Table 1: Relationships between lifecycle terms
FUNCTIONS Originate/Receive
STATES Archive/Restore Update
Attest Verify Activated (On/Off) Extract Retain Coded/Unstructured Link/Unlink Deprecated (On/Off) Merge/Unmerge Disclosed Labeled Transform Legal Hold (On/Off) De-Id Verified Encrypt/De-Crypt Validated Pseudo/Re-ID
Access Report (Output) Delete Destroy Disclose Transmit Mike Davis
The entry point for the above table is at the origination or receipt of a record. At that point, it can be retained and then any combination of archived, restored, updated, transformed, and then retained again. It can also undergo any combination of access, report (output), delete, destroy, disclose, and transmit without subsequent retention as such events do not change the content of the record. A record which is being updated can have multiple things being done to it prior to being retained again, such as attested to, verified, extracted, labeled, linked or unlinked, and merged or unmerged. Likewise, a record which has been transformed can also be de-identified, encrypted or decrypted, or pseudonymized or re-identified and then retained again. At any point in time, state can be described/added to the record or changed but is not explicitly part of the EHR LCE definitions..
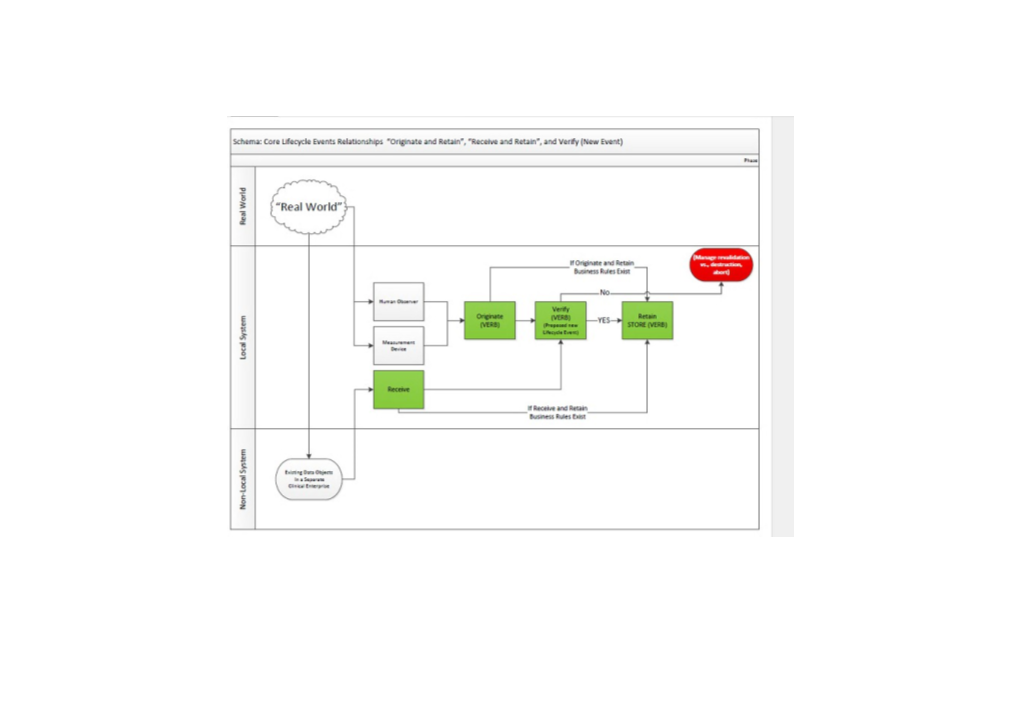
1. Originate and Retain Lifecycle Event
a. Description: As part of trusted record management, this is the record lifecycle event describing when an agent performs two activities: the agent initiates the entry of data as potential content for an EHR record (originate) and enters that data into storage considered permanent (retain).
Originate (v) Definition: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition: To initiate entry of data objects as potential content for an EHR record. Contrast with "To Agent has Receive." logged into the EHR "To Originate" is an activity within EHR Records Management. "To Ontological View: system. Originate" includes the option of an interim state that permits an intermediate assessment of new data or data objects prior to commitment Class: Records Management Agent has Sub-class: Originate to long-term management. That intermediate assessment is intended to “Create” determine whether to store the initially captured data or data objects or to Permission destroy them as ephemera or a rejected draft. "To Originate" may “Create” include the use of volatile memory or other means which offer a temporary function cache or cache-like status for the interim state. activated At outset, entity contains, Properties: at most, data New data object associated Potential, interim status (or State) with a template.
