Supplementary content
Behaviour of sartans (hypertension drugs) in wastewater treatment plants and their risk for the aquatic environment
Anne Bayer, Robert Asner, Walter Schüssler, Willi Kopf, Klaus Weiß, Manfred Sengl,
Marion Letzel
Analytical methods
MS-conditions for target analysis (result of automatic optimization by software Analyst 1.5,
Applied Biosystems) are given in Table S1 in detail. Results for direct injection and standard addition method are compared in Table S2.
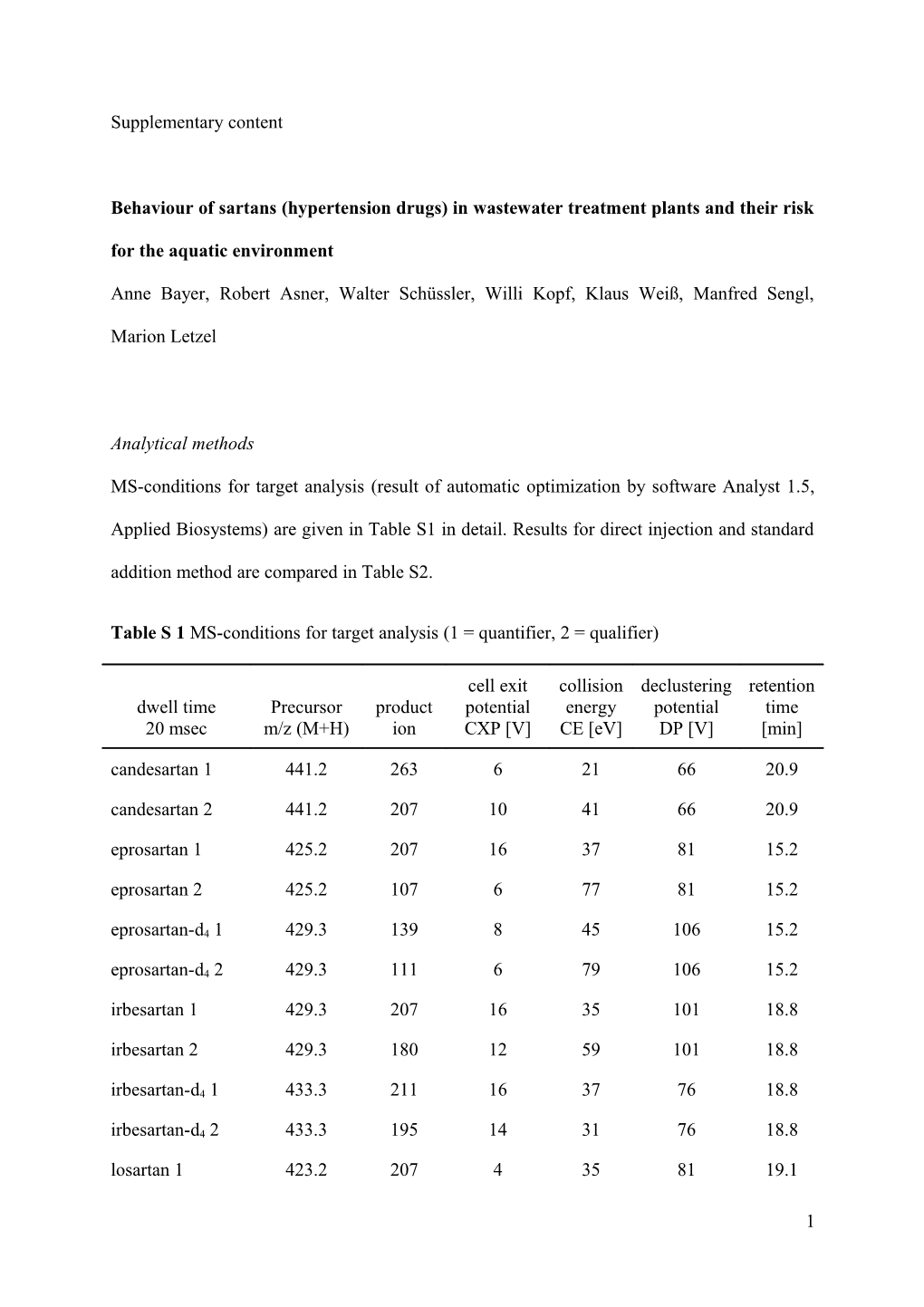
Table S 1 MS-conditions for target analysis (1 = quantifier, 2 = qualifier)
cell exit collision declustering retention dwell time Precursor product potential energy potential time 20 msec m/z (M+H) ion CXP [V] CE [eV] DP [V] [min] candesartan 1 441.2 263 6 21 66 20.9 candesartan 2 441.2 207 10 41 66 20.9 eprosartan 1 425.2 207 16 37 81 15.2 eprosartan 2 425.2 107 6 77 81 15.2 eprosartan-d4 1 429.3 139 8 45 106 15.2 eprosartan-d4 2 429.3 111 6 79 106 15.2 irbesartan 1 429.3 207 16 35 101 18.8 irbesartan 2 429.3 180 12 59 101 18.8 irbesartan-d4 1 433.3 211 16 37 76 18.8 irbesartan-d4 2 433.3 195 14 31 76 18.8 losartan 1 423.2 207 4 35 81 19.1
1 losartan 2 423.2 180 12 57 81 19.1 olmesartan 1 447.3 207 12 39 81 15.2 olmesartan 2 447.3 180 16 57 81 15.2 olmesartan-d4 1 451.3 211 16 41 71 15.2 olmesartan-d4 2 451.3 180 14 85 71 15.2 telmisartan 1 515.3 497 28 51 126 18,5 telmisartan 2 515.3 276 2 67 126 18,5 telmisartan-d3 1 518.3 500 14 49 126 18,5 telmisartan-d3 2 518.3 279 8 73 126 18,5 valsartan 1 436.3 291 16 21 76 20.1 valsartan 2 436.3 306 8 21 76 20.1
Table S 2 Comparison of results for direct injection and standard addition methods
river water [ng L-1] wastewater [ng L-1]
direct standard addition direct standard addition injection method injection method
