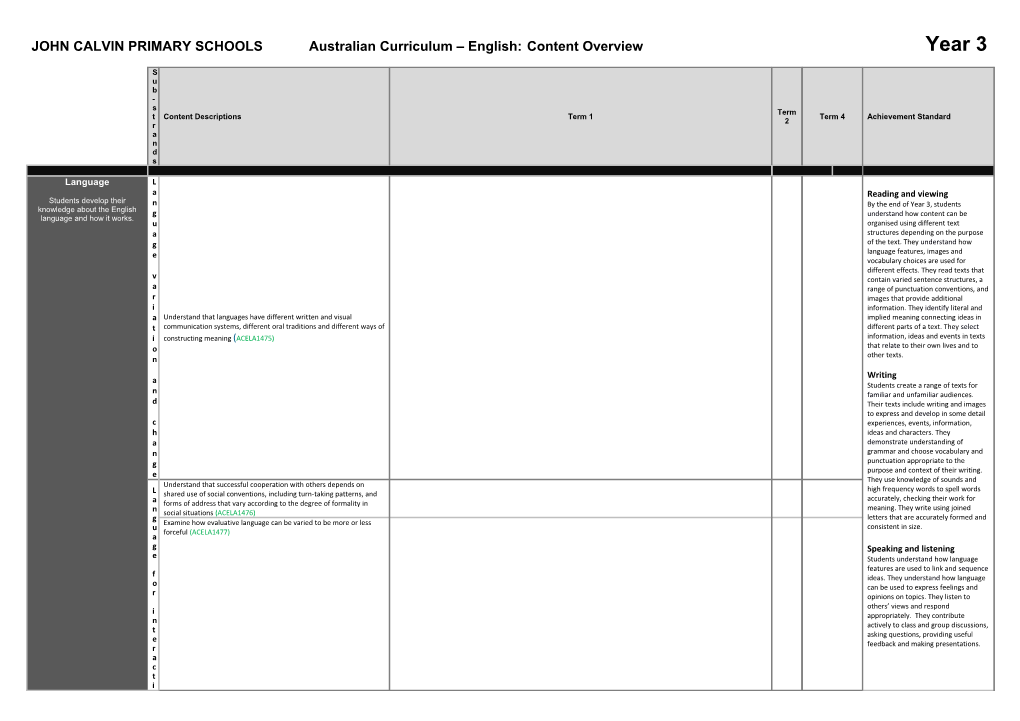
JOHN CALVIN PRIMARY SCHOOLS Australian Curriculum – English: Content Overview Year 3
S u b - s Term t Content Descriptions Term 1 Term 4 Achievement Standard 2 r a n d s
Language L a Reading and viewing Students develop their n By the end of Year 3, students knowledge about the English g understand how content can be language and how it works. u organised using different text a structures depending on the purpose g of the text. They understand how e language features, images and vocabulary choices are used for
different effects. They read texts that v contain varied sentence structures, a a range of punctuation conventions, and r images that provide additional i information. They identify literal and a Understand that languages have different written and visual implied meaning connecting ideas in t communication systems, different oral traditions and different ways of different parts of a text. They select i constructing meaning (ACELA1475) information, ideas and events in texts o that relate to their own lives and to other texts. n
Writing a Students create a range of texts for n familiar and unfamiliar audiences. d Their texts include writing and images to express and develop in some detail c experiences, events, information, h ideas and characters. They a demonstrate understanding of n grammar and choose vocabulary and g punctuation appropriate to the e purpose and context of their writing. They use knowledge of sounds and Understand that successful cooperation with others depends on high frequency words to spell words L shared use of social conventions, including turn-taking patterns, and accurately, checking their work for a forms of address that vary according to the degree of formality in meaning. They write using joined n social situations (ACELA1476) g letters that are accurately formed and Examine how evaluative language can be varied to be more or less u consistent in size. forceful (ACELA1477) a g Speaking and listening e Students understand how language features are used to link and sequence f ideas. They understand how language o can be used to express feelings and r opinions on topics. They listen to
others’ views and respond i appropriately. They contribute n actively to class and group discussions, t asking questions, providing useful e feedback and making presentations. r a c t i o n Understand how different types of texts vary in use of language T choices, depending on their purpose and context (for example, tense e and types of sentences) (ACELA1478) x Understand that paragraphs are a key organisational feature of t written texts (ACELA1479) Know that word contractions are a feature of informal language and s that apostrophes of contraction are used to signal missing letters t (ACELA1480) r u c t u r e a n d Identify the features of online texts that enhance navigation o (ACELA1790) r g a n i s a t i o n Understand that a clause is a unit of grammar usually containing a E subject and a verb and that these need to be in agreement x p (ACELA1481) r Understand that verbs represent different processes, for e example doing, thinking, saying, and relating and that these processes s are anchored in time through tense (ACELA1482) s Identify the effect on audiences of techniques, for example shot size, i vertical camera angle and layout in picture books, advertisements and n film segments (ACELA1483) g Learn extended and technical vocabulary and ways of expressing opinion including modal verbs and adverbs (ACELA1484) a Understand how to use sound–letter relationships and knowledge of n spelling rules, compound words, prefixes, suffixes, morphemes and d less common letter combinations, for example ‘tion’ (ACELA1485)
Recognise high–frequency sight words (ACELA1486) d e v e l o p i n g i d e a s
Literacy T e Students develop the knowledge x and skills to interpret and create t spoken, written, visual & multimodal texts. s
i n Identify the point of view in a text and suggest alternative points of view (ACELY1675) c o n t e x t I Listen to and contribute to conversations and discussions to share n information and ideas and negotiate in collaborative situations t (ACELY1676) e Use interaction skills, including active listening behaviours and communicate in a clear, coherent manner using a variety of everyday r and learned vocabulary and appropriate tone, pace, pitch and volume a (ACELY1792) c t i n g
w i t Plan and deliver short presentations, providing some key details in h logical sequence (ACELY1677)
o t h e r s I Identify the audience and purpose of imaginative, informative and n persuasive texts (ACELY1678) t Read an increasing range of different types of texts by combining e contextual, semantic, grammatical and phonic knowledge, using text processing strategies, for example monitoring, predicting, confirming, r rereading, reading on and self-correcting (ACELY1679) p Use comprehension strategies to build literal and inferred meaning r and begin to evaluate texts by drawing on a growing knowledge of e context, text structures and language features (ACELY1680) t i n g ,
a n a l y s i n g
a n d
C Plan, draft and publish imaginative, informative and persuasive texts r demonstrating increasing control over text structures and language e features and selecting print, and multimodal elements appropriate to a the audience and purpose (ACELY1682) t Reread and edit texts for meaning, appropriate structure, grammatical i choices and punctuation (ACELY1683) n Write using joined letters that are clearly formed and consistent in g size (ACELY1684)