Process:
The object is defined, iterated. Post-Activity Options :
Discard Entity Verify and/or Validate Entity Retain Entity
Retai Definition: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition n (v) To persist data or data objects by saving onto electronically accessible 1. An object exists which needs devices. to be saved. Process: Properties: Ontological View 1. The object is selected and Can be performed on any object, whether Class: Record Management space is opened in memory. previously retained or not. Sub-class: Retain 2. Object is written to and manipulated in memory. Multiple activities can be performed on 3. Object is placed in a attributes of the object during the permanent storage location. retention process, such as: 4. Finally, the data object has o Change of name been persisted as a new EHR o Updates to provenance (eg: last information object. agent who saved/modified object) Post-event Options o Change of storage location 1. Object A’ available for use o Change of time stamp Is performed on objects in memory. Final results are written to designated storage location. 2. Amend (Update) Lifecycle Event
b. Description: As part of trusted record management, this is the record lifecycle event describing when an agent makes any changes to the content of data currently residing in storage considered permanent. For the purposes of Amend (Update) Lifecycle Event, amend and update are considered synonymous.
Update (v) Definition: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition to perform an operation that results only in the revision or Process: alteration of an object Properties: [HL7 EHR, Security, and Post-event Options Privacy Joint Vocabulary Alignment Project] Ontological View Class: Update Amend (v) Definition: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition
as part of trusted record Process: management, to make Properties: changes in record Post-event Options content in order to make it fairer, more accurate, consistent, complete and/or up-to-date [Oxford Dictionary, modified]
to change some of the words and often the meaning of (a law, document, etc.)
to change and improve (something, such as a mistake or bad situation) [Merriam-Webster http://www.merriam- webster.com/dictionary/appen d]
Content is modified (from its original or previously retained state) – typically upon conclusion of an Action, to correct, update or complete content (HL7 EHRS-FM Record Lifecycle Events on FHIR, draft 16 Feb 2015) Ontological View Class: Update Sub-class: Amend 3. Transform or Translate Lifecycle Event
c. Description: As part of trusted record management, this is the record lifecycle event describing when an agent makes any changes to the form (transform), language, or coding system (translate) used to represent data currently residing in storage considered permanent.
Transfor Definition: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition m (v) conversion or change of data/record content from one format to another, from one arrangement to Process: another, from one structure to another Post-event Options a thorough or dramatic change in form or Properties: appearance [Oxford Dictionary] The content of the record is not Ontological View changed. The only thing that is Class: Data Conversion changed is the appearance of the Sub-class: Translate data.
Translat Definition: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition e (v) Definition of Translate: As part of trusted Process: record management, conversion of Record Entry content from one coding/ classification Post-event Options system to another or from one human Properties: language to another The content of the record is not Ontological View changed. The only thing that is Class: Data Conversion changed is the language or coding Sub-class: Translate system used to communicate the information. 4. Attest Lifecycle Event
d. Description: As part of trusted record management, this is the record lifecycle event describing when an agent performs a formal validation on the contents of data objects.
Attest (v) Definition: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition formal validation by one or more identified stakeholder Process: that the contents of data objects is true and accurate Result may be linked Properties: [based on definition of to or merged with the validation from PMBOK] entity in accordance with Ontological View organizational policy. Class: Update Post-event Options Sub-class: Attest See table 1.
Validate (v): Definitions: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition to confirm that the contents of data objects meet the needs of Data object has been Properties: identified stakeholders (i.e., originated, received, or healthcare providers, patients). retained. Boolean state on the entity. Contrast with verify. [Derived Process: from PMBOK definition of Can be performed on an object which validation.] 1. An object is selected for is in either an interim state or Ontological View: verification. permanently retained state. Class: Object State Object parameters are Sub-class: Validate 2. Uses externally imposed criteria. compared with external Returns a result that shows success or specifications. failure of validation. 3. Results are returned that if comparison is successful, object(s) is validated, else Note: How the validation attribute is bound validation failed. to the object is a business decision. Post-event Options
See table 1. 5. Access or View Lifecycle Event
e. Description: As part of trusted record management, this is the record lifecycle event describing when an agent is obtaining data from one or more record entries.
