A-Level Physical Geography Revision : Rivers, floods and management March Holiday 2009
This table summarises the content of the module and what you should be able to achieve by the end of it. You need to tick if you have the class work in your folder, completed revision notes (over the easter holidays) and then completed at least two revision sessions for each topic prior to your mocks.
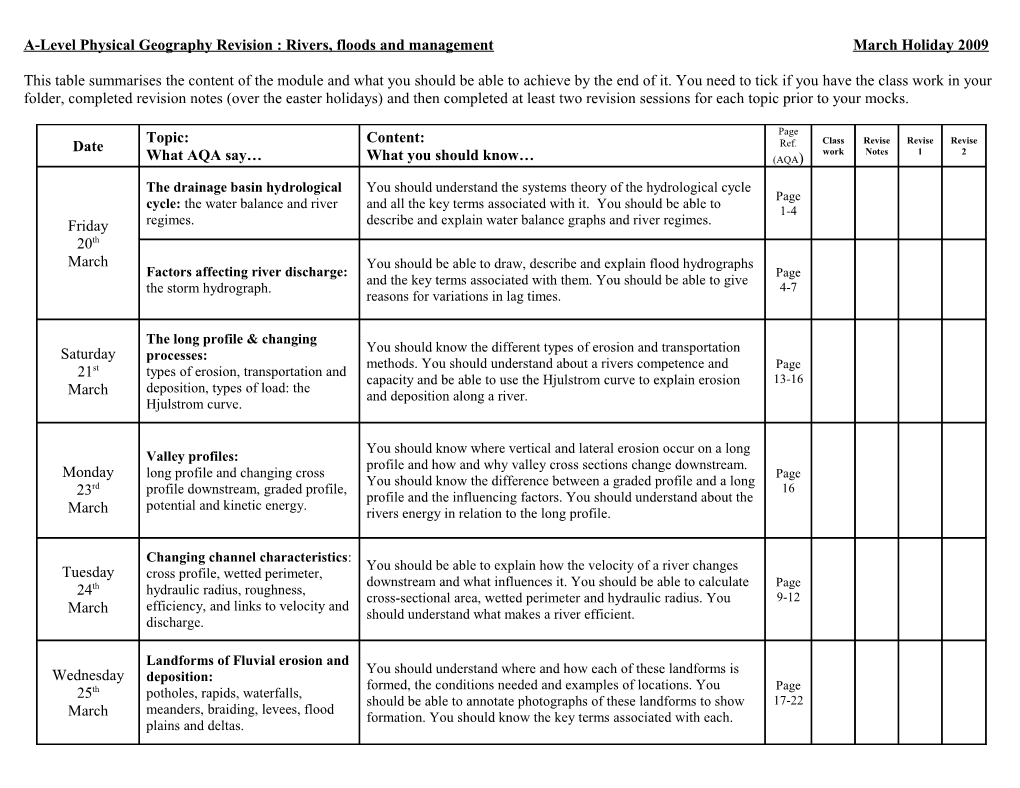
Page Topic: Content: Ref. Class Revise Revise Revise Date work Notes 1 2 What AQA say… What you should know… (AQA)
The drainage basin hydrological You should understand the systems theory of the hydrological cycle Page cycle: the water balance and river and all the key terms associated with it. You should be able to 1-4 Friday regimes. describe and explain water balance graphs and river regimes. 20th March You should be able to draw, describe and explain flood hydrographs Factors affecting river discharge: Page and the key terms associated with them. You should be able to give the storm hydrograph. 4-7 reasons for variations in lag times.
The long profile & changing You should know the different types of erosion and transportation Saturday processes: methods. You should understand about a rivers competence and Page 21st types of erosion, transportation and capacity and be able to use the Hjulstrom curve to explain erosion 13-16 deposition, types of load: the March and deposition along a river. Hjulstrom curve.
You should know where vertical and lateral erosion occur on a long Valley profiles: profile and how and why valley cross sections change downstream. Monday long profile and changing cross Page You should know the difference between a graded profile and a long rd profile downstream, graded profile, 16 23 profile and the influencing factors. You should understand about the potential and kinetic energy. March rivers energy in relation to the long profile.
Changing channel characteristics: You should be able to explain how the velocity of a river changes Tuesday cross profile, wetted perimeter, downstream and what influences it. You should be able to calculate Page 24th hydraulic radius, roughness, cross-sectional area, wetted perimeter and hydraulic radius. You 9-12 efficiency, and links to velocity and March should understand what makes a river efficient. discharge.
Landforms of Fluvial erosion and You should understand where and how each of these landforms is Wednesday deposition: formed, the conditions needed and examples of locations. You Page 25th potholes, rapids, waterfalls, should be able to annotate photographs of these landforms to show 17-22 meanders, braiding, levees, flood March formation. You should know the key terms associated with each. plains and deltas. Page Topic: Content: Ref. Class Revise Revise Revise Date work Notes 1 2 What AQA say… What you should know… (AQA)
Thursday Process and impact of You should know the causes of rejuvenation and how it changes the rejuvenation: valley long profile and cross profile. You should be able to identify, Page 26th knick points, waterfalls, river describe and explain landforms which have occurred as a result of 22-23 March terraces and incised meanders. rejuvenation.
Physical and human causes of flooding: You should understand that flooding can be caused by both human location of areas of high risk in a and physical factors and be able to give examples from case studies Page2 Friday MEDC and a LEDC. Flood in a LEDC and MEDC. You should understand the factors which put 4-27 27th magnitude, frequency and risk a country at a high risk from flooding and their frequency. analysis. March
Impact of flooding: You should know the impact of flooding in two different areas. Page two case studies of recent events Comparing short and long term impacts, positive and negative 28-29 from contrasting areas of the world. effects and social, environmental and economic ones.