t Use software including word processing programs with growing speed e and efficiency to construct and edit texts featuring visual, print and x audio elements (ACELY1685) t s
Literature L i Students understand, respond t to, analyse, evaluate, and create e literature. r a t u r e Discuss texts in which characters, events and settings are portrayed in a different ways, and speculate on the authors’ reasons (ACELT1594) n d
c o n t e x t R Draw connections between personal experiences and the worlds of e texts, and share responses with others (ACELT1596) s Develop criteria for establishing personal preferences for literature p (ACELT1598) o n d i n g t o l E Discuss how language is used to describe the settings in texts, and x explore how the settings shape the events and influence the mood of a the narrative (ACELT1599) m i n i n g l Discuss the nature and effects of some language devices used to i enhance meaning and shape the reader’s reaction, including rhythm t and onomatopoeia in poetry and prose (ACELT1600) e r a t u r e C Create imaginative texts based on characters, settings and events r from students’ own and other cultures using visual features, for e example perspective, distance and angle (ACELT1601) a t i n g l Create texts that adapt language features and patterns encountered i in literary texts, for example characterisation, rhyme, rhythm, mood, t music, sound effects and dialogue (ACELT1791) e r a t u r e Australian Curriculum – English Content Map: Term 1 Term 2 Term 3 Term 4 Year 3 Reading & Viewing
Understandings, Elements Content and Achievement Standard Strategies
Non-fiction texts Fiction texts Electronic devices Reading and viewing Year 3 – Discuss features of non-fiction Discuss features of fiction texts Use electronic devices to: By the end of Year 3, students understand how content can be organised using different text structures depending on texts including including: the purpose of the text. They understand how language features, images and vocabulary choices are used for different Reading effects. They read texts that contain varied sentence structures, a range of punctuation conventions, and images that - Navigate websites and apps provide additional information. They identify literal and implied meaning connecting ideas in different parts of a text. - Various types of captions (eg - Compare page layout for a particular purpose using and They select information, ideas and events in texts that relate to their own lives and to other texts. images and diagrams) between front cover and a variety of techniques (eg buttons, bars, scrolling, - Different kinds of contents inside pages Viewing enhancing, minimizing, Receptive (listening, reading & viewing) pages - Compare the effect of enlarging text) By the end of Year 3, students understand how content can be organised using different text structures depending - Purpose of indexes (including differing text sizes on the - Understand how hyperlinks page numbering) page layout (eg speech on the purpose of the text. They understand how language features, images and vocabulary choices are used for bubbles in images, larger font work and use them to move different effects. They read texts that contain varied sentence structures, a range of punctuation conventions, and - Purpose and structure of for expressive words, from one area of a website to glossary (including capitalisation for expression) another to access more images that provide additional information. They identify literal and implied meaning connecting ideas in different alphabetical order) information Concepts of Print & - Discuss structural devices parts of a text. They select information, ideas and events in texts that relate to their own lives and to other texts. - Headings (including how to Screen such as chapters and their - Compare and understand the They listen to others’ views and respond appropriately. write a short, meaningful purpose (eg show how design of various screen heading to summarise chapters signal a break in layouts and site maps information) time between one chapter (ACELA1790) - Different types of page layout and the next) and how they appeal to an - Compare illustrations audience (eg comparing (consider POV, camera angles layouts and discussing what and shot size) layout is more appealing) (ACELA1483) - Identifying paragraphs and how information is grouped into categories (ACELA1479) (ACELA1483) Phonological Word Attack and Decoding Skills Awareness Morphemes: Inflectional General word attack and Suffixes Prefixes endings decoding skills - Adding ‘y’ {for adjectives} - ‘mis’ as in Apply morpheme knowledge - Rapid recall of high as in ‘grassy’ ‘misunderstood’, ’mistake’ to: frequency sight words - ‘ful’ {meaning: ‘to be - ‘up’ as in ‘upward’, - Rapid decoding of characterized by’} as in ’upstairs’ Single syllable words (eg - diagraphs, trigraphs and ‘shameful’, ‘thoughtful’, - ‘un’ as in ‘unwind’, changing the word jumped to ‘beautiful’ quad-graphs ‘unconcerned’, ‘undo’ jumping) - ‘ful’ {meaning ‘to be able - Use knowledge of - ‘re’ as in ‘reconsider’, - Plurals including to’} as in ‘wakeful’, ‘harmful’ segmenting and blending to ‘redo’ conventional plurals (eg decode unfamiliar words - ‘ful’ {meaning ‘to show (ACELA1485) changing bat/bats or mix/ Syllabification of words measurement‘} as in mixes) and non-conventional - ‘spoonful’, ‘cupful’ plurals (mouse/mice, (when using syllabification for sheep/sheep, fish/fish). decoding, teach students - ‘less’ {‘to create an where to place verbal adjective from a noun - Understand how to change emphasis) meaning ‘without’} as in a word from past to present Look at the placement of ‘childless’, ‘paperless’ tense and the inflectional - vowels and how they dictate endings required to do this pronunciation - ‘less’ {to create an (ACELA1485) - Recognise how sounds adjective from a verb to do and letters connect in with performance} as in predictable relationships (eg ‘tireless’, ‘relentless’ ‘tion’ in commotion) - ‘ness’ {forming an - Identify known parts of an abstract noun denoting unknown word and use quality and state} as in graphophonic knowledge to ‘darkness’, ‘goodness’, decode words ‘kindness’, ‘faithfulness’, (ACELA1485) ‘righteousness’ (ACELA1485) (ACELA1486) Discussion based learning Action based learning Text Purpose Text Structure Vocabulary