Access (v) Definition: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition To be able to obtain, inspect, review, and/or The agent must have, at a minimum, read make use of data or permissions on the Properties: information system. Process: [CPRI (modified)] Includes all levels of access. Ontological View Post-event Options Class: Record Management Sub-class: Access See table 1
View (v) Definition: to look at Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition attentively or to inspect [Merriam-Webster, modified] The agent must have Ontological View read permissions on Class: Access the system. Properties: Process: Sub-class: View Post-event Options Data is accessed on a “read only” basis. See table 1 Is a type of “access.” 6. Report (Output) Lifecycle Event
f. Description: As part of trusted record management, this is the record lifecycle event describing when an agent produces and delivers the content of a record in the form expected by the recipient. Note: For the purposes of the Report (Output) Life Cycle Event, report and output are considered synonymous.
Output (v) Definition: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition to produce and deliver Record Entry content in the form and The system or device For the purposes of the EHR Lifecycle manner expected by a viewer containing or Events, output and record are used or recipient (e.g., printout, generating the data visual rendering, tagged or must have the synonymously. However, “output” can also delimited data stream) capability to send be viewed as the more general case where Ontological View that data to an there can be different types of outputs, with Class: Record Management outside system or record being one. device. Sub-class: Output Process: Properties: Post-event Options See table 1. Report (v) Definition: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition to make a written record or summary of The system or device [Merriam-Webster] For the purposes of the EHR Lifecycle Events, containing or output and record are used synonymously. Ontological View generating the data Class: Output must have the However, “output” can also be viewed as the capability to send that Sub-class: Report more general case where there can be different data to an outside types of outputs, with record being one. system or device. Process: Properties: Post-event Options See table 1.
7. Disclose Lifecycle Event
g. Description: As part of trusted record management, this is the record lifecycle event describing when an agent releases, transfers, provisions access to, or divulges in any other manner, information to third parties within or outside the healthcare provider organization from an individual’s health record, with or without the consent of the individual to whom the record pertains.
Disclose (v) Definition: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition To release, transfer, provision access to, or divulge in any The owner of the data other manner, information to has consented to its third parties within or outside disclosure. Properties: the healthcare provider Process: organization from an individual’s health record, with Doesn’t change the content of the System creates a or without the consent of the report which data. individual to whom the record conforms with May be limited and controlled by pertains. (Derived from HIPAA privacy policies. and CPRI definitions of security and privacy labels. “disclosure of health Report is sent to the information”) designated recipient. Post-event Options Ontological View Class: Privacy Considerations See table 1. Sub-class: Disclose 8. Transmit Lifecycle Event
h. Description: As part of trusted record management, this is the record lifecycle event describing when an agent sends EHR content from one system (EHR/PHR/other) to another.
Transmit (v) Definition: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition to sends Record Entry content from one (EHR/PHR/other) Communications system to another. channels between sender and receiver Properties: Ontological View are open and available. Data may or may not be encrypted. Class: A trust relationship Sub-class: Transmit exists between sender and receiver. Process:
The system sends a message to a trusted receiver. Post-event Options
See table 1 9. Receive and Retain Lifecycle Event
i. Description: As part of trusted record management, this is the record lifecycle event describing when an agent both acquires data that exist elsewhere as potential content for an EHR record (receive) and enters that data into storage considered permanent (retain). (See “1. Originate/Retain Lifecycle Event” for the definition of “Retain (v).”)