candesartan 85 73 600 600
eprosartan 42 56 2500 overflow
irbesartan 130 83 1200 1200
losartan <50 <50 400 400
olmesartan 370 350 1700 overflow
telmisartan <50 <50 650 750
valsartan <50 <50 60 <50
2 Monitoring
The different sampling sites of wastewater effluents and rivers in Bavaria, Germany, are described in detail in Table S3 and S4, respectively.
Table S 3 Sampling sites with population equivalents (PE) and a short description of the sewage treatment plants (STP), all with C and N elimination
STP PE Description of the STP
STP A 1,400,000 biological treatment
two-staged biological treatment, downstream sand filter, wastewater STP B 1,000,000 disinfection via UV-radiation between 15th April - 30th September
STP C 430,000 biological treatment, downstream filter
STP D 250,000 biological treatment, downstream sand filter
STP E 125,000 biological treatment
STP F 50,000 biological treatment
Table S 4 Sampling sites with a short characterisation of rivers including the proportion of treated municipal wastewater at average discharge assumed with a greater model
proportion of geographic catchment area average length treated municipal Cartesian River in Germany discharge [km] wastewater at coordinates (UTM) [km²] [m3 s-1] average discharge northing/easting
Ebrach 23 48 <1 7% 5326683/4499475
Regnitz 58 7,500 33 5% 5506049/4431254 site A
Regnitz 51.8 5% 5522519/4423938 site B
Wuerm 35 386 4.7 5% 5349781/4461098
Franconian Rezat site 64 376 0.7 3% 5451777/4419061 A 3 Franconian Rezat site 3% 5450540/4428127 B
Main 524 27,300 225 3% 5526196/4327351
Danube 2857 65,000 1,490 2% 5421027/4501128
Isar site A 259 7,965 22.7 5% 5363390/4483663
Isar site B 175 2% 5404149/4565117
not influenced by Wern 64 602 0.31 5546385/4369505 wastewater
4