- Explore how the purpose of - Understand the purpose and Use extended technical the text influences language structure of paragraphs and vocabulary choices of tense and types of how paragraphs are sentences (eg an information organized (eg with topic - Words or phrases that are report will be written in sentences, linked ideas) primarily used in a specific present tense) (ACELA1479) field of interest or subject (ACELA1478) area - Focus on a clause as a unit of Use extended vocabulary grammar where the subject and verb are in agreement. Grammar & When reading, consider use - Use modal verbs and Vocabulary of punctuation and adverbs to express a conjunctions to identify range of feelings clauses (eg commas to break (ACELA1477) up complex sentences, the Use a range of vocabulary word ‘and’ to link clauses). - to express judgments and (ACELA1481) support a personal position about characters and events (ACELA1484) Certainty Modal Verbs/Adverbs Strong is, will, can not, must, always, never, clearly Moderat should, would, can, usually, likely, probably, generally, often, e frequently, rarely Tentative may, might, could, possible, sometimes, occasionally, perhaps, maybe
Comprehension Modelled Authors Text Purpose Text Structure Advertisements Comprehension Skills Research Skills linked to Guided comprehension Build literal and inferred Application - Discuss how characters, - Identify the purpose of a - Explore how the settings - Identify the purpose of events and settings are selected imaginative, shape the events of a text advertisements (ie to meaning about key events, - Record existing knowledge ideas and information in texts portrayed in different ways, informative and - Explore how the settings persuade the viewer to onto a graphic organizer and speculate on persuasive text (ACELY1678) engage with the message and analyse the information influence the mood of a Record questions about and take action such as - the authors’ reasons narrative (ACELT1599) presented by: think, do or buy the the text in writing before - Identify the point of advertised item) beginning reading - Connecting view in a text and suggest - Identify and describe the - Begin to use library alternative points of structure of o text to own classification to find reference experience materials view (ACELY1675) advertisements (ie large title, clear illustrations, text to other texts Locate information within (ACELT1594) o - simple message, o information with a text using headings, sub- Visual Comprehension Audience identification of seller, headings, page numbers, etc. price of product) print/image - Scan and skim for key - Activating prior knowledge - Identify the various Discussion and Action Based - Identify and describe the words and phrases features of advertisements techniques used to create Learning - Recording and sharing ‘I - Make clear notes using illustrations (eg colour, size or images wonder why . . . ‘ questions and words, modal verbs) key words, phrases and o camera angle (worm’s - Identify the effect of visual - Asking and answering sentences grouped together - Show understanding and eye view/bird’s eye view techniques used in picture questions drawing on Summarise and synthesise knowledge of - etc) books or advertisements knowledge of topic (specific information gathered advertisements by technical vocabulary and shot size (close up, far have on an audience (ACELY1675) (ACELY1679) o creating an advertisement experience of texts on the Identify the audience of a (ACELY1680) (ACELT1596) away) - for a selected audience same/similar topic selected imaginative, - Explore various page (ACELA1483) (ACELY1678) informative and - Using search tools layouts (position of efficiently to locate persuasive illustrations, texts, titles etc) text information either in written (ACELA1483) (ACELA1483) (ACELY1678) or digital texts Language Features Responding to Literature - Determining important ideas, events or details in - Explore language features - Explore personal texts and devices, and how they preferences when selecting o determining the main enhance the meaning of the texts idea/s text (ACELT1600) - Build a conscious o selecting events from a - Explore how language understanding of preference text for a specific features shape the reader’s through the selection of purpose (select relevant reactions literature, followed by an parts of a text) explanation of preference o Onomatopoeia - imitates o explicit reference to or suggests the source of - Develop criteria for information found in the sound that it establishing personal texts describes. preference for literature (eg - Inference making (giving o Alliteration select a book for a peer and explain to their peer why they reasons for inferences taking o Repetition think it is suitable for them into account topic knowledge and why they would enjoy it) or a character’s likely actions - Explore how language and feelings) features are used to create (ACELT1598) the setting in a text (eg ‘Once - Paraphrasing upon a time…) - Synthesizing (ACELT1599) - Cause and Effect (ACELY1679)
Reading Expression Text Processing Strategies Goals
- Read narrative, informative Contextual, grammatical, Reading Recovery Levelled and persuasive texts with Semantic and Phonic Texts expression, fluency and knowledge prosody (eg use of Readers Expected minimum home Theater, choral reading, Monitor meaning by: reading level at end of Year 3 repeated reading, guided is 25. reading). Texts should Predicting contain varied sentence - structures, punctuation - Confirming conventions and images for Re-reading In order to achieve the additional information. - - Reading on standard required at each level Reading Fluency & - When reading aloud, ensure the student must demonstrate Self-correcting Expression that tone, pace and - the following with confidence: expression engages the - Use of illustrations, selected audience diagrams, graphics, sound (ACELY1679) natural phrasing, using brief and movement in multimodal - texts pauses between more (ACELY1679) complex words or phrases - expressive tone and intonation to engage with the intended audience - comprehension of literal and inferred information contained within the text (ACELY1680)
Australian Curriculum – English Content Term 1 Term 2 Term 3 Term 4 Year 3 Map: Writing
Understandings, Elements Content & Achievement Standard Strategies Purpose and structure Literary Devices Writing Writing Students create a range of texts for familiar and unfamiliar audiences. Their texts include writing and images to express and develop in some detail experiences, - Read a wide range of - Build appreciation and Year 3 literature aloud to understanding of the events, information, ideas and characters. They demonstrate understanding of grammar and choose vocabulary and punctuation appropriate to the purpose and students to identify effects of literary context of their writing. They use knowledge of sounds and high frequency words to spell words accurately, checking their work for meaning. They write using and discuss the devices that engage joined letters that are accurately formed and consistent in size. features of various the reader and shape text types. their response to Productive modes (speaking, writing and creating) o Identif enhance meaning Students how language features are used to link and ideas. They how language can be used to express feelings and including: understand sequence understand y simple elements of structure (eg o font opinions on topics. Their texts include writing and images to express and develop in some detail experiences, events, information, ideas and characters. when reading a size Students create a range of texts for familiar and unfamiliar audiences. They contribute actively to class and group discussions, asking questions, providing report, o use of deconstruct the bold print useful feedback and making presentations. They demonstrate understanding of grammar and choose vocabulary and punctuation appropriate to the purpose framework of title, and context of their writing. They use knowledge of sounds and high frequency words to spell words accurately, checking their work for meaning. They write using headings, o use of joined letters that are accurately formed and consistent in size. Deconstruction of description, italics texts paragraphs etc). o vocabul o Deter ary choices mine purpose for o onomat the main three opoeia categories of text (imaginative, o alliterati informative, on persuasive) o rhythm (ACELT1599) (ACELT1791) (ACELY1679) (ACELY1682) (ACELT1600)
Planning Drafting Editing
- Articulate the - Draft texts using - Use editing techniques to revise drafts - appropriate audience information Consider publishing method and intended audience and purpose of contained on - writing of a given planning documents (ACELY1682) (ACELY1683) (ACELY1685) text structure (graphic organisers) - Use graphic (ACELY1682) organisers to plan (shared and Text Processes individual planning) a range of text types - Use knowledge of purpose, audience, literary devices and vocabulary to enhance planning (ACELY1678) (ACELA1478) (ACELY1682) (ACELT1600)
Text Creation Imaginative Informative Persuasive Narrative Narrative Poetry Recount Procedures Report Argument Modelling Narrative Illustrations Cinquains Journal Entries/Diaries Purpose Purpose Exposition Joint Construction Purpose Purpose Purpose Purpose - To provide logical, - To describe and Purpose Application - To entertain or inform sequential series of steps classify information the readers - To help the reader - To describe - To create a historical record of an to create a product Structure - To persuade the reader to a Structure visualize what they are the topic of event from the perspective of Structure particular opinion reading the poem self/character/historical figure Classification Structure Full sequence of events in - - To use illustrations to Structure Structure - Title (goal – a narrative order: - Description (of enhance or develop statement of what is to be physical appearance) - Introduction with position meaning - Line1: One - Date written at the top achieved) statement o Orientation Structure word (noun) - Location - Either written to someone (Dear - Materials/equipment - Each reason given expanded - Conclusion o Build Up towards - Line2: Two Diary) or personal reflection - Method (sequenced in a paragraph with opening conflict - Introduce illustrator Features words - Includes details of events, thoughts steps to achieve goal) statements techniques that allow (adjectives o Conflict and feelings Features - Conclusion them to vary the image that describe - Each report section o Resolution created line 1) Features - Create procedures is written as a Features paragraph with an Features o POV, angle to image - Line 3: independently for others opening statement o Distance to image (e.g. Three words - Allows the inclusion of personal to follow. - Paragraphs (verbs that - Headings for each worm’s eye, bird’s eye writing style - Have students - Develop main relate to line section - Persuasive language and and face-to-face view) st rd document each step to characters using a 1) - 1 or 3 person phrases (I believe that . . . We making an object and - Images in the character profile (eg o Medium of illustration - Verbal, visual (webcam etc.) or can solve this by . . .) personality of character, - Line 4: change this into a report should include (eg watercolour, written - Causal language – so, because appearance of character) Four words (a procedure. captions collage) (ACELA1477)(ACELA1479) phrase or - Can be written from the POV of - Use of present tense - Clearly labeled - Develop story setting, o Colour of illustration feelings that (ACELA1484) (ACELY1678) another character diagrams using appropriate and the impact it has relate to line - Each step to start with (ACELA1479) language to develop the (eg bad character has 1) - Build awareness of audience and a command verb mood of the story darker colours, good the type of information to be written (ACELT1596) - Line 5: One - Illustrate steps and character has bright Intrapersonal – only the writer - Use of paragraphs word o final product where colours) reads - Include dialogue Features (synonym of possible between characters to line 1) o Interpersonal – selected audience (ACELY1677) build relationship and - Generally or everyone Understand that an story line. Use - displayed in a (ACELT1596) (ACELT1791) appropriate dialogue illustration brings diamond conventions additional information to shape the reader about a text - Introduce complexity Features (ACELT1601) (ACELA1483) through minor conflicts building to major dilemma - Nouns, (ACELT1599) (ACELT1791) adjectives, (ACELT1601) verbs, feelings, synonyms (ACELA1481) (ACELA1482) (ACELT1600)
Sentence Structure Text Structure Parts of Speech Cohesive Devices
- Identify clauses found - Explore the connection - Understand parts of speech terminology (noun, verb, adjective, adverb - - Extend vocabulary using synonyms and antonyms in texts between text type and etc) - (ACELA1484) - Identify subject verb structure and the type - Use terminology to discuss how to enhance writing of sentences used. (eg agreement within short precise - Use terminology to evaluate a character (adjectives, adverbs, nouns and clauses (eg ‘We are sentences are used in verbs) fishing’ not ‘We is procedures; historical (ACELA1477) fishing’) language is used in - Understand how tense recounts) changes with singular (ACELA1478) and plural subjects (eg ‘is’ and ‘are’ for Paragraphs present tense and ‘was’ and ‘were’ for past tense as in ‘I am - Explore paragraph Grammar fishing. He is fishing. structure as an We are fishing’ organisational feature of text - Apply knowledge of (ACELA1479) clauses to the creation of simple and compound sentences Contractions in all forms of writing (ACELA1478) - Understand that they (ACELA1481) are used in informal language - Understand the purpose of apostrophes in contractions - Identify contractions in texts (ACELA1480)
Write legibly using correct Write legibly with growing letter formation, sizing, and fluency using joined letter Handwriting acceptable pencil grip with formation, sizing, and joined script. (ACELY1684) acceptable pencil grip. (ACELY1684) Spelling Write a large bank of high Focus on plurals. For Explore compound words through games as a Te Teach common spelling patterns/rules to assist in Teach syllabification to assist frequency words. strategy for assisting in spelling and understanding ac correctly spelling words. in spelling of more complex Explicitly teach less familiar new words. (ACELA1485) h (ACELA1485) multi-syllabic words (eg letter combinations to spell example: us en/vi/ron/ment) words. Include tri-graphs, e (ACELA1485) quad-graphs, homophones, of diphthongs Adding ‘s’ pr (ACELA1486) adding ‘es’. Use the efi following endings: s xe (ACELA1485) (grass/grasses) , sh s (push/pushes), ch an (lunch/lunches), z d (quiz/quizzes), or x suf (fox/foxes). fix es. Adding ‘ies’ (eg baby – (S babies – remembering to ee drop the ‘y’ before adding list ‘ies’ in re Adding ‘ves’ (leaf – leaves adi – remembering to change ng ‘f’ to ‘v’) se (ACELA1485) cti on un de r ph on olo gic al aw ar en es s for de tail s). (A CE LA 14 85 ) Punctuation Editing for Spelling Editing for Meaning
- Teach correct - Use editing and proof - Edit to enhance writing by re-structuring sentences to improve meaning - punctuation for reading to identify and - Edit to correct grammatical errors contractions. correct spelling errors - Reread work to improve structural aspects of the text (including flow, headings, Punctuation & - Teach correct (ACELY1683) and titles) punctuation for Editing (ACELY1683) dialogue including internal punctuation when using dialogue (eg “Boo,” screamed the little boy) (ACELY1683) Australian Curriculum – English Content Map: Term 1 Term 2 Term 3 Term 4 Year 3 Speaking & Listening
Understandings, Elements Content & Achievement Standard Strategies
Responding to others Setting (formal and Body Movement and Language Speaking and listening informal) Students understand how language features are used to link and sequence Listener Listen actively for specific Explore the differences in Li ideas. They understand how language can be used to express feelings and opinions on topics. They listen to others’ views and respond appropriately. They information. Accurately communication - follow 2 or 3 step multi- conventions of different Posture contribute actively to class and group discussions, asking questions, providing instruction sentences. styles and formalities - useful feedback and making presentations. such as turn taking in a Listen and contribute to - Engage in active listening behaviours - small group, (waiting for Receptive (listening) conversations and an appropriate interval to smile, maintain eye contact with the speaker, open posture toward the speaker, no - o S discussions to share ideas speak) or large group fiddling, doodling etc) By the end of Year 3, students understand how content can be organised and information (hands up, turn taking Gestures/Actions using different text structures depending on the purpose of the text. Learn to negotiate in when an adult is present - They understand how language features, images and vocabulary choices are collaborative ways (win- or without) (ACELA1476) - use appropriate and agreed upon methods to show active listening (eg verbal - used for different effects. win solutions) agreement or nonverbal agreement such as a nod) - Listen and respond Speaker They identify literal and implied meaning connecting ideas in different parts appropriately to the of a text. They select information, ideas and events in texts that relate to Posture Interaction Skills viewpoints of others their own lives and to other texts. They listen to others’ views and respond (ACELY1676) (ACELY1792) appropriately. - Upright, open and engaging posture Productive modes (speaking and creating) - maintain eye contact with the audience Students understand how language features are used to link - smile or show active interest Gestures and sequence ideas. They understand how language can be used to express feelings and opinions on topics. - natural hand gestures They contribute actively to class and group discussions, asking questions, - begin to use visual materials providing useful feedback and making presentations. Understanding Body Language
- identify the engagement of listener and begin to adjust presentation if needed to re- engage the audience (ACELY1792)
Communication (understandings) Discuss differences Build an understanding of Understand that Identify roles and collaborative Participate Learn the specific speaking or Use language appropriately in different between speech and different oral traditions and successful patterns for successful group in pair, listening skills of different situations such as making a request of a writing. When we speak, different ways of communication and communication. group and group roles, for example teacher, explaining a procedure to a we make up the words as constructing meaning cooperation (ACELA1476) (ACELY1676) class group leader, note taker and classmate, engaging in a game with we go along. When we (fables, folklore, etc) depends on shared speaking reporter. (ACELA1476) friends. (ACELA1476) (ACELY1792) write, we need to take (ACELA1475) use of social and (ACELY1792) (ACELA1477) (ACELY1676) much more care in putting conventions. listening the words together. In (ACELA1479) situations, speaking we can use ‘body including language’ and mime and informal gestures to make the words conversatio interesting and make ns, class everything clear. In writing, discussions we have to follow the rules and (eg proper sentences, good presentatio spelling, making sense). ns. (ACELA1475) (ACELA1476 ) (ACELY 1792) (ACELY1676 ) Oral Presentations Poetry: Limericks Reviews Purpose - To share information Purpose Purpose with an audience - To entertain or inform Structure - the readers - To share personal experience and opinion about a book, event, place or object - Greeting Structure Structure - - Content - - Conclusion - ABAB or AABB rhyme - Title - structure - - Question time - Content (what is the work, object or event?) - Rhythm patterns - - Approx. 2-3 minutes in - Description (what are the features of the work, object or event?) length (stress and intonation) - Features Features - Judgment (what does the writer think about the work, object or event) - Spoken in full Features sentences - Take a familiar chant - Logical sequence of and replace the words to - Introducing text structure content create a new chant with the same rhythm pattern. - Personal opinion - Use props to support - Descriptive language speech - Use of humour (ACELT1600) Suggestion – Book Reviews - Speak clearly, using Presentation Skills correct pronunciation (ACELA1477)(ACELA1484) - Consolidating presentation speaking behaviours o engaging the audience through eye contact, body language and verbal volume, tone and intonation - Engage in active listening behaviours o attentive listening in order to respond to the speaker o listening for specific information (ACELA1479) (ACELA1480) (ACELT1596) (ACELY1677) Australian Curriculum – English Links with Term 1 Term 2 Term 3 Term 4 Year 3 other Curriculum Areas
GENERAL CAPABILITIES & CROSS-CURRICULUM PRIORITIES Aboriginal & Torres Strait Asia & Australia’s Critical and Creative Personal and Social Intercultural Cross-Curriculum General Capabilities Literacy LIT Numeracy NUM ICT Competence ICT Ethical Behaviour ETH Islander histories & engagement with Asia Sustainability SUS Thinking CCT Competence P&S Understanding ICU Priorities cultures ATSI ASIA ENGLISH Language Understand that languages have different U Examine how Understand how Understand that Know that word Identify the features of online texts that enhance navigation (ACELA1790) ICT written and visual communication systems, n evaluative language different types of texts paragraphs are a key contractions are a