Receive (v) Definition: Pre-conditions: Extended Definition: To acquire data objects that existed "To Receive" is an activity within EHR Records Management. "To elsewhere for potential inclusion in an 1. Commu Receive" includes the option of an interim state that permits an EHR record. Contrast with Originate. nication intermediate assessment of data objects that existed elsewhere and is s conveyed for consideration for commitment to long-term management. channel The data object existing elsewhere is processed as a message pending s qualifying it as a locally stored object. The intermediate assessment is betwee intended to determine whether to store initially captured data objects n or to destroy them as ephemera or rejected data objects. "To Receive" sender may include the use of volatile memory or other means which offer a Ontological View: and temporary cache or cache-like status for the interim state. Class: Record Management receiver Sub-class: Receive are Properties: open 1. Existing data object from sender is used in a message. and 2. Object received resides exclusively in the receiver’s message space. availabl e Process:
1. Initially the messag e is present ed to receiver . 2. Subseq uently, the original messag e is copied into the recipien t’s messag e space. Post-Activity options
1. Discard original messag e 2. Copy messag e into receiver ’s address space. 10. De-Identify (Anonymize) Lifecycle Event
j. Description: As part of trusted record management, this is the record lifecycle event describing when an agent performs the process of reducing the association between a set of identifying data and the data subject in a way that is not reversible. . Note: For the purposes of the De-identify (Anonymize) Life Cycle Event, de-identify and anonymize are considered synonymous.
De-Identify (v) Definition: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition To reduce the association between a set of identifying An entity exists which contains data and the data subject. personally Properties: [ISO 25237 Health identifiable information (PII) Informatics - Not reversible. Pseudonymisation] Process: Ontological View PII is removed and all Class: Privacy Considerations association with the Sub-class: De-identify rest of the information in the record is destroyed. Post-event Options
See table 1. 11. Pseudonymize Lifecycle Event
k. Description: As part of trusted record management, this is the record lifecycle event describing when an agent performs de-identification which may be reversible.
Pseudonimiz Definition: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition e (v) Pseudonymization is a sub-class of de- identification which “can be performed with or An entity exists which contains without the possibility of re-identifying the personally Properties: subject of the data (reversible or irreversible” identifiable (Taken from the body of ISO 25237, section information (PII) Process: May be reversible based on 5.1.2.) organizational policy. Ontological View PII is made Class: Privacy Considerations inaccessible and the Sub-class: Pseudonymize association between PII and the rest of the data in the record is removed. Post-event Options
See table 1. 12. Re-Identify Lifecycle Event
l. Description: As part of trusted record management, this is the record lifecycle event describing when an agent restores individual identity in Record Entry content, usually from a previously pseudonymized record, that allows the identification of the source of the information or the information subject.
Re-Identify (v) Definition: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition To restore individual identity in Record Entry content that The entity has This affects privacy concerns around allows the identification of the undergone possible disclosure of PII. source of the information or pseudonymization. the information subject Process: [HL7 Version 3 Standard: Properties: Security and Privacy Personally Ontology, Release 1, modified] identifiable Reverses pseudonimization Ontological View information (PII) is Class: Privacy Considerations restored to the record. Sub-class: Re-Identify Post-event Options
See table 1. 13. Extract Lifecycle Event
m. Description: As part of trusted record management, this is the record lifecycle event describing when an agent pulls out a set of health data or record content from a larger volume of data using explicit criteria.
Extract (v) Definition: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition To pull out a set of health data/record content from a Source entity is larger volume of data using identified explicit criteria. Process: Properties:
Ontological View A portion of the Content of the source entity is not Class: Update source entity is copied and used to affected. Sub-class: Extract create a new entity or May result in a new entity. added to an existing May result in an existing entity being entity. updated. Post-event Options
See table 1. 14. Archive Lifecycle Event
n. Description: As part of trusted record management, this is the record lifecycle event describing when an agent moves the contents of a data object to long-term storage.
Archive (v) Definition: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition 1)Move (the content of) an object to long term storage. An archive system (HL7 RBAC) must exist. 2) To STORE data by moving Process: Properties: the data to long-term storage media and deleting or purging Post-event Options data on the original online Delete or purge the original data from the storage, according to scope of See table 1. EHR system. practice, organizational policy, Keep the original data on the EHR system. and/or jurisdictional law. (HL7 EHR Functional Model) Ontological View 15. Restore Lifecycle Event
o. Description: As part of trusted record management, this is the record lifecycle event describing when an agent recreates Record Entries and their content from a previously created archive artifact.
