problem? Ask about functional activity?
GENERAL SYMPTOMS
Related to joint
• Pain • Swelling • Difficulty in movement • Stiffness
Extra articular
• Fever • Loss of appetite • Weight loss • Involvement of other organs like Eye, lungs etc SCREENING EXAMINATION
GALS ( gait, arms, legs, spine)
• Gait • Arms • Legs • Spine
DEGENERATIVE ARTHRITIS (OSTEOARTHRITIS)
• Age related degenerative changes
• Involves weight bearing joints like knee & hip joint
• Pain in affected joint which get worse on walking
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
• Autoimmune in nature
• Involves small joints of hands
• Morning stiffness
• Polyarticular
• Symmetrical in nature
• Often associated with deformities SEPTIC ARTHITIS
Infectious in origin
Usually involves single joint
Joint is markedly inflamed
Extremely painful
GOUT ( CRYSTAL INDUCED)
Starts with single joint (monoarticular)
Later becomes polyarticular
Crystallization of uric acid in joint
Acute attack is highly painful ( Inflammation)
WORKUP FOR ARTHRITIS
• BLOOD CP-ESR
• X-RAYS OF INVOLVED JOINTS
• CRP
• URIC ACID LEVELS
• SYNOVIAL FLUID ANALYSIS
• AUTOIMMUNE PROFILE
• MRI SYNOVIAL FLUID
• Fluid present in joint cavity • Secreted by synovial membrane • Making a thin layer of 50 millimicron • Composed on hyaluronic acid, glycosaminoglycans and lubricin • Provides lubrication ( weeping lubrication) • Provides nutrition to articulating
ROLE OF SYNOVIAL FLUID IN ARTHRITIS
There are many changes in synovial fluid in different types of arthritis which helps in making the diagnoses
Normal Group I Group II Group III Measure (Noninflammatory (Inflammatory) (Purulent)
Volume (ml) (knee) < 3.5 Often >3.5 Often >3.5 Often >3.5
Clarity Transparent Transparent Translucent to Opaque opaque Color Clear Yellow Yellow to Yellow to Opalescent Green WBC (per mcl) < 200 200 – 300 2000–75,000 >100,000
Polymorphonuclear < 25% < 25% 50% or more 75% or more leukocytes
Culture Negative Negative Negative Usually Positive
ARTHROSCOPY