different oral traditions and different ways of d can be varied to be vary in use of organisational feature feature of informal constructing meaning (ACELA1475) e more or less forceful language choices, of written texts language and that r depending on their apostrophes of CCT, ICU, ATSI, ASIA (ACELA1477) (ACELA1479) s purpose and context contraction are used CCT, P&S, SUS t (for example, tense to signal missing a and types of letters n sentences) (ACELA1480) d (ACELA1478)
t h a t s u c c e s s f u l c o o p e r a t i o n
w i t h
o t h e r s d e p e n d s o n
s h a r e d u s e o f s o c i a l c o n v e n t i o n s , i n c l u d i n g t u r n - t a k i n g p a t t e r n s , a n d f o r m s o f a d d r e s s t h a t v a r y a c c o r d i n g
t o t h e d e g r e e o f f o r m a li t y i n
s o c i a l s i t u a t i o n s ( A C E L A 1 4 7 6 ) P & S , Understand that a clause is a unit of U Identify the effect on Learn extended and Understand how to Recognise high–frequency sight words (ACELA1486) grammar usually containing a subject and a n audiences of technical vocabulary use sound–letter verb and that these need to be in d techniques, for and ways of relationships and agreement (ACELA1481) e example shot size, expressing opinion knowledge of spelling r vertical camera angle including modal verbs rules, compound s and layout in picture and adverbs words, prefixes, t books, advertisements (ACELA1484) suffixes, morphemes a and film segments and less common P&S, ATSI, ASIA n letter combinations, d (ACELA1483) for example ‘tion’
NUM (ACELA1485) t h a t v e r b s r e p r e s e n t d i f f e r e n t p r o c e s s e s , f o r e x a m p l e d o i n g , t h i n k i n g , s a y i n g , a n d r e l a t i n g
a n d
t h a t t h e s e p r o c e s s e s a r e a n c h o r e d
i n
t i m e t h r o u g h
t e n s e ( A C E L A 1 4 8 2 ) Literature Discuss texts in which characters, Draw Develop criteria for Discuss how language Discuss the nature and Create imaginative Create texts that adapt language features and patterns encountered in literary texts, for example characterisation, rhyme, events and settings are portrayed in connect establishing personal is used to describe the effects of some texts based on rhythm, mood, music, sound effects and dialogue (ACELT1791) ICU, ATSI, ASIA different ways, and speculate on the ions preferences for settings in texts, and language devices used characters, settings authors’ reasons (ACELT1594) betwee literature explore how the to enhance meaning and events from n settings shape the and shape the students’ own and CCT, ICU, ATSI, ASIA (ACELT1598) persona events and influence reader’s reaction, other cultures using CCT, P&S l the mood of the including rhythm and visual features, for experie narrative onomatopoeia in example perspective, nces (ACELT1599) poetry and prose distance and angle and the worlds CCT (ACELT1600) (ACELT1601) of texts, CCT, ASIA CCT, ICU and share respons es with others (ACE LT15 96) CCT, P&S, ETH, ICU, ATSI, ASIA Identify the Listen to and contribute to Use interaction skills, Plan and deliver short Identify the audience Read an increasing Use comprehension Plan, draft and publish Reread Write using joined Use software including point of view conversations and discussions including active presentations, and purpose of range of different strategies to build literal imaginative, informative and and edit letters that are clearly word processing in a text and to share information and ideas listening behaviours providing some key imaginative, types of texts by and inferred meaning and persuasive texts demonstrating texts for formed and consistent programs with growing suggest and negotiate in collaborative and communicate in a details in logical informative and combining contextual, begin to evaluate texts by increasing control over text meaning in size speed and efficiency to alternative situations (ACELY1676) clear, coherent sequence persuasive texts semantic, grammatical drawing on a growing structures and language , (ACELY1684) construct and edit points of manner using a and phonic knowledge of context, text features and selecting print,and appropri texts featuring visual, P&S (ACELY1677) (ACELY1678) view variety of everyday knowledge, using text structures and language multimodal elements ate print and audio CCT, P&S CCT, P&S (ACELY1 and learned processing strategies, features appropriate to the audience and structure elements vocabulary and for example (ACELY1680) ICT, purpose (ACELY1682) , (ACELY1685)ICT 675) CCT, appropriate tone, monitoring, predicting, gramma Literacy CCT, P&S, SUS ICT, CCT P&S pace, pitch and confirming, rereading, tical volume reading on and self- choices (ACELY1792) correcting and punctuat P&S (ACELY1679) ion P&S, ATSI, ASIA (ACEL Y168 3) ICT MATHEMATICS Understanding Reasoning includes connecting number representations with number sequences, includes using generalising from number properties and results of calculations, comparing angles, creating and interpreting variations in the results of data collections and data displays Proficiency Strands partitioning and combining numbers flexibly, representing unit fractions, using appropriate language to communicate times, and identifying environmental symmetry Number & Algebra Investigate the Recognise, model, Apply place value to Recognise and explain Recall addition facts