Restore (v) Definition: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition as part of trusted record management, to recreate An entity has been Record Entries and their rendered content from a previously inaccessible but not Properties: created archive artifact destroyed. Backups and/or (as recover): to restore an Entity content is returned to the information system back to an archived copies of the entity must exist. most recent state available, which error-free and secure state may or may not be the same state it from which normal operation Process: can resume was in at the time it became [HL7 Security Services Entity is made inaccessible. Framework] accessible. Post-event Options to produce another object with the same content as one See table 1. previously backed up (i.e., recreates a readily usable copy) [HL7 Version 3 Standard: Security and Privacy Ontology, Release 1] Ontological View Class: Data Recovery Sub-class: Restore 16. Destroy or Delete Lifecycle Event
p. Description: As part of trusted record management, this is the record lifecycle event describing when an agent either permanently erases data from the system (destroy) or just makes the data inaccessible to the application by removing the information about an object from memory or storage (delete).
Destroy (v) Definition: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition a method of sanitization that renders target data recovery An entity exists infeasible using state of the Process: art laboratory techniques and results in the subsequent Properties: The entity is inability to use the media for completely removed storage of data 1. This activity isn’t reversible. Once and rendered [NIST SP 800-88, Guidelines inaccessible in a way data has been destroyed, it can’t be for Media Sanitization] that is not reversible. recovered. Post-event Options Ontological View Class: Record Management None Sub-class: Destroy
Delete (v) Definition: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition 1) Fundamental operation in an Information System (IS) An entity exists that results only in the Process: Properties: removal of information The entity is about an object from rendered 1. This activity could be reversible. The memory or storage. [HL7 inaccessible through data may be recovered. RBAC] logical or physical processes. 2. May be done through a change in the 2) To REMOVE data by Post-event Options “Active” state or through physical making it inaccessible to the removal of the entity from memory application. [HL7 EHR FM] Restoration or storage. Ontological View Re-activation Class: Record Management Sub-class: Delete 17. Deprecate Lifecycle Event
q. Description: As part of trusted record management, this is the record lifecycle event describing when an agent designates data or record content as obsolete, erroneous or untrustworthy in order to warn against its use in the future.
Deprecat Definition: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition e (v) To designate data/record content as obsolete, erroneous or untrustworthy to warn against its use Deprecate state on A deprecated record can be in an active in the future so that it may be phased out. entity is “No,” “Off,” state, meaning it is available for use but not or “False.” Ontological View recommended. Class: Object State Process: Sub-class: Deprecate (Boolean) The Deprecate state Properties: on the entity is changed to “Yes,” Boolean state on the entity. “On,” or “True.” Deprecation does not change the Post-event Options entity content, only its state. See table 1 Event when Deprecate state is on, Activate state may be off or on, depending on organizational policy. 18. Re-Activate Lifecycle Event
r. Description: As part of trusted record management, this is the record lifecycle event describing when an agent recreates previously deleted or deprecated record entries and restores them to full active status.
Re-Activate (v) Definition: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition To recreate Record Entries and their content from a Activate state on The “Active” state of a record can be used by previous state of deletion or entity is “No,” “Off,” deprecation and restore full or “False.” itself or in conjunction with other states to status to Record Entries Process: describe a variety of record states. previously deprecated The Activate state on A record with an “Active” state of “False” could Ontological View the entity is changed be used to indicate a record that is in an interim to “Yes,” “On,” or state and that needs to undergo additional Class: Object State “True.” Sub-class: Activate (Boolean) Post-event Options actions, such as verification or validation, prior to being activated. Once activated, the record is See table 1 then considered to be a permanent part of the system and is available for use.
Another example is that a deprecated record can still be active, meaning it is available for use but not recommended.
Properties:
Boolean state on entity Recorded as a state change where “Activate” is “Yes,” “On,” or “True.” 19. Merge Lifecycle Event
s. Description: As part of trusted record management, this is the record lifecycle event describing when an agent performs an activity which combines the content of two or more Record Entries, resulting in a single record entry.
Merge (v) Definition: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition To combine the content of two or more Record Entries, Two or more entities resulting in a single record are identified for entry merging. Properties: Ontological View Process: Class: Update 1. This activity may be reversible The content of the Sub-class: Merge identified entities is depending on organizational policy. combined. 2. This activity results in a new entity. Post-event Options 3. The original entities may or may not be retained. See table 1. 20. Unmerge Lifecycle Event
t. Description: As part of trusted record management, this is the record lifecycle event describing when an agent performs an activity which reverses a previously executed merge operation.
