Strand = Roman Numeral FINE ARTS - MUSIC Standard = Underline Scope & Sequence Benchmark = Bullets High School Articulation = Dash –
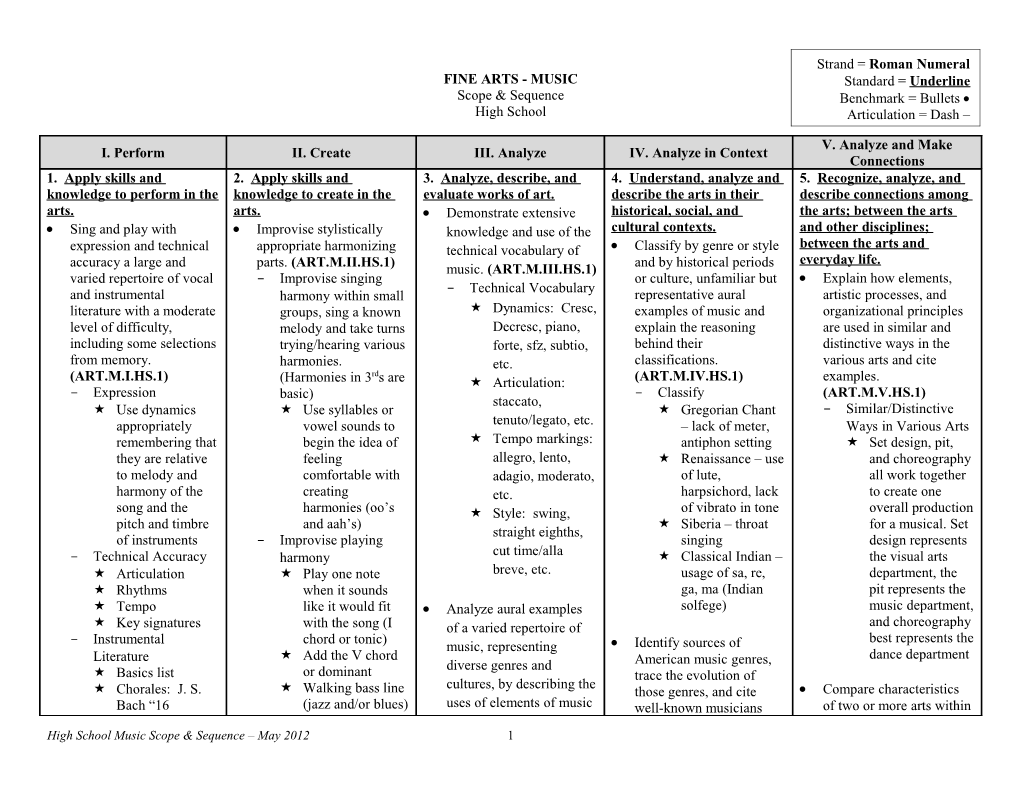
V. Analyze and Make I. Perform II. Create III. Analyze IV. Analyze in Context Connections 1. Apply skills and 2. Apply skills and 3. Analyze, describe, and 4. Understand, analyze and 5. Recognize, analyze, and knowledge to perform in the knowledge to create in the evaluate works of art. describe the arts in their describe connections among arts. arts. Demonstrate extensive historical, social, and the arts; between the arts Sing and play with Improvise stylistically knowledge and use of the cultural contexts. and other disciplines; between the arts and expression and technical appropriate harmonizing technical vocabulary of Classify by genre or style everyday life. accuracy a large and parts. (ART.M.II.HS.1) music. (ART.M.III.HS.1) and by historical periods varied repertoire of vocal - Improvise singing or culture, unfamiliar but Explain how elements, Technical Vocabulary and instrumental harmony within small - representative aural artistic processes, and literature with a moderate groups, sing a known Dynamics: Cresc, examples of music and organizational principles level of difficulty, melody and take turns Decresc, piano, explain the reasoning are used in similar and including some selections trying/hearing various forte, sfz, subtio, behind their distinctive ways in the from memory. harmonies. etc. classifications. various arts and cite rd (ART.M.I.HS.1) (Harmonies in 3 s are Articulation: (ART.M.IV.HS.1) examples. - Expression basic) - Classify (ART.M.V.HS.1) staccato, Use dynamics Use syllables or Gregorian Chant - Similar/Distinctive appropriately vowel sounds to tenuto/legato, etc. – lack of meter, Ways in Various Arts remembering that begin the idea of Tempo markings: antiphon setting Set design, pit, they are relative feeling allegro, lento, Renaissance – use and choreography to melody and comfortable with adagio, moderato, of lute, all work together harmony of the creating etc. harpsichord, lack to create one song and the harmonies (oo’s Style: swing, of vibrato in tone overall production pitch and timbre and aah’s) Siberia – throat for a musical. Set straight eighths, of instruments - Improvise playing singing design represents - Technical Accuracy harmony cut time/alla Classical Indian – the visual arts Articulation Play one note breve, etc. usage of sa, re, department, the Rhythms when it sounds ga, ma (Indian pit represents the Tempo like it would fit Analyze aural examples solfege) music department, Key signatures with the song (I of a varied repertoire of and choreography Instrumental chord or tonic) best represents the - music, representing Identify sources of Literature Add the V chord dance department diverse genres and American music genres, Basics list or dominant trace the evolution of cultures, by describing the Chorales: J. S. Walking bass line those genres, and cite Compare characteristics Bach “16 (jazz and/or blues) uses of elements of music well-known musicians of two or more arts within
High School Music Scope & Sequence – May 2012 1 V. Analyze and Make I. Perform II. Create III. Analyze IV. Analyze in Context Connections Chorales” and expressive devices. associated with them. a particular historical Marches: Improvise rhythmic and (ART.M.III.HS.2) (ART.M.IV.HS.2) period or style and cite composers, Karl melodic variations given - Musical genres and - Identify American examples from various King, John music genres cultures. pentatonic melodies, and cultures Phillip Sousa, etc. melodies in major and Jazz (Duke (ART.M.V.HS.2) Have students Ballads minor keys. Ellington, Ella - Renaissance Periods Overtures (ART.M.II.HS.2) describe the Fitzgerald, Billie Does music from - Vocal Literature - Improvise Singing difference Holiday, the Renaissance Eric Whitacre – Have students between Jazz and Theloneus Monk, period match up Seal Lullaby take a familiar Blues Miles Davis, with the visual Randall piece, classical or Have students Charlie Parker, arts from the same Thompson – The Winton period? popular, best to describe the Pasture find a karaoke or Marseilles) Does music from difference Moses Hogan – I instrumental Rap (Sugar Hill the Renaissance Am His Child recording, change between the Gang – Rappers period match up Persichetti – the rhythm and different eras of Delight, Run with