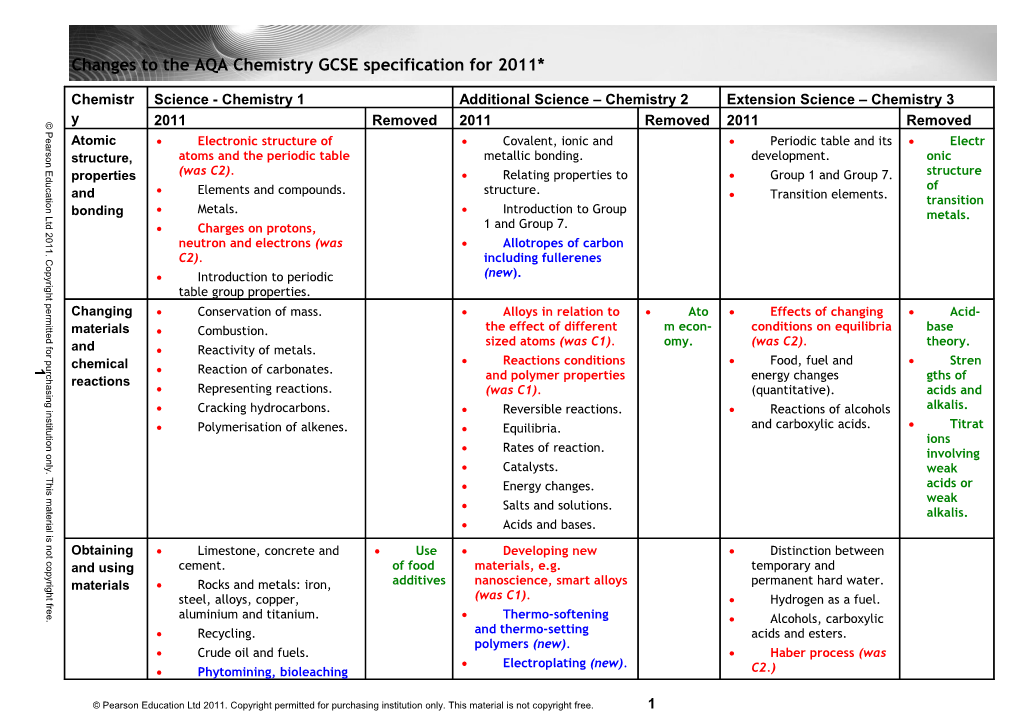
Changes to the AQA Chemistry GCSE specification for 2011*
Chemistr Science - Chemistry 1 Additional Science – Chemistry 2 Extension Science – Chemistry 3
© y 2011 Removed 2011 Removed 2011 Removed
P
e
a Atomic Electronic structure of Covalent, ionic and Periodic table and its Electr
r
s
o
n structure, atoms and the periodic table metallic bonding. development. onic
E
d (was C2). Relating properties to Group 1 and Group 7. structure u properties
c of a Elements and compounds. structure. t and i Transition elements. o transition
n
Metals. Introduction to Group L bonding
t metals.
d
1 and Group 7. 2 Charges on protons,
0
1
1 neutron and electrons (was Allotropes of carbon
.
C C2). including fullerenes
o
p
y (new).
r Introduction to periodic
i
g
h
t table group properties.
p
e
r
m Changing Conservation of mass. Alloys in relation to Ato Effects of changing Acid-
i
t
t e materials Combustion. the effect of different m econ- conditions on equilibria base
d
f sized atoms (was C1). omy. (was C2). theory. o and r Reactivity of metals.
p
u Reactions conditions Food, fuel and Stren 1 chemical
r
c Reaction of carbonates.
h and polymer properties energy changes gths of a reactions
s
i Representing reactions. (was C1). (quantitative). acids and
n
g
i alkalis. n Cracking hydrocarbons. Reversible reactions. Reactions of alcohols
s
t
i
t u Polymerisation of alkenes. Equilibria. and carboxylic acids. Titrat
t
i o ions
n
o Rates of reaction.
n involving
l
y
. Catalysts.
weak
T
h
i acids or s Energy changes.
m weak
a
t Salts and solutions. e alkalis.
r
i
a
l Acids and bases.
i
s
n
o
t Obtaining Limestone, concrete and Use Developing new Distinction between
c
o
p and using cement. of food materials, e.g. temporary and
y
r
i g Rocks and metals: iron, additives nanoscience, smart alloys permanent hard water.
h materials
t
(was C1).
f
r steel, alloys, copper, Hydrogen as a fuel.
e
e . aluminium and titanium. Thermo-softening Alcohols, carboxylic Recycling. and thermo-setting acids and esters. polymers (new). Crude oil and fuels. Haber process (was Electroplating (new). Phytomining, bioleaching C2.)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2011. Copyright permitted for purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. 1 (new). Extraction of Biodegradable polymers aluminium (was C1). (new). Electrolysis of sodium chloride. © Plant oils and emulsions.
P
e Hydrophobic and
a
r
s
o hydrophilic properties of
n
E emulsifiers (new).
d
u
c Distillation (crude oil, plant
a
t
i o oils and air).
n
L
t
d Biofuels (new).
2
0
1 Using vegetable oils in
1
.
C cooking (new).
o
p
y Earth and Earth and its atmosphere. Uses Water for drinking. Water
r
i
g
h environme of noble cycle. t Early atmosphere.
Water treatment.
p
e gases.
r ntal m Absorption of carbon Hard water.
i
t
t science e dioxide by the oceans (new). d Fluoride in drinking
f
o
r water.
p
u
1
r
c Chemical Reaction of Instrumental Chemical analysis Tests
h
a
s detection carbonates with acid and the methods for chemical including tests for ions. for
i
n
g analysis (gas
i use of limewater to detect ammonium
n
s chromatography and mass
t
i
t carbon dioxide (was C3). and nitrate
u
t spectrometry) (was C3).
i o ions.
n
o Chemical analysis for
n
l Identi y additives in food (was
.
T fication of h C1).
i
s
m organic
a
t
e compounds
r
i
a
l
i Chemical Relative Energy changes. Solubi s Conservation of mass.
n
o calculation atomic/formula masses, lity of t Titrations.
c
o moles. solutes
p s
y
r
i Reacting masses from
g and gases.
h
t chemical equations,
f
r
e
e percentage yield, atom . economy. *Subject to Ofqual accreditation.
© Pearson Education Ltd 2011. Copyright permitted for purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. 2