Flood management strategies: You should understand how people seek to reduce the effects of Hard engineering – dams, flooding on humans through both hard and soft engineering straightening, building up of levees, strategies and what influences their choice. You should be able to Have not diversion spillways and Soft give examples of places where a range of strategies have been used Page completed engineering – forecasts and and the reasons for this. You should be able to compare management 30-40 yet. warnings, land use management on strategies in different places. You should understand that different flood plain, wetland and river bank groups in society hold conflicting views on how to manage flood conservation and river restoration. risk.
Class Revise Revise Revise Main Case Studies (lots of small examples during the course to be revised as well). work Notes 1 2 Bangladesh – Bramaputra, Causes and impacts of flooding in 1998 and management LEDC 41-45 Meghna and Ganges of flood risk since. Causes, impacts and responses of flooding in February LEDC Mozambique - Limpopo - 2000. MEDC Brunei – Sungai Gadong!! Casues and impacts of flooding in January 2009. - MEDC USA – Mississippi Comparison of management strategies for each drainage basin. Causes and impacts covered to understand Geo Factsheet LEDC Egypt - Nile processes. A-Level Physical Geography Revision : Coastal Environments March Holiday 2009
This table summarises the content of the module and what you should be able to achieve by the end of it. You need to tick if you have the class work in your folder, completed revision notes (over the easter holidays) and then completed at least two revision sessions for each topic prior to your mocks.
Page Topic: Content: Ref. Class Revise Revise Revise Date work Notes 1 2 What AQA say… What you should know… (AQA)
You should know the characteristics of different wave types, what The coastal system: causes them, how they influence beaches and what happens to them. constructive and destructive waves Pages You should know about different types of tides and how these affect tides, sediment sources and cells 82-86 the coastline. You should be able to explain about sediment sources wave refraction. Saturday and cells and their purpose. 14th March Coastal processes: You should be able to explain the difference between sub-aerial and marine erosion, transportation and marine erosion and all their different types. You should know the Pages deposition, land based sub-aerial types of mass movement and how the geology (rock slope and type) 87-89 weathering, mass movement and affects it. You should understand about longshore (littoral) drift and cliff structure. when and why deposition occurs along the coastline.
Case study of coastal erosion: Here we studied West Bay in Dorset, you should have a case study specific physical and human card on this. We looked at the specific reasons why this place is In file cause(s) and its physical and socio- Sunday eroding. Do not be afraid to use others examples that you of as well. economic effects 15th March Landforms of erosion: headlands and bays, blow holes Pages arches and stacks, cliffs and wave You need to be able to explain where and why each of these 92-94 cut platforms. landforms occurs and the conditions needed for each. You should be able to name examples of each along the Dorset coastline and be Landforms of deposition: able to annotate photographs explaining their formation. You should beaches and associated features, Pages also know about plant succession on sand dune ecosystems. berms, runnels and cusps, spits and 95-98 bars, dunes and salt marshes Monday 16th Sea level change: March eustatic and isostatic change. You need to be able to discuss the difference between the different Pages Coastlines of submergence and types of sea level change and the features that result. Rias, Fjords, 106 emergence and associated raised beaches etc. You should understand by using examples of to landforms. Impact of present and Tuvalu and the Maldives the impacts of sea rise. 108 predicted sea level increase. Page Topic: Content: Ref. Class Revise Revise Revise Date work Notes 1 2 What AQA say… What you should know… (AQA)
Tuesday Case study of coastal flooding: You should be able to compare the storm surge of 1953, that resulted Pages specific physical and human in coastal flooding, with that from Hurricane Katrina and New 109 17th cause(s) and its physical and socio Orleans. You should know the effects and be able to categorise to March – economic effects. them. You should know what the purpose of the Thames barrier is. 112
Coastal protection objectives and You should know the advantages and disadvantages of each strategy management strategies: and be able to annotate photographs showing these. You should hard engineering: sea walls, Wednesday name examples of where they have been used; Hurst Castle Spit, Pages revetments, rip rap, gabions, 113 18th Barton on Sea. You should know the difference between cliff foot groynes and barrages. Soft to and cliff face strategies and hard and soft engineering. You should March engineering: beach nourishment, 118 understand about land use at the coast and the conflicts strategies dune regeneration, marsh creation, may cause. You should also understand about cost/benefit ratios. land use/activity management. Case studies of two contrasting areas: You should know in details your case studies for Tahuna Beach and one where hard engineering has Brighton and Hove and understand why they are so different. How Thursday been dominant, one where soft successful are they, what are the cost/benefits of each scheme, what In 19th March engineering has been dominant. To are their key features. Can you compare and contrast them? Is it file. investigate issues relating to costs possible to manage the coastline sustainably: do you have examples? and benefits of schemes, including How can costs be minimized? the potential for sustainability. Class Revise Revise Revise Main Case Studies (lots of small examples during the course to be revised as well). work Notes 1 2 Tahuna Beach, New An example of soft engineering and sustainable coastal MEDC In File Zealand management. Brighton and Hove, An example of hard engineering and unsustainable MEDC In File England coastal management strategies. North Sea, England and MEDC Examples of coastal flooding and their impacts. In File New Orleans, USA Hurst Castle Spit and Examples of places experiencing coastal management MEDC In File Barton on Sea, England strategies. MEDC West Bay, Dorset An example of coastal erosion. In FIle