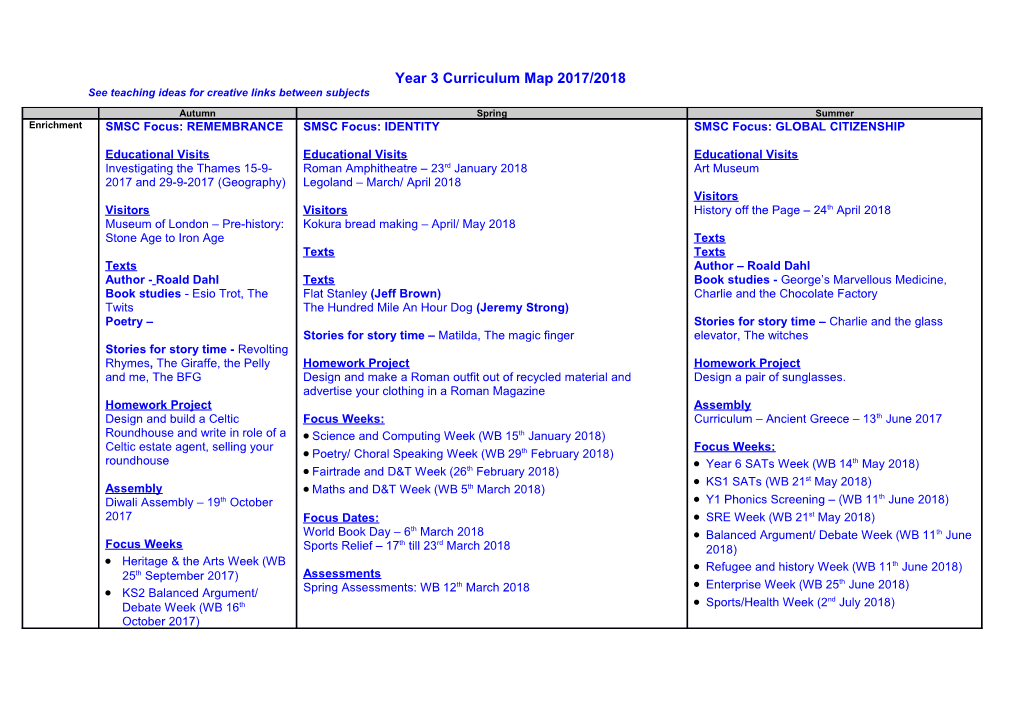
Year 3 Curriculum Map 2017/2018 See teaching ideas for creative links between subjects
Autumn Spring Summer Enrichment SMSC Focus: REMEMBRANCE SMSC Focus: IDENTITY SMSC Focus: GLOBAL CITIZENSHIP
Educational Visits Educational Visits Educational Visits Investigating the Thames 15-9- Roman Amphitheatre – 23rd January 2018 Art Museum 2017 and 29-9-2017 (Geography) Legoland – March/ April 2018 Visitors Visitors Visitors History off the Page – 24th April 2018 Museum of London – Pre-history: Kokura bread making – April/ May 2018 Stone Age to Iron Age Texts Texts Texts Texts Author – Roald Dahl Author - Roald Dahl Texts Book studies - George’s Marvellous Medicine, Book studies - Esio Trot, The Flat Stanley (Jeff Brown) Charlie and the Chocolate Factory Twits The Hundred Mile An Hour Dog (Jeremy Strong) Poetry – Stories for story time – Charlie and the glass Stories for story time – Matilda, The magic finger elevator, The witches Stories for story time - Revolting Rhymes, The Giraffe, the Pelly Homework Project Homework Project and me, The BFG Design and make a Roman outfit out of recycled material and Design a pair of sunglasses. advertise your clothing in a Roman Magazine Homework Project Assembly Design and build a Celtic Focus Weeks: Curriculum – Ancient Greece – 13th June 2017 Roundhouse and write in role of a Science and Computing Week (WB 15th January 2018) Celtic estate agent, selling your Focus Weeks: Poetry/ Choral Speaking Week (WB 29th February 2018) roundhouse Year 6 SATs Week (WB 14th May 2018) Fairtrade and D&T Week (26th February 2018) KS1 SATs (WB 21st May 2018) Assembly Maths and D&T Week (WB 5th March 2018) th Diwali Assembly – 19th October Y1 Phonics Screening – (WB 11 June 2018) 2017 Focus Dates: SRE Week (WB 21st May 2018) th World Book Day – 6 March 2018 Balanced Argument/ Debate Week (WB 11th June th rd Focus Weeks Sports Relief – 17 till 23 March 2018 2018) Heritage & the Arts Week (WB Refugee and history Week (WB 11th June 2018) 25th September 2017) Assessments th Enterprise Week (WB 25th June 2018) KS2 Balanced Argument/ Spring Assessments: WB 12 March 2018 nd Debate Week (WB 16th Sports/Health Week (2 July 2018) October 2017) Rights and Respect Week – Focus Dates: th th Safety/ friendship, anti- Sports Day – 12 and 13 July 2017 th bullying (WB 13th November Carnival – WB 16 July 2018 2017) Assessments Work Week (WB 27th Summer Assessments: WB 18th June 2018 November 2017)