Unmerge (v) Definition: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition To perform an operation that reverses a previously Entity is the result of executed merge operation a merge of two or (see merge) more entities Properties: Ontological View Process: Class: Update The content of all entities involved is Entities are restored Sub-class: Unmerge to their previously restored to their pre-merged state. unmerged states. Post-event Options
See table 1. 21. Link Lifecycle Event
u. Description: As part of trusted record management, this is the record lifecycle event describing when an agent performs an activity which connects two or more separate record entries so that access or use of one record entry means equal access to and ability to use all of the connected record entries.
Link (v) Definition: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition To perform an operation that connects two or more Two or more entities separate Record Entries so are identified which that access or use of one need to be linked. Properties: necessarily means access or Process: use of all the connected Record Entries 1. This activity is reversible. A link table is created Ontological View which records the 2. This activity doesn’t change the Class: Update association between content of the linked entities. the identified entities. Sub-class: Link Post-event Options:
See table 1. 22. Unlink Lifecycle Event
v. Description: As part of trusted record management, this is the record lifecycle event describing when an agent performs an activity which undoes any linked record entries, rendering them separate again.
Unlink (v) Definition: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition To undo an operation that previously connected two or Entity is linked with more Record Entries, another entity. rendering them separate again Process: (see link) Properties: Ontological View The link table which The content of the entities being Class: Update recorded the link between entities is unlinked doesn’t change, only the Sub-class: Unlink deleted. link is deleted. Post-event Options
See table 1. 23. Add Legal Hold Lifecycle Event
w. Description: As part of trusted record management, this is the record lifecycle event describing when an agent places a tag or otherwise indicates special access management and suspension of destruction for record entries deemed relevant to a law suit, are reasonably anticipated to be relevant, or are consistent with organization policy under the legal doctrine of “duty to preserve.”
Add Legal Hold (v) Definition: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition To perform an operation that tags or otherwise cues special Legal Hold state on access management and entity is “No,” “Off,” destruction suspension for or “False.” Properties: Record Entries deemed Process: relevant, consistent with organization policy under the The legal hold state Boolean state on entity legal doctrine of “duty to on the entity is Recorded as a state change where “Legal preserve” changed to “Yes,” Hold” is “Yes,” “On,” or “True.” “On,” or “True.” a temporary suspension of a Post-event Options company’s document retention destruction policies See table 1 for the documents that may be relevant to a law suit or that are reasonably anticipated to be relevant [http://definitions.uslegal.com/ l/litigation-hold/] Ontological View Class: Object State Sub-class: Legal Hold (Boolean) 24. Remove Legal Hold Lifecycle Event
x. Description: As part of trusted record management, this is the record lifecycle event describing when an agent removes a tag or other cues for special access management and suspension of destruction for record entries deemed relevant to a law suit, are reasonably anticipated to be relevant, or are consistent with organization policy under the legal doctrine of “duty to preserve.”
Remove Legal Hold (v) Definition: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition As part of trusted record management, to perform an Legal Hold state on operation that untags or entity is “Yes,” “On,” otherwise removes cues for or “True.” Properties: special access management Process: and destruction suspension for Record Entries as Boolean state on entity The legal hold state organization policy had on the entity is Recorded as a state change where required under the legal changed to “No,” “Legal Hold” is “No,” “Off,” or “False.” doctrine of “duty to preserve” “Off,” or “False.” Post-event Options provide notification to the records owners of the release of data and that the company See table 1 will resume normal data retention and destruction processes Ontological View Class: Object State Sub-class: Legal Hold (Boolean) 25. Verify Lifecycle Event
y. Description: As part of trusted record management, this is the record lifecycle event describing when an agent evaluates the compliance of data objects with regulations, requirements, specifications, or other internally imposed conditions based on organizational policy.