theatre? Dominic Has a melody in a slight classical music DMC, Jay-Z) dance? Doll variation Have students Country – (Hank Are the - Improvise Playing describe the Williams, Glen characteristics Campbell, Minnie similar culture to Sing music written in four Have solo(ists) difference parts, with or without Pearl, Patsy Cline, culture? improvise a between early accompaniment. melody using only Dolly Parton, (throughout the rock and current (ART.M.I.HS.2) the 5 notes of the Kenny Rodgers, world?) - Sing Pentatonic scale rock and roll. Taylor Swift, Ralph Manuel – while band plays Lady Antebellum) Explain ways in which the Alleluia I-IV-V-I Identify and explain Rock – Elvis, principles and subject Beatles, Rolling The Awakening Have students compositional devices and matter of various Stones, disciplines outside the arts improvise melody techniques and their Perform an appropriate using pentatonic Aerosmith, are interrelated with those purposes, giving examples part in large and small scale plus other Metallica, of music. ensembles, demonstrating neighboring tones of other works that make AC/DC) (ART.M.V.HS.3) well-developed ensemble Improvise similar uses of these Pop – The - Various Subject Matters skills. (ART.M.I.HS.3) harmony devices and techniques. Temptations, The Science – physics Funk Brothers, - Perform underneath a (ART.M.III.HS.3) (frequency) Aretha Franklin, Using all musical pentatonic Identify History – music - Stevie Wonder, skills: dynamics, melody, either history compositional devices Michael Jackson, articulation, major and/or (composers, and techniques Cyndi Lauper, High School Music Scope & Sequence – May 2012 2 V. Analyze and Make I. Perform II. Create III. Analyze IV. Analyze in Context Connections correct notes, key minor Finale, Sibelius, Madonna, Mariah styles) signature SmartMusic, Carey, Celine English – lyrical changes, time Improvise original GarageBand Dion) assessment signature changes Mathematics – melodies over given chord - Explain compositional Listening to their progressions, each in a Identify various roles that note values, time devices and own sections and constant style, meter, and musicians perform, cite signatures, other sections in tonality. techniques representative individuals addition, ensemble, (ART.M.II.HS.3) Have students who have functioned in subdivision whether they are - Improvise Singing compose a short each role, and describe instrumental Have students song using the their activities and Explain how the roles of and/or vocal create melodies above stated achievements. creators, performers, and using scat software (ART.M.IV.HS.3) others involved in the Perform music using syllables (Jazz) to - Identify various roles production and instruments (traditional begin Composer- one presentation of the arts are and non-traditional) and - Improvise Playing Evaluate the use of music who creates/ similar to and different electronic media. Have students in mixed media writes music from one another in the (ART.M.I.HS.4) create melodies environments. Arranger- one various arts and - Instruments using a small (ART.M.III.HS.4) who takes an disciplines outside of the arts. (ART.M.V.HS.4) Traditional: portion of the - Movies already composed flute, clarinet, main theme piece and creates - Roles in the Various Have students saxophones, Have students a variation on it Arts trumpet/cornet, create a melody describe how Lyricist – one Musical: etc. using the entire various types of who creates lyrics Choreographer- Non-traditional: main theme music affects the to set to a dance; Director – Blue Man Group mood of the provided melodic oversees all , light style; brooms, Compose music in several various scenes in line or chord design; Set trash cans, progressions Design – creates different styles; a movie utensils, etc. Instrumentalist – sets for the stage, demonstrate creativity in - Radio - Electronic Media using the elements of those who play scene-to-scene; Have students Use of iPad/iPod music for expressive instruments Sound Engineer- apps, Finale, effect. (ART.M.II.HS.4) experiment with Vocalist – those microphones, who sing levels; Vocal Sibelius, Smart - Compose sound effects, for Conductor – one Director – Music, etc. Sing basic chord example a radio who leads a large instructs vocal progressions show vocal or lines, soloists, and Perform from an (I.IV.V) and have instrumental chorus instrumental or vocal students create Make informed, critical ensemble