Assessments Baseline Assessments: WB 11th September 2017 Autumn Assessments: 20th November 2017 Maths Assess prior knowledge before starting Assess prior Assess prior knowledge Assess prior knowledge before Assess prior knowledge Assess prior knowledge unit to establish starting point. knowledge before before starting unit to starting unit to establish starting before starting unit to before starting unit to Unit 1 starting unit to establish starting point. point. establish starting point. establish starting point. Numbers to 10,000 establish starting Unit 8 Unit 10 Unit 13 Unit 16 point. Solving multiplication and Money Bar graphs Angles NC Activity 3.1: Unit 5 division word problems Compare and order numbers up to 1000 Multiplying by 6,7,8 Assess prior knowledge before Assess prior knowledge Review 7 and 9 Assess prior knowledge starting unit to establish starting before starting unit to Assess prior knowledge before starting before starting unit to point. establish starting point. Assess prior knowledge unit to establish starting point. Assess prior establish starting point. Unit 11 Unit 14 before starting unit to Unit 2 knowledge before Unit 9 Length, mass and volume Fractions establish starting point. Addition within 10,000 starting unit to Mental calculations Unit 17 establish starting NC Activity 3.7: NC Activity 3.6: Perpendicular and parallel NC Activity 3.3: point. ** Additional unit – Measure, compare, add and Count up and down in lines Add and subtract numbers mentally, Unit 6 Read and write Roman subtract: lengths (m/cm/mm); mass tenths; recognise that tenths including a 3-digit number and ones, a 3- Multiplication numerals to 1 (link to history) (kg/g); volume/capacity (l/ml) arise from dividing an object NC Activity 3.11: digit number and tens, a 3-digit number into 10 equal parts and in Draw 2-D shapes and make and hundreds Review 3 Review 4 Assess prior knowledge before dividing 1-digit numbers or 3-D shapes using modelling starting unit to establish starting quantities by 10 materials; recognise 3-D Review 1 Assess prior Assessment test 4 point. shapes in different knowledge before Unit 12 Review 6 orientations and describe Assessment test 1 starting unit to Solving problems; length, mass and them establish starting volume Assessment test 6 Assess prior knowledge before starting point. Assess prior knowledge unit to establish starting point. Unit 7 Review 5 Assess prior knowledge before starting unit to Unit 3 Division before starting unit to establish starting point. Subtraction within 10,000 Assessment test 5 establish starting point. Unit 18 Assessment test Unit 15 Area and perimeter Unit 4 3 Time Solving addition and subtraction word Review 8 problems NC Activity 3.8: Tell and write the time from Assessment test 7 Review 2 an analogue clock, including using Roman numerals from Assessment test 2 I to XII, and 12-hour and 24- hour clocks.
