Lymphatic System & Blood Vocabulary Quiz B
Part I: Blood Vocab
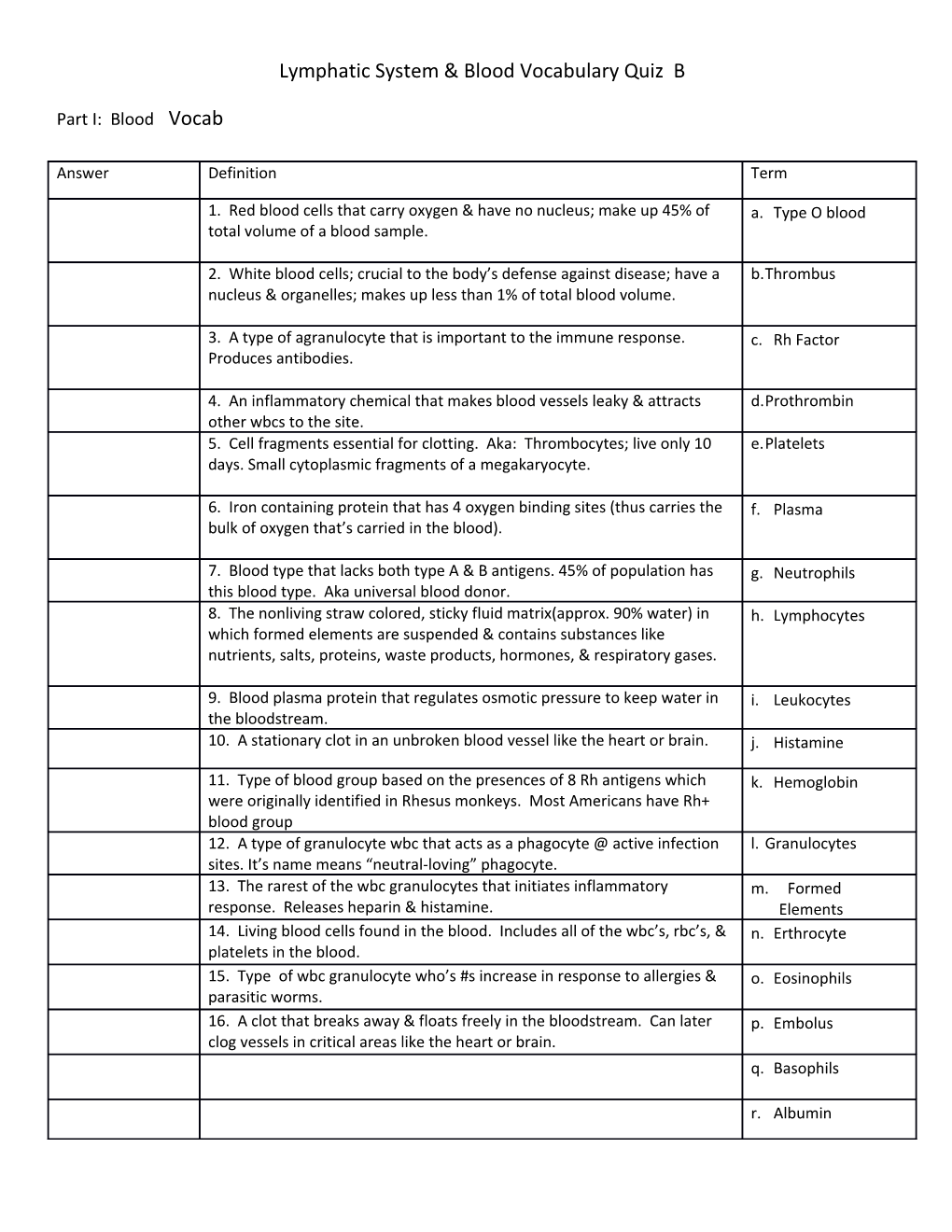
Answer Definition Term
1. Red blood cells that carry oxygen & have no nucleus; make up 45% of a. Type O blood total volume of a blood sample.
2. White blood cells; crucial to the body’s defense against disease; have a b.Thrombus nucleus & organelles; makes up less than 1% of total blood volume.