score of at least four melodies first, Producer – one High School Music Scope & Sequence – May 2012 3 V. Analyze and Make I. Perform II. Create III. Analyze IV. Analyze in Context Connections staves. (ART.M.I.HS.5) followed by lyrics evaluations of the quality who provides Analyze and consider the - Perform Students should and effectiveness of musical direction, use of music and media Perform an use solfege to help performances, facilitator and for the future. notate their mixes music as accompanied compositions, (ART.M.V.HS.5) duet, trio, quartet, melodies on staff well as creates arrangements, and - Analyze Music & 4 part voicing, paper music, especially Media improvisations applying etc. for pop genres Discuss how Arrange pieces for voices specific criteria. music is used in Sight read accurately and or instruments, other than (ART.M.III.HS.5) Analyze the impact of various media expressively, music with those for which the pieces - Critique electronic music media in forms today a moderate level of were written, in ways that Have students society and culture. Bring/show difficulty. preserve or enhance the critique a (ART.M.IV.HS.4) examples (ART.M.I.HS.6) Based off of expressive effect of the performance, - Electronic music in - Accurately Sight music. (ART.M.II.HS.5) society/culture music and media either their own Read - Arrange pieces for How has in the past five Time signature, voices and/or another technology years, discuss any changes Arranging vocal group within evolved in the where it can go in Key signature, lines that may school or outside past 10 years? In the next five years any changes benefit not only of school the past 20 years? Repeats, coda’s the piece but also How has (D.S., D.C., Fine) the choir in a technology Evaluate a performance, Accidentals/ better way changed the face transitions Having alto’s sing composition, of music? Style changes a baritone part an arrangement, or Listen to music (straight eighths, octave higher improvisation by from the 50’s and swing, cut time, Arranging a pop comparing it to similar or today. How much etc.) choral exemplary models. is live versus Tempo, any arrangement from (ART.M.III.HS.6) electronic? What changes what is written in other similarities/ Compare/contrast Solfege syllables the score to what - differences are - Expressively Sight is truer from the Have students there? Read original recording listen to a Dynamics - Arrange pieces for professional Mood instruments recording and a Arrange a part for recording of the another same song they instrument that is played and High School Music Scope & Sequence – May 2012 4 V. Analyze and Make I. Perform II. Create III. Analyze IV. Analyze in Context Connections not present in the explain the band or needs similarities and extra differences. reinforcement
Compose and arrange music for voices and various acoustic and electronic instruments, demonstrating knowledge of the ranges and traditional usage of the sound sources. (ART.M.II.HS.6) - Compose/Arrange for voices Students compose an 8-16 measure piece using 2 part harmonies, keeping in mind the ranges of each part Students compose an 8-16 measure piece using 4 part harmonies, keeping in mind the ranges of each part Students adapt/arrange a familiar song, popular or classical, creating simple 2, 3 or 4- part harmonies
High School Music Scope & Sequence – May 2012 5 V. Analyze and Make I. Perform II. Create III. Analyze IV. Analyze in Context Connections - Compose/Arrange for instruments Have students compose a simple 8-10 measure song for their instrument Have students compose a simple 8-10 measure song for an instrument not theirs or in their family, for example a woodwind compose for a brass or percussion
Create or adapt music to integrate with other media. (ART.M.II.HS.7) - Create/Adapt Watch a relatively short movie scene without any audio. Have students interpret what is occurring in the scene and decide what kind of music will help enhance the emotions within the scene Have students use
High School Music Scope & Sequence – May 2012 6 V. Analyze and Make I. Perform II. Create III. Analyze IV. Analyze in Context Connections recording software (e.g. GarageBand) to record music they either composed as a band/choir or arranged off of a familiar piece and set it to the movie clip Have students assess the scene for sound effects (not music related) that can be added to the scene
High School Music Scope & Sequence – May 2012 7