Designing for Behavior Change Framework: Encouraging a non-hungry Child to Eat (Burundi)
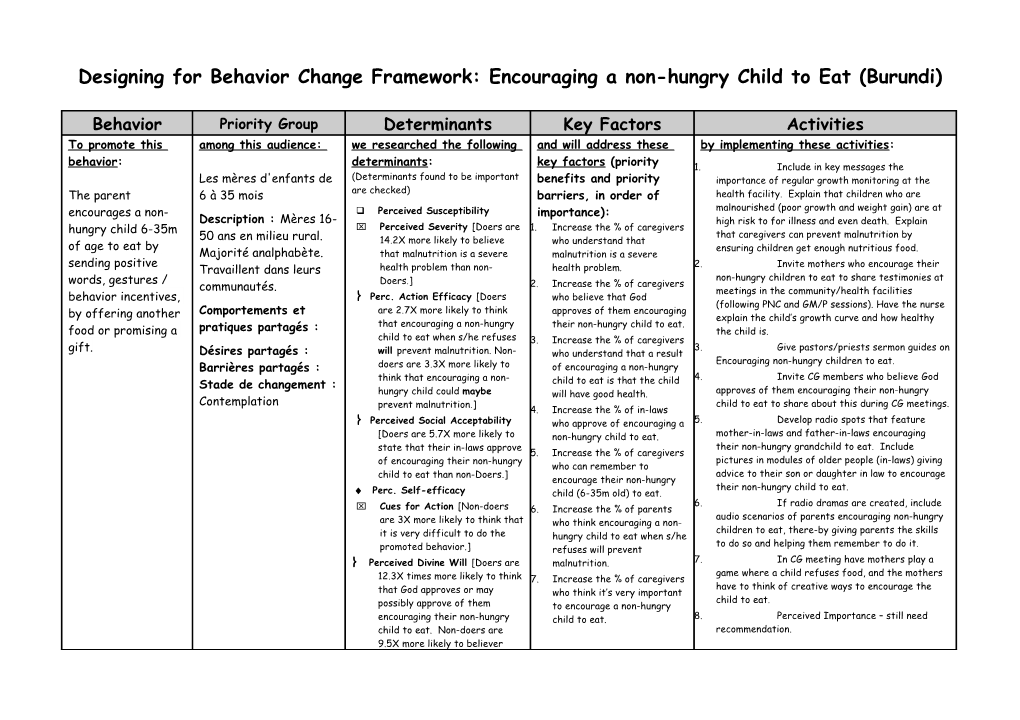
Behavior Priority Group Determinants Key Factors Activities To promote this among this audience: we researched the following and will address these by implementing these activities: behavior: determinants: key factors (priority 1. Include in key messages the Les mères d'enfants de (Determinants found to be important benefits and priority importance of regular growth monitoring at the The parent 6 à 35 mois are checked) barriers, in order of health facility. Explain that children who are encourages a non- Perceived Susceptibility importance): malnourished (poor growth and weight gain) are at Description : Mères 16- high risk to for illness and even death. Explain Perceived Severity [Doers are 1. Increase the % of caregivers hungry child 6-35m that caregivers can prevent malnutrition by 50 ans en milieu rural. 14.2X more likely to believe who understand that of age to eat by ensuring children get enough nutritious food. Majorité analphabète. that malnutrition is a severe malnutrition is a severe sending positive 2. Invite mothers who encourage their Travaillent dans leurs health problem than non- health problem. non-hungry children to eat to share testimonies at words, gestures / Doers.] 2. Increase the % of caregivers communautés. meetings in the community/health facilities behavior incentives, Perc. Action Efficacy [Doers who believe that God (following PNC and GM/P sessions). Have the nurse Comportements et are 2.7X more likely to think approves of them encouraging by offering another explain the child’s growth curve and how healthy that encouraging a non-hungry their non-hungry child to eat. food or promising a pratiques partagés : the child is. child to eat when s/he refuses 3. Increase the % of caregivers 3. Give pastors/priests sermon guides on gift. Désires partagés : will prevent malnutrition. Non- who understand that a result Encouraging non-hungry children to eat. Barrières partagés : doers are 3.3X more likely to of encouraging a non-hungry think that encouraging a non- 4. Invite CG members who believe God Stade de changement : child to eat is that the child hungry child could maybe will have good health. approves of them encouraging their non-hungry Contemplation prevent malnutrition.] child to eat to share about this during CG meetings. 4. Increase the % of in-laws Perceived Social Acceptability who approve of encouraging a 5. Develop radio spots that feature [Doers are 5.7X more likely to non-hungry child to eat. mother-in-laws and father-in-laws encouraging state that their in-laws approve their non-hungry grandchild to eat. Include 5. Increase the % of caregivers of encouraging their non-hungry pictures in modules of older people (in-laws) giving who can remember to child to eat than non-Doers.] advice to their son or daughter in law to encourage encourage their non-hungry their non-hungry child to eat. Perc. Self-efficacy child (6-35m old) to eat. 6. If radio dramas are created, include Cues for Action [Non-doers 6. Increase the % of parents audio scenarios of parents encouraging non-hungry are 3X more likely to think that who think encouraging a non- children to eat, there-by giving parents the skills it is very difficult to do the hungry child to eat when s/he to do so and helping them remember to do it. promoted behavior.] refuses will prevent Perceived Divine Will [Doers are malnutrition. 7. In CG meeting have mothers play a game where a child refuses food, and the mothers 12.3X times more likely to think 7. Increase the % of caregivers have to think of creative ways to encourage the that God approves or may who think it’s very important child to eat. possibly approve of them to encourage a non-hungry encouraging their non-hungry child to eat. 8. Perceived Importance – still need child to eat. Non-doers are recommendation. 9.5X more likely to believer Behavior Priority Group Determinants Key Factors Activities that God does not approve of them encouraging their non- hungry child to eat.] Perceived Positive/Negative Attributes of the Action [Doers are 6.1X more likely to mention that an advantage of encouraging a non-hungry child to eat is that the child will have good health. Perceived Importance of the Action [Doers are 2.7X more likely to think that encouraging a non-hungry child to eat is very important. Non-doers are 6.8X as likely to say it is a little important.]