3. A type of agranulocyte that is important to the immune response. c. Rh Factor Produces antibodies.
4. An inflammatory chemical that makes blood vessels leaky & attracts d.Prothrombin other wbcs to the site. 5. Cell fragments essential for clotting. Aka: Thrombocytes; live only 10 e.Platelets days. Small cytoplasmic fragments of a megakaryocyte.
6. Iron containing protein that has 4 oxygen binding sites (thus carries the f. Plasma bulk of oxygen that’s carried in the blood).
7. Blood type that lacks both type A & B antigens. 45% of population has g. Neutrophils this blood type. Aka universal blood donor. 8. The nonliving straw colored, sticky fluid matrix(approx. 90% water) in h. Lymphocytes which formed elements are suspended & contains substances like nutrients, salts, proteins, waste products, hormones, & respiratory gases.
9. Blood plasma protein that regulates osmotic pressure to keep water in i. Leukocytes the bloodstream. 10. A stationary clot in an unbroken blood vessel like the heart or brain. j. Histamine
11. Type of blood group based on the presences of 8 Rh antigens which k. Hemoglobin were originally identified in Rhesus monkeys. Most Americans have Rh+ blood group 12. A type of granulocyte wbc that acts as a phagocyte @ active infection l. Granulocytes sites. It’s name means “neutral-loving” phagocyte. 13. The rarest of the wbc granulocytes that initiates inflammatory m. Formed response. Releases heparin & histamine. Elements 14. Living blood cells found in the blood. Includes all of the wbc’s, rbc’s, & n. Erthrocyte platelets in the blood. 15. Type of wbc granulocyte who’s #s increase in response to allergies & o. Eosinophils parasitic worms. 16. A clot that breaks away & floats freely in the bloodstream. Can later p. Embolus clog vessels in critical areas like the heart or brain. q. Basophils
r. Albumin Lymphatic System Vocabulary Test Part II. Matching: Answer Statement Term 1. (also called hypersensitivities) are abnormally vigorous immune responses a. Autoimmune which causes tissue damage as it fights off a perceived “threat” that would otherwise be Disease: harmless to the body.
2. (a type of lymphoid organ) acts as a blood reservoir, that filters blood of bacteria, b. Antigens: viruses, & other debris & is located in the left side of the abdominal cavity & curls around the anterior aspect of the stomach.
3. fluid accumulation within the tissues that causes swelling. (medical name for swelling) c. Antibodies:
4. a cell that engulfs a foreign particle that may be dangerous to that cell, much the way d. B an amoeba ingests a food particle. Ex. Macrophage or neutrophil. lymphocytes
5. is any substance capable of exciting our immune system & causing an immune e. . Fever: response. (Pathogen’s name tag.)
6. cells that help make antibodies & oversee humoral immunity. (also called B cells): f. Pyrogens:
7. cells that slow or stops the activity of B & T cells once the infection has been g. Spleen: conquered
8. also called immunoglobulins; They make the gamma globulin part of blood proteins & h. Active are made by B cells. Immunity:
9. type of immunity naturally obtained during bacterial & viral infections where you i. Thymus: develop symptoms of the disease & suffer a little while & then recover.
10. systemic response triggered by pyrogens; Normal body temperature is regulated by j. Suppressor T the hypothalamus. Cell:
11. condition where the immune system loses its ability to distinguish friend from foe & k. Phagocytes: attack or damage the body’s own tissues. Ex. MS, Graves disease, Rheumatoid arthritis 12. another name for a lymph cell. It is important to your immune system. Two types are l. Allergies: B & T cells.
13. (a type of lymphoid organ) functions at peak levels only during youth, found in the m. Edema: throat overlying the heart. It produces hormones that cause T cell maturation.
14. a nonspecific protective response against invading pathogens includes undamaged n. Cytotoxic T skin, tears, & mucous membranes. cell:
15. fire chemicals secreted by WBC’s exposed to foreign substances in the body which o. Lymphocytes: causes the normal body temperature to increase
16. (also called a Killer T cell) it kills virus-invaded body cells, as well as body cells that p. First Line of have become cancerous; & ia involved in graft rejection. Defense: