CURRICULUM AREA: Digital Technologies toward Level 8 Achievement Standard
Context: Big Data Students explore large data sets and develop an understanding of their structure. They will also explore how data can be sorted. Students use this understanding to develop their own datasets based on a personal interest. The teaching and learning plan focuses on the strand of Data and Information.
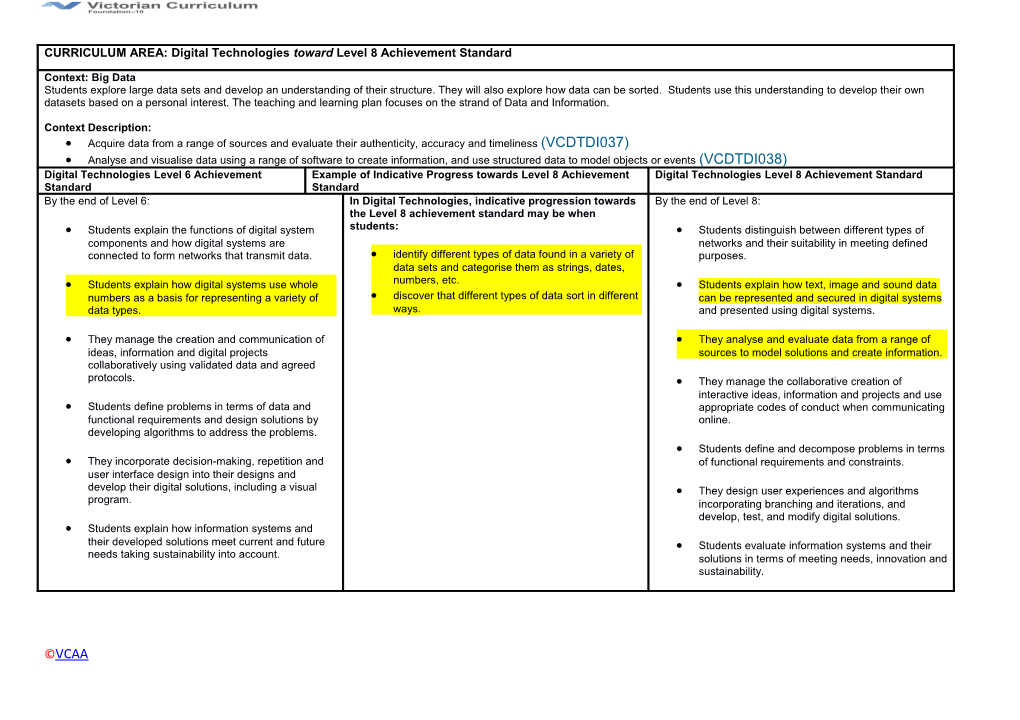
Context Description: Acquire data from a range of sources and evaluate their authenticity, accuracy and timeliness (VCDTDI037) Analyse and visualise data using a range of software to create information, and use structured data to model objects or events (VCDTDI038) Digital Technologies Level 6 Achievement Example of Indicative Progress towards Level 8 Achievement Digital Technologies Level 8 Achievement Standard Standard Standard By the end of Level 6: In Digital Technologies, indicative progression towards By the end of Level 8: the Level 8 achievement standard may be when Students explain the functions of digital system students: Students distinguish between different types of components and how digital systems are networks and their suitability in meeting defined connected to form networks that transmit data. identify different types of data found in a variety of purposes. data sets and categorise them as strings, dates, Students explain how digital systems use whole numbers, etc. Students explain how text, image and sound data numbers as a basis for representing a variety of discover that different types of data sort in different can be represented and secured in digital systems data types. ways. and presented using digital systems.
They manage the creation and communication of They analyse and evaluate data from a range of ideas, information and digital projects sources to model solutions and create information. collaboratively using validated data and agreed protocols. They manage the collaborative creation of interactive ideas, information and projects and use Students define problems in terms of data and appropriate codes of conduct when communicating functional requirements and design solutions by online. developing algorithms to address the problems. Students define and decompose problems in terms They incorporate decision-making, repetition and of functional requirements and constraints. user interface design into their designs and develop their digital solutions, including a visual They design user experiences and algorithms program. incorporating branching and iterations, and develop, test, and modify digital solutions. Students explain how information systems and their developed solutions meet current and future Students evaluate information systems and their needs taking sustainability into account. solutions in terms of meeting needs, innovation and sustainability.
©VCAA CURRICULUM AREA: Digital Technologies toward Level 8 Achievement Standard
Context: Binary Students explore the links between binary and text, image and sounds. They develop an understanding of how file size and file type can impact the time it takes websites to load. The teaching and learning plan focuses on the strand of Data and Information.
Content Description: Investigate how digital systems represent text, image and sound data in binary (VCDTDI036)
Digital Technologies Level 6 Achievement Example of Indicative Progress towards Level 8 Achievement Digital Technologies Level 8 Achievement Standard Standard Standard By the end of Level 6: In Digital Technologies, indicative progression towards the Level 8 By the end of Level 8: achievement standard may be when students: Students explain the functions of digital Students distinguish between different types of system components and how digital recognise the different types of data used by digital systems. networks and their suitability in meeting defined systems are connected to form They make connections between the size, quality and type of purposes. networks that transmit data. the file and discuss how these influence the selection of a particular file (size, type) when creating websites. Students explain how text, image and sound data Students explain how digital systems can be represented and secured in digital systems use whole numbers as a basis for and presented using digital systems. representing a variety of data types. They analyse and evaluate data from a range of They manage the creation and sources to model solutions and create information. communication of ideas, information and digital projects collaboratively using They manage the collaborative creation of validated data and agreed protocols. interactive ideas, information and projects and use appropriate codes of conduct when communicating Students define problems in terms of online. data and functional requirements and design solutions by developing Students define and decompose problems in terms algorithms to address the problems. of functional requirements and constraints.
They incorporate decision-making, They design user experiences and algorithms repetition and user interface design into incorporating branching and iterations, and develop, their designs and develop their digital test, and modify digital solutions. solutions, including a visual program. Students evaluate information systems and their Students explain how information solutions in terms of meeting needs, innovation and systems and their developed solutions sustainability. meet current and future needs taking sustainability into account.
©VCAA CURRICULUM AREA: Digital Technologies toward Level 8 Achievement Standard
Context: Cloud Computing Students develop an understanding of how the internet uses various protocols to enable data such as images on a website to be shared and transmitted around the world. The teaching and learning plan focuses on the strands of Digital Systems and Data and Information.
Content Descriptions: Investigate how data are transmitted and secured in wired, wireless and mobile networks (VCDTDS035) Investigate how digital systems represent text, image and sound data in binary (VCDTDI036) Digital Technologies Level 6 Achievement Standard Example of Indicative Progress towards Level 8 Digital Technologies Level 8 Achievement Standard Achievement Standard By the end of Level 6: In Digital Technologies, indicative progression towards By the end of Level 8: the Level 8 achievement standard may be when Students explain the functions of digital system students: Students distinguish between different types of components and how digital systems are connected networks and their suitability in meeting defined to form networks that transmit data. can name three common types of networks and purposes. describe a situation where the different aspects of Students explain how digital systems use whole these networks would be beneficial. Students explain how text, image and sound data can numbers as a basis for representing a variety of data be represented and secured in digital systems and types. can explain that encryption keeps data safe by presented using digital systems. only allowing ‘trusted’ systems to read it. They manage the creation and communication of They analyse and evaluate data from a range of ideas, information and digital projects collaboratively sources to model solutions and create information. using validated data and agreed protocols. They manage the collaborative creation of interactive Students define problems in terms of data and ideas, information and projects and use appropriate functional requirements and design solutions by codes of conduct when communicating online. developing algorithms to address the problems. Students define and decompose problems in terms of They incorporate decision-making, repetition and functional requirements and constraints. user interface design into their designs and develop their digital solutions, including a visual program. They design user experiences and algorithms incorporating branching and iterations, and develop, Students explain how information systems and their test, and modify digital solutions. developed solutions meet current and future needs taking sustainability into account. Students evaluate information systems and their solutions in terms of meeting needs, innovation and sustainability.
©VCAA ©VCAA CURRICULUM AREA: Digital Technologies toward Level 8 Achievement Standard
Context: Game Development Students will be introduced to the fundamentals of game making and software development through designing algorithms and user interfaces. They will transition from being content consumers to content creators. Students will develop higher order thinking skills including computational, design and systems thinking skills. The teaching and learning plan focuses on the strand of Creating Digital Solutions.
Content Descriptions: Design algorithms represented diagrammatically and in English, and trace algorithms to predict output for a given input and to identify errors (VCDTCD042) Develop and modify programs with user interfaces involving branching, iteration and functions using a general-purpose programming language (VCDTCD043) Digital Technologies Level 6 Achievement Standard Example of Indicative Progress towards Level 8 Achievement Digital Technologies Level 8 Achievement Standard Standard By the end of Level 6: In Digital Technologies, indicative progression towards the Level By the end of Level 8: 8 achievement standard may be when students: Students distinguish between different types Students explain the functions of digital system of networks and their suitability in meeting components and how digital systems are connected design games by designing algorithms and taking into defined purposes. to form networks that transmit data. account the user experiences. Students explain how text, image and sound Students explain how digital systems use whole data can be represented and secured in numbers as a basis for representing a variety of data test existing or peer developed games and modify elements digital systems and presented using digital types. from these into their own digital solutions. systems. They manage the creation and communication of They analyse and evaluate data from a ideas, information and digital projects collaboratively range of sources to model solutions and using validated data and agreed protocols. create information. Students define problems in terms of data and They manage the collaborative creation of functional requirements and design solutions by interactive ideas, information and projects developing algorithms to address the problems. and use appropriate codes of conduct when They incorporate decision-making, repetition and communicating online. user interface design into their designs and develop Students define and decompose problems in their digital solutions, including a visual program. terms of functional requirements and Students explain how information systems and their constraints. developed solutions meet current and future needs They design user experiences and taking sustainability into account. algorithms incorporating branching and iterations, and develop, test, and modify digital solutions. Students evaluate information systems and their solutions in terms of meeting needs, innovation and sustainability.
©VCAA CURRICULUM AREA: Digital Technologies toward Level 10 Achievement Standard
Context: Algorithms Students learn to write algorithms, using both flowcharts and structured English. They will design and create an algorithm for a café/restaurant ordering app for a mobile device. The teaching and learning plan focuses on the strand of Creating Digital Solutions.
Content Description: Design algorithms represented diagrammatically and in structured English and validate algorithms and programs through tracing and test cases (VCDTCD052) Digital Technologies Level 8 Achievement Standard Example of Indicative Progress towards Level 10 Digital Technologies Level 10 Achievement Standard Achievement Standard By the end of Level 8: In Digital Technologies, indicative progression towards By the end of Level 10: the Level 10 achievement standard may be when Students distinguish between different types of students: Students explain the control and management of networks and their suitability in meeting defined networked digital systems and the data security purposes. design an algorithm (as a flowchart) and in implications of the interaction between hardware, structured English (pseudocode) for an ordering software and users. Students explain how text, image and sound data process in café/restaurant. can be represented and secured in digital systems test their algorithm to demonstrate a successful Students explain simple data compression, and why and presented using digital systems. outcome. content data are separated from presentation.
They analyse and evaluate data from a range of They take account of privacy and security requirements sources to model solutions and create information. when selecting and validating data and use digital systems to analyse, visualise and model salient They manage the collaborative creation of interactive aspects of data. ideas, information and projects and use appropriate codes of conduct when communicating online. Students share and collaborate online, establishing protocols for the legal and safe use, transmission and Students define and decompose problems in terms maintenance of data and projects. of functional requirements and constraints. Students define and decompose complex problems in They design user experiences and algorithms terms of functional and non-functional requirements. incorporating branching and iterations, and develop, test, and modify digital solutions. They design and evaluate user experiences and algorithms, and develop and test modular programs, Students evaluate information systems and their including an object-oriented program. solutions in terms of meeting needs, innovation and sustainability. Students evaluate their solutions and information systems in terms of risk, sustainability and potential for innovation.
©VCAA CURRICULUM AREA: Digital Technologies toward Level 10 Achievement Standard
Context: Decomposing App Requirements Students read correspondence from a client to determine their needs in relation to creating an ordering app for a restaurant or cafe. They compile questions to ask the client to gain further information and identify potential stakeholders. Students then decompose the app requirements into functional and non-functional requirements. The teaching and learning plan focuses on the strand of Creating Digital Solutions.
Content Description: Define and decompose real-world problems precisely, taking into account functional and non-functional requirements and including interviewing stakeholders to identify needs (VCDTCD050) Digital Technologies Level 8 Achievement Standard Example of Indicative Progress towards Level 10 Digital Technologies Level 10 Achievement Standard Achievement Standard By the end of Level 8: In Digital Technologies, indicative progression towards the By the end of Level 10: Level 10 achievement standard may be when students: Students distinguish between different types of Students explain the control and management networks and their suitability in meeting defined Explain the difference between functional and non- of networked digital systems and the data purposes. functional requirements of an app solution and break down security implications of the interaction between the solution needs into its two broad elements. Students hardware, software and users. Students explain how text, image and sound data identify obvious stakeholders. can be represented and secured in digital systems Students explain simple data compression, and presented using digital systems. and why content data are separated from presentation. They analyse and evaluate data from a range of sources to model solutions and create information. They take account of privacy and security requirements when selecting and validating They manage the collaborative creation of interactive data and use digital systems to analyse, ideas, information and projects and use appropriate visualise and model salient aspects of data. codes of conduct when communicating online. Students share and collaborate online, Students define and decompose problems in terms establishing protocols for the legal and safe of functional requirements and constraints. use, transmission and maintenance of data and projects. They design user experiences and algorithms incorporating branching and iterations, and develop, Students define and decompose complex test, and modify digital solutions. problems in terms of functional and non- functional requirements. Students evaluate information systems and their solutions in terms of meeting needs, innovation and They design and evaluate user experiences sustainability. and algorithms, and develop and test modular programs, including an object-oriented program.
©VCAA Students evaluate their solutions and information systems in terms of risk, sustainability and potential for innovation.
CURRICULUM AREA: Digital Technologies toward Level 10 Achievement Standard
Context: Legal Responsibilities Students, who as part of a larger project are planning and developing a mobile application for a cafe or restaurant, will explore the legal responsibilities involved when collecting and storing data for use in a mobile application. The teaching and learning plan focuses on the strands of Data and Information and Creating Digital Solutions.
Content Description: Develop techniques for acquiring, storing and validating quantitative and qualitative data from a range of sources, considering privacy and security requirements (VCDTDI047) Evaluate critically how well student-developed solutions and existing information systems and policies take account of future risks and sustainability and provide opportunities for innovation (VCDTCD054) Digital Technologies Level 8 Achievement Standard Example of Indicative Progress towards Level 10 Achievement Digital Technologies Level 10 Achievement Standard Standard By the end of Level 8: In Digital Technologies, indicative progression towards the By the end of Level 10: Level 10 achievement standard may be when students: Students distinguish between different types of Students explain the control and management networks and their suitability in meeting defined identify privacy and security requirements that existing of networked digital systems and the data purposes. social media platforms and mobile applications use when security implications of the interaction between collecting personal data. hardware, software and users. Students explain how text, image and sound data can be represented and secured in digital systems describe potential risks in the storage and access to Students explain simple data compression, and presented using digital systems. customer personal data when the student developed and why content data are separated from mobile application is used to place an order. presentation. They analyse and evaluate data from a range of sources to model solutions and create information. They take account of privacy and security requirements when selecting and validating They manage the collaborative creation of interactive data and use digital systems to analyse, ©VCAA ideas, information and projects and use appropriate visualise and model salient aspects of data. codes of conduct when communicating online. Students share and collaborate online, Students define and decompose problems in terms establishing protocols for the legal and safe of functional requirements and constraints. use, transmission and maintenance of data and projects. They design user experiences and algorithms incorporating branching and iterations, and develop, Students define and decompose complex test, and modify digital solutions. problems in terms of functional and non- functional requirements. Students evaluate information systems and their solutions in terms of meeting needs, innovation and They design and evaluate user experiences sustainability. and algorithms, and develop and test modular programs, including an object-oriented program.
Students evaluate their solutions and information systems in terms of risk, sustainability and potential for innovation.
©VCAA