NC Activity 3.10: Know the number of seconds in a minute and the number of days in each month, year and leap year Literacy Reading Reading Reading (Word Reading) (Word Reading) (Word Reading) Apply their growing knowledge of root Apply their growing knowledge of root words, prefixes and suffixes (etymology and Apply their growing knowledge of root words, prefixes and words, prefixes and suffixes (etymology morphology), both to read aloud and to understand the meaning of new words they suffixes (etymology and morphology), both to read aloud and to and morphology), both to read aloud and meet. understand the meaning of new words they meet. to understand the meaning of new words Read further exception words noting the unusual correspondences between spelling Read further exception words noting the unusual they meet. and sound, and where these occur in the word correspondences between spelling and sound, and where Read further exception words noting the these occur in the word unusual correspondences between Reading spelling and sound, and where these (Comprehension) Reading (Comprehension) occur in the word Increase their familiarity with a wide range of books, including fairy stories, myths and Read aloud poems and perform play scripts Reading legends, and retelling some of these orally. (Comprehension) Identify themes and conventions in a wide range of books. Discuss words and phrases that capture the reader’s interest and imagination. Listen to and discuss a wide range of Understand what they read by asking questions to improve their understanding of the fiction, poetry, plays, non-fiction text Recognise some different forms of poetry (e.g. free verse, narrative poetry) Read books that are structured in Understand what they read by predicting what might happen from details stated different ways and reading for a range of Understand what they read by identifying main ideas drawn Retrieve and record information from non-fiction purposes. from within one paragraph and summarise these Check that text makes sense by Writing Participate in reasoned discussion about books, poems and discussing their understanding of words (Transcription) other material that are read to them and those they can read for Draw inferences such as inferring Spell further homophones. themselves taking turns and listening to what others say characters feelings, thoughts and Spell words that are often misspelt Writing motives from their actions and justifying (Transcription) inferences with evidence Spell words containing the ‘I’ sound spelt ‘y’ elsewhere than at the end of the words Write from memory simple sentences, dictated by the teacher, Identify how language, structure, and e.g. myth that include words and punctuation taught so far. presentation contribute to meaning to Spell words containing the ‘u’ sound apelt ‘ou’ e.g. young include paragraphs, headings, inverted Spell words with the ‘sh’ sound spelt ‘ch’ e.g. chef Spell words with the ‘k’ sound spelt ‘ch’ e.g. scheme commas to punctuate speech Spell words with the ‘ay’ sound spelt ‘ei’ or ‘ey’ e.g. eight or Increase the legibility, consistency and quality of their handwriting, e.g. by ensuring Writing they (Transcription) that the down strokes of letters are parallel and equidistant; that lines of writing are spaced sufficiently so that the ascenders and descenders of letters do not touch. Use the first two or three letters of a word to check its spelling Use the prefixes un-, dis-, mis-, re-, pre- in a dictionary Writing Increase the legibility, consistency and quality of their Add suffixes beginning with vowel letters (Composition) to words of more than one syllable e.g handwriting, e.g. by ensuring that the down strokes of letters forgetting, preferred Plan their writing by discussing and recording ideas with a given structure are parallel and equidistant; that lines of writing are spaced sufficiently so that the ascenders and descenders of letters do Use the suffix –ly Draft and write by organising paragraphs around a theme. not touch. Spell words with endings sounding like Evaluate and edit by proof-reading for spelling and punctuation errors – including full ‘zh’ and ‘ch’ e.g. treasure, nature stop, apostrophe, comma, question mark, exclamation and inverted commas for Writing speech Spell words with endings which sound (Composition) like ‘zhun’ e.g. division Grammar and Punctuation Plan their writing by discussing and recording ideas. Use the diagonal and horizontal strokes Identify word families based on common root words (e.g. solve, solution, solver, Draft and write by, in narratives, creating settings, characters that are needed to join letters and dissolve, insoluble) and plot, understand which letters, when adjacent to one another, are best left not joined. Use headings and sub heading to aid presentation Draft and write non-narrative material, using simple organisational devices such as headings and sub-headings. Writing Evaluate and edit by reading aloud their own writing, to a group (Composition) or the whole class, using appropriate intonation and controlling Plan their writing by discussing writing the tone and volume so that the meaning is clear. similar to that which they are planning to write in order to understand and learn Grammar and Punctuation from its structure, grammar and Form nouns using a range of prefixes, such as super-, anti-, vocabulary. auto. Draft and write by composing and Use determiners according to whether the next word begins rehearsing sentences orally (including with a consonant or vowel) dialogue), progressively building a varied and rich vocabulary and an increasing Use and understand the grammatical terminology (word family, range of sentence structures. conjunction, adverb, preposition, direct speech, inverted commas/speech marks, prefix, consonant, vowel, consonant Evaluate and edit by assessing the letter, vowel letter, clause, subordinate clause) effectiveness of their own and others’ writing proposing changes to grammar and vocabulary linked to the use of a/an, conjunctions, adverbs and prepositions
Grammar and Punctuation Express time, place and cause using conjunctions, e.g. when, before, after, while, so, if, because, adverbs (e.g. then, next, soon, therefore) or prepositions (e.g. before, after, during, in, because of) Use the present perfect form of verbs instead of the simple past (he has gone out to play – he went out Begin to use paragraphs as a way to group related material Begin to use inverted commas to punctuate direct speech Science Forces and Magnets Animals, including humans Plants Compare how things move on different Identify that animals including humans need the right types and amount of Identify and describe the function of different parts of flowering surfaces nutrition and that they cannot make their own food; they get nutrition from what they plants; roots, stem/trunk, leaves and flowers, eat Notice that some forces need contact Explore the requirements of plants for life and growth (air, between two objects and some forces Identify that humans and some animals have skeletons and muscles for light, water, nutrients from soil and room to grow) and how act at a distance support, protection and movement they vary from plant to plant Observe how magnets attract or repel Pupils might work scientifically by: Investigate the way in which water is transported within plants, each other and attract some materials •identifying and grouping animals with and without skeletons and observing and Explore the part that flowers play in the life cycle of flowering and not others comparing their movement; •exploring ideas about what would happen if humans did not have skeletons. plants, including pollination, seed formation and seed dispersal Compare and group together a variety of •They might compare and contrast the diets of different animals (including their pets) everyday materials on the basis of Pupils might work scientifically by: and decide ways of grouping them according to what they eat. whether they are attracted to a magnet • comparing the effect of different factors on plant growth, for •They might research different food groups and how they keep us healthy and design and identify some magnetic materials example, the amount of light, the amount of fertiliser; meals based on what they find out. Describe magnets as having two poles • discovering how seeds are formed by observing the different Rocks stages of plant life cycles over a period of time; looking for patterns in the structure of fruits that relate to how Pupils might work scientifically by: Compare and group together different klnds of rocks on the basis of their • the seeds are dispersed. • comparing how different things move appearance and simple physical properties and grouping them; • They might observe how water is transported in plants, for Describe in simple terms how fossils are formed when things that have lived • raising questions and carrying out tests example, by putting cut, white carnations into coloured water to find out how far things move on are trapped within rock and observing how water travels up the stem to the flowers. different surfaces and gathering and Recognise that soils are made from rock and organic matter recording data to find answers their Light questions; Pupils might work scientifically by: Recognise that he/she needs light in order to see things and • observing rocks, including those used in buildings and gravestones, and exploring how • exploring the strengths of different that dark is the absence of light magnets and finding a fair way to and why they might have changed over time; compare them; • using a hand lens or microscope to help them to identify and classify rocks according Notice that light is reflected from surfaces • sorting materials into those that are to whether they have grains or crystals, and whether they have fossils in them. • Pupils might research and discuss the different kinds of living things whose fossils are Recognise that light from the sun can be dangerous and that magnetic and those that are not; there are ways to protect eyes • looking for patterns in the way that found in sedimentary rock and explore how fossils are formed. magnets behave in relation to each other • Pupils could explore different soils and identify similarities and differences between Recognise that shadows are formed when the light from a light and what might affect this, for example, them and investigate what happens when rocks are rubbed together or what changes source is blocked by a solid object the strength of the magnet or which pole occur when they are in water. Find patterns in the way that the size of shadows change faces another; They can raise and answer questions about the way soils are formed. Identifying how these properties make Pupils might work scientifically by: magnets useful in everyday items and Looking for patterns in what happens to shadows when the suggesting creative uses for different magnets. light source moves or the distance between the light source and the object changes. Geography AUTUMN 1 SPRING 2 SUMMER 2 Settlement, Rivers and the water cycle Countries of UK & topographical features + contrasting locality Mapping skills & carnival country Ask and answer geographical questions. Use and interpret maps, globes, atlases, and digital mapping to find countries and key Ask and answer geographical questions. E.g. describe the E.g. describe the landscape. Why is it features landscape. Analyse evidence and draw conclusions such as like this? How have people affected what make comparisons between locations using aerial Point to where countries are within the UK and their key topographical features it looks like? What do you think about photos/pictures. that? What do you think it might be like Name and locate the cities of the UK Use basic geographical words such as cliff, ocean, valley, if… continues? Show some sense of how places relate to each other vegetation, soil and mountain. Understand and use geographical terms such as meander, floodplain, location, Understand that people hold different views about an issue and begin to understand Make detailed fieldwork sketches/diagrams. industry, transport, settlement, water some of the reasons why cycle Understand why there are similarities and differences between Use fieldwork instruments e.g. camera, Communicate findings in appropriate ways places rain gauge Use basic geographical words such as port, harbour, factory, Understand the water cycle office. Use four figure grid references Use the 8 points of a compass Make plans and maps using symbols and keys History AUTUMN 2 SPRING 1 SUMMER 1 Early Britons - Stone Age, Bronze Age The Romans The Greeks and Iron Age Use an increasing range of common words and phrases relating to the passing of Use an increasing range of common words and phrases Use an increasing range of common time relating to the passing of time. words and phrases relating to the Describe where people and events fit within a timeline Show understanding of some of the ways in which we find out passing of time – chronological about the past and identify different ways in which it is understanding Show understanding of some of the ways in which we find out about the past and represented. Use a wide vocabulary of everyday identify different ways in which it is represented. Describe memories of key events in his/her life using historical historical terms. vocabulary. Ask and answer questions, choosing and using parts of stories and other sources History off the page workshop – Life in Ancient Greece Day to show that I know and understand key (24th April 2018) features. Speak about how I have found out about the past. Record what I have learned by drawing and writing. ART AUTUMN 2 SPRING 1 Painting Light and Dark – Using the festival of Holi as a the Celtic Art – digital media Animal sculpture basis Create sketch books to record Improve mastery of techniques such as drawing painting and sculpture with materials Improve mastery of techniques such as drawing painting and observations and use them to review (e.g. pencil, charcoal, paint , clay) sculpture with materials (e.g. pencil, charcoal, paint , clay) and revisit ideas, and collect visual Learn about the greatest artists, architects and designers in history(Auguste Rodin) Learn about the greatest artists, architects material to help develop ideas Learn about the greatest artists, architects and designers in history(Jen Delyth) D&T AUTUMN 1 SPRING 2 Design a piece of equipment that the Ancient Greeks would Design a house on the Thames Bread making around the world use Investigate and test a range of materials Understand seasonality, and know where and how a variety of ingredients are grown, Plan designs using spider diagrams and sketches reared, caught and processed Plan designs using spider diagrams and Generate, develop, model and communicate their ideas sketches Understand and apply the principles of a healthy and varied diet through talking, drawing templates, mock-ups and information and communication technology Build structures, exploring how they can Prepare and cook a variety of predominantly savoury dishes using a range of cooking be made stronger, stiffer and more techniques stable Apply understanding to strengthen their structures Computing Online-Safety (Me online) – Use of LGFL Online-Safety (Me online) – Use of LGFL Cyberpass (Violet’s Permission – Runs Online-Safety (Me online) – Use of LGFL Cyberpass (Violet’s Cyberpass (Violet’s Permission – Runs off SIMS Data) Assess needs and teach accordingly. Permission – Runs off SIMS Data) Assess needs and teach off