PHYSICS LECTURE WS – 2: STANDING WAVES
Reading Assignment: Chapter 11 Pages 385 – 387, 393 – 394, 422 – 429
SPEED OF A WAVE v = f
______
EXAMPLE: A piano string tuned to middle C vibrates with a frequency of 262 Hz. Assuming the speed of sound in air is 343 m/s, find the wavelength of the sound waves produced by the string. G: ______
______
U: ______
E: ______
S: ______
S: ______
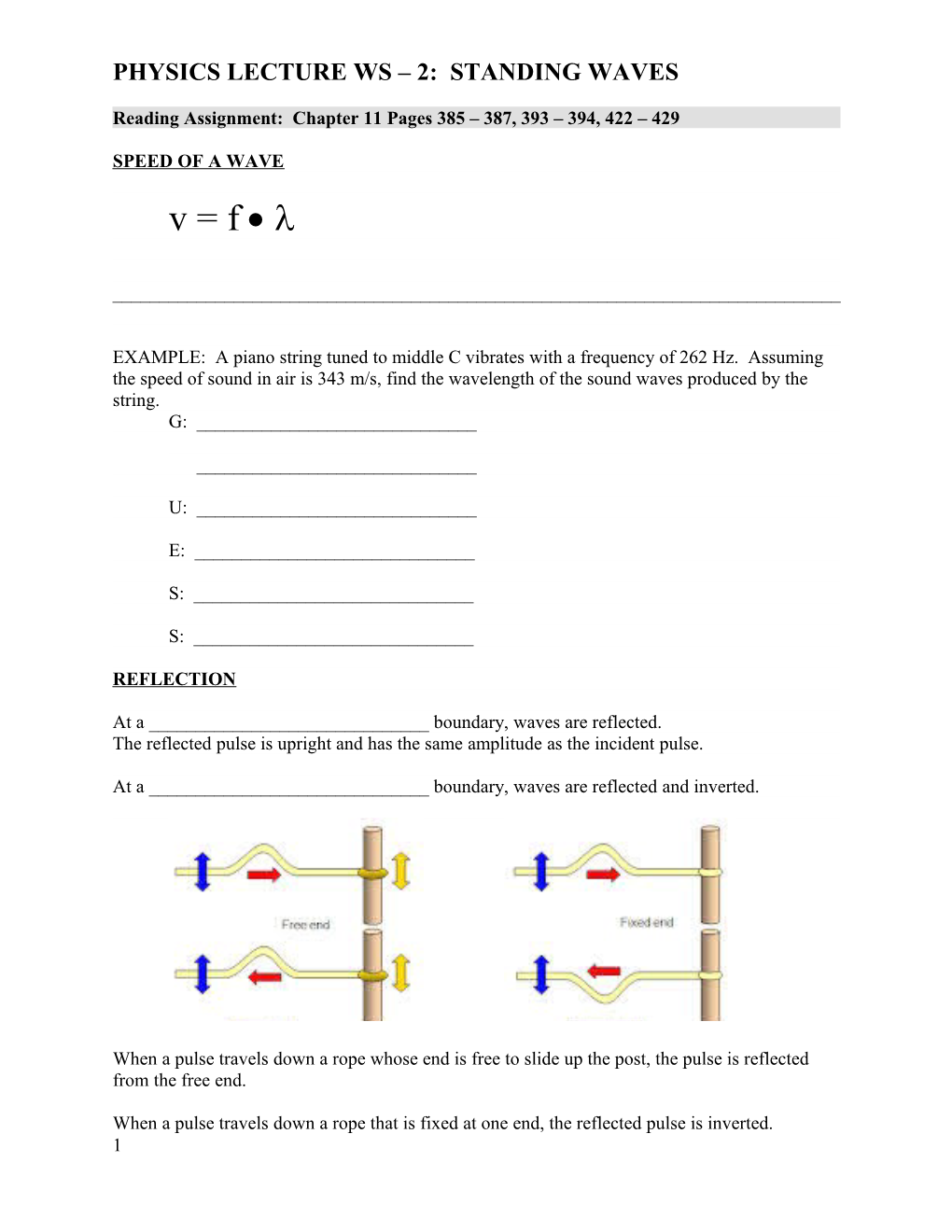
REFLECTION
At a ______boundary, waves are reflected. The reflected pulse is upright and has the same amplitude as the incident pulse.
At a ______boundary, waves are reflected and inverted.
When a pulse travels down a rope whose end is free to slide up the post, the pulse is reflected from the free end.
When a pulse travels down a rope that is fixed at one end, the reflected pulse is inverted. 1 PHYSICS LECTURE WS – 2: STANDING WAVES
STANDING WAVES
. A ______wave is a wave pattern that results when two waves of the same frequency, wavelength, and amplitude travel in opposite directions and interfere. . The resultant wave pattern of a standing wave appears to be stationary. . The standing wave consists of alternating regions of constructive and destructive interference.
. ______are the points on a standing wave at which complete destructive interference happens . There is no motion at the nodes.
. ______are midway between two adjacent nodes where vibration occurs with the largest amplitude.
. Only certain frequencies, and therefore wavelengths, produce standing waves. . The ends of a standing wave must be nodes because these points cannot vibrate. . A standing wave can be produced for any wavelength that allows both ends to be nodes. . The wavelength of standing waves depends on length of media (L). . Possible wavelengths to produce a standing wave in a string of length L include 2L, L and 2/3 L.
2 PHYSICS LECTURE WS – 2: STANDING WAVES
HARMONIC SERIES
______: the lowest frequency of vibration of a standing wave.
______: integer multiples of the fundamental frequency.
______: a series of frequencies that includes the fundamental frequency and integer multiples of the fundamental frequency.
3