Verify (v) Definitions: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition
1. To evaluate the Data object has been Properties: compliance of data objects originated/received and/or with regulations, retained. 1. Can be performed on an interim or requirements, specifications, Process: or other internally imposed retained object. conditions based on 1. An object is selected for 2. Uses internally imposed criteria. organizational policy. verification. 3. Returns a result that shows success or Contrast with validate. 2. Object parameters are failure of verification. This can be 2. To affirm the compliance compared with internal recorded as a state change on the of data or data objects with specifications. specified trust qualifications. object. A result is returned that, if Contrast with To Attest 3. comparison is successful, Ontological View object(s) is verified, else Note: How the verification attribute is bound verification failed. Class: Object state to the object is a business decision. Sub-class: Verify Post-event Options See Table 1. 26. Encrypt Lifecycle Event
z. Description: As part of trusted record management, this is the record lifecycle event describing when an agent performs an activity which renders information unreadable by algorithmically transforming plain text into ciphertext.
Encrypt (v) Definition: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition To encode data/record content in a cipher. An entity exists which may or may generic term encompassing not be encrypted. Properties: encipher and encode Process: [NSTISSI No. 4009, National Information Systems Security 1. Is reversible. Entity is put through (INFOSEC) Glossary] an algorithm which 2. Can be repeated multiple times transforms it into without reversing. to render information ciphertext. unreadable by algorithmically Post-event Options transforming plaintext into ciphertext [HL7 Version 3 Standard: See Table 1. Security and Privacy Ontology, Release 1]
convert (information or data) into a cipher or code, especially to prevent unauthorized access [Oxford Dictionary]
Ontological View Class: Transform Sub-class: Encrypt
27. Decrypt Lifecycle Event
aa. Description: As part of trusted record management, this is the record lifecycle event describing when an agent performs an activity which renders information readable by algorithmically transforming ciphertext into plaintext. [ENCRYPT concept in HL7 ActCode code system, HL7 v3 ObligationPolicy value set, modified]
Decrypt (v) Definition: Pre-Conditions: Extended Definition To decode data/record content from a cipher Entity must be encrypted. Render information readable Process: by algorithmically Properties: transforming ciphertext into The encrypted entity plaintext undergoes a process [ENCRYPT concept in HL7 which restores it to ActCode code system, HL7 v3 plain text. ObligationPolicy value set, Post-event Options modified] Ontological View See table 1. Class: Transform Sub-class: Decrypt
28. CRUDE Definitions Create: Fundamental operation in an IS that results only in the act of bringing an object into existence. Read: Fundamental operation in an IS that results only in the flow of information about an object to a subject. Update: Fundamental operation in an IS that results only in the revision or alteration of an object. Delete: Fundamental operation in an IS that results only in the removal of information about an object from memory or storage. Execute: Fundamental operation in an IS that results only in initiating performance of a single or set of programs. 29. Other Definitions
Address space: A defined range of discrete addresses, each of which may correspond to a network host, peripheral device, disk sector, a memory cell or other logical or physical entity.
Cache (in computing): A collection of data duplicating original values stored elsewhere on a computer (from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cache_%28computing%29 ) o CPU cache, a small area of fast memory used by the central processing unit o Disk buffer, the small amount of buffer memory present on a hard drive o Page cache, the cache of disk pages kept by the operating systems, stored in unused main memory o Web cache, a mechanism for the temporary storage of web documents to increase performance o DNS cache, a server in the domain name system which stores queried results for a period of time o P2P caching, a technique used to reduce bandwidth costs for content on peer-to-peer networks o Database caching, a mechanism used to cache database content in multi-tier applications Agent: An agent ◊ is something that bears some form of responsibility for an activity taking place, for the existence of an entity, or for another agent's activity. (http://www.w3.org/TR/prov-dm/ Section 5.3.1 Agent) Activity: An activity is something that occurs over a period of time and acts upon or with entities; it may include consuming, processing, transforming, modifying, relocating, using, or generating entities (http://www.w3.org/TR/prov-dm/ Section 2.1.1 Entity and Activity) Entity: An entity is a physical, digital, conceptual, or other kind of thing with some fixed aspects; entities may be real or imaginary (http://www.w3.org/TR/prov-dm/ Section 2.1.1 Entity and Activity) Template: A preset format used as a starting point or guide for a particular application so that the format does not have to be recreated each time it is used. (Derived from http://www.thefreedictionary.com/template)