SIMS Data) Assess needs and teach accordingly. Describe how internet search engines find and store data; use search engines accordingly. effectively; be discerning in evaluating digital content; respect individuals and Describe how internet search engines find and store data; use Describe how internet search engines intellectual property; use technology responsibly, securely and safely - Two lessons search engines effectively; be discerning in evaluating digital find and store data; use search engines per term. content; respect individuals and intellectual property; use effectively; be discerning in evaluating technology responsibly, securely and safely - Two lessons digital content; respect individuals and We Are Programmers (Unit 3.1) per term. intellectual property; use technology Use sequence, selection, and repetition in programs; work with variables and various responsibly, securely and safely - Two GREEN SCREEN PROJECT – LINKED TO LEGOLAND lessons per term. forms of input and output; generate appropriate inputs and predicted outputs to test (PERSUASIVE ADVERT TO VISIT LEGOLAND) programs. Possible Secondary School Link – Eastlea – MicroBits or Scratch NPW – Stop Frame Animation Rainbow Matrix. We Are Presenters (Unit 3.3) Introduced to stop frame animation and Use a combination of graphics and text. work collaboratively to produce a short Understand what algorithms are, how they are implemented film linked to a curricular topic. – J2e Spotlight – Use of Wallace and Gromit as programs on digital devices, and that programs execute by – Hook following a sequence of instructions PE Athletics – Naser Mohammed Gymnastics – Natasha Gyral Cricket – Naser Mohammed Develop flexibility, strength, technique, Use running and jumping in isolation and in combination. Play competitive games, modified where appropriate, and apply control and balance, through athletics. basic principles suitable for attacking and defending Netball - teachers Use running, jumping, catching and throwing in isolation and in Tennis - teachers Play competitive games, modified where appropriate, and apply basic principles combination. Play competitive games, modified where suitable for attacking and defending appropriate, and apply basic principles Games - Teachers suitable for attacking and defending Play competitive games, modified where appropriate, and apply basic principles suitable for attacking and defending Use running, jumping, catching and throwing in isolation and in combination.
Dance Perform dances using a range of movement patterns. Compare their performances with previous ones to achieve their personal best. Music Play and perform in solo and ensemble Improvise and compose music using the inter-related dimensions of music separately Play and perform in solo and ensemble contexts, using their contexts, using their voice and play and in combination. voice and play musical instruments with increasing accuracy, musical instruments with increasing control and expression. Listen with attention to detail and recall sounds with increasing aural memory. accuracy, control and expression. Improvise and compose music using the inter-related Appreciate and understand a wide range of high-quality live and recorded music from Use and understand the basics of staff dimensions of music separately and in combination. and other musical notations. different traditions and from great musicians and composers. Develop an understanding of the history of music. RE Signs and symbols in religion Sikhism Holi/Hinduism Understand how special symbols are What do Sikh sayings tell us about Sikh beliefs Understand how and why Hindu’s celebrate Holi used in religions Judaism Jesus and Buddha Light in religion Understand how Jews celebrate Understand the effect of Jesus and Buddha’s teachings Understand the significance of light in religions PSHE Living in the wider world Health and well being Relationships SRE lessons Rights and responsibility Week Drugs and alcohol lessons Identify different viewpoints Work week Healthy living Question each other’s viewpoints Heritage week Health Living in the Wider World – objectives Turn statements into questions and outcomes Identify different question categories Explore the meaning of concepts Identify concepts within statements MFL: Greetings, Sounds/Alphabet, Numbers Traditional games, Numbers 11-15, Classroom objects Days of the week, Numbers 20-31, Months of the year Spanish 1-10 Develop accurate pronunciation Describe people orally and in writing Listen attentively to spoken language Appreciate stories, songs and poems in the language and show understanding by joining in Understand basic grammar appropriate to the language such and responding. Colours, Articles (The, a), Numbers 16-20 as masculine/feminine forms Explore the patterns and sounds of Speak in sentences, using familiar vocabulary, phrases and basic language structures Nouns (gender and number), Around The House, Birthday language through songs and rhymes and Cards link the spelling, sound and meaning of Develop accurate pronunciation words. Identify key features/patterns of the language Family, Personal information, Christmas Cards Engage in conversations; ask and answer questions