Recall multiplication Represent and solve problems Model and represent unit R Describe, continue, and create number patterns conditions required for a represent and order partition, rearrange the connection for single-digit facts of two, three, involving multiplication using efficient fractions including 1/2, e resulting from performing addition or subtraction number to be odd or numbers to at least and regroup numbers between addition and numbers and related five and ten and mental and written strategies and 1/4, 1/3, 1/5 and their pr (ACMNA060) LIT, ICU even and identify odd 10 000 to at least 10 000 to subtraction subtraction facts to related division facts appropriate digital technologies multiples to a complete es and even numbers (ACMNA052) assist calculations and (ACMNA054) develop increasingly (ACMNA056) (ACMNA057) LIT, NUM ICT, CCT whole (ACMNA058) e solve problems efficient mental nt (ACMNA051) LIT, LIT LIT, CCT NUM, CCT, ICU, ASIA strategies for m CCT (ACMNA053) computation on LIT, NUM, CCT (ACMNA055)CCT ey va lu es in m ul ti pl e w ay s an d co u nt th e ch an g e re q ui re d fo r si m pl e tr an sa cti on s to th e n ea re st fiv e ce nt s ( A C M N A 0 5 9 ) LI T, N U M, C C T, IC U, A SI A Measurement & Measure, order and compare objects using T Make models of three- Create and interpret Identify symmetry in Identify angles as measures of turn and compare angle sizes in everyday situations (ACMMG064) LIT, NUM Geometry familiar metric units of length, mass and e dimensional objects simple grid maps to the environment capacity (ACMMG061) LIT, NUM, CCT, ll and describe key show position and (ACMMG066) ti features pathways ICU, ASIA LIT, NUM, ICU, ATSI m (ACMMG063) (ACMMG065) e LIT, NUM, ICU, ASIA LIT, NUM, CCT t o t h e m i n u t e a n d i n v e s ti g a t e t h e r e l a ti o n s h i p b e t w e e n u n it s o f ti m e ( A C M M G 0 6 2 ) L I T , N U M Statistics & Conduct chance experiments, identify and describe possible C Interpret and compare data displays (ACMSP070) LIT, NUM, CCT Probability outcomes and recognise variation in results (ACMSP067) LIT o ll e c t d a t a , o r g a n is e i n t o c a t e g o ri e s a n d c r e a t e d is p l a y s u si n g li s t s, t a b l e s, p ic t u r e g r a p h s a n d si m p l e c o l u m n g r a p h s, w it h a n d w it h o u t t h e u s e o f d i g it a l t e c h n o l o g i e s ( A C M S P 0 6 9 ) LI T , I C T , C C T , S U S SCIENCE Science Living things can be grouped on the basis of observable features Ear Heat can be produced in many ways and can move from one object to another (ACSSU049) LIT, NUM, CCT Understanding and can be distinguished from non-living things (ACSSU044) th’ s LIT, CCT rot ati on on its axi s cau ses reg ula r cha ng es, incl udi ng nig ht an d da y (A C S S U 0 4 8) LIT, NU M, CC T Science as a human Science involves making predictions and describing patterns and relationships (ACSHE050) LIT, CCT, ICU, ATSI Science knowledge helps people to understand the effect of their actions (ACSHE051) LIT, CCT, P&S, ETH, ICU, ATSI, SUS endeavour With guidance, identify questions in Suggest Safely use appropriate Use a range of Compare results with Reflect on the Represent and communicate ideas and findings in a variety of ways such as diagrams, physical representations and simple familiar contexts that can be ways to materials, tools or methods including predictions, investigation, reports (ACSIS060) LIT, NUM P&S investigated scientifically and predict plan equipment to make tables and simple suggesting possible including whether a what might happen based on prior and and record column graphs to reasons for findings test was fair or not knowledge (ACSIS053) LIT, CCT, conduct observations, using represent data and to (ACSIS215) LIT, (ACSIS058) LIT, investig formal measurements identify patterns and P&S NUM, CCT CCT, P&S ations and digital trends to find technologies as (ACSIS057) LIT, answers appropriate NUM CCT to (ACSIS055) LIT, Science Inquiry Skills questio NUM, ICT, P&S ns (ACSI S054 ) LIT, NUM, ICT, CCT, P&S HISTORY Who lived here first and how do we know? Wh How and why do people choose to remember significant events of the past? at is the nat ure of the con trib uti on ma de by diff Key Inquiry Questions ere nt gro ups an d ind ivid ual s in the co m mu nit y? The importance of Country and Place to Aboriginal and/or Torres Strait Days and weeks Celebrations and commemorations in other places around the world; for example, Bastille Day in France, Independence Day in the USA, including those that are observed in Islander peoples who belong to a local area. (This is intended to be a local celebrated or Australia such as Chinese New Year, Christmas Day, Diwali, Easter, Hanukkah, the Moon Festival and Ramadan (ACHHK064) ICT, CCT, ICU, ASIA area study with a focus on one Language group; however, if information or commemorated in sources are not readily available, another representative area may be Australia (including studied) (ACHHK060) LIT, P&S, ICU, ATSI Australia Day, ANZAC Day, Harmony Week, Historical Knowledge National Reconciliation & Understanding Week, NAIDOC week and National Sorry Day) and the importance of symbols and emblems. (ACHHK063) LIT, CCT, ICU, ATSI Sequence historical people and Use Pose a range of Identify sources Locate relevant Identify different Develop texts, particularly narratives (ACHHS070) LIT Use a range of communication events (ACHHS065) LIT, historical questions about the (ACHHS215) information from points of view forms (oral, graphic, written) terms past sources provided and digital technologies NUM, CCT CCT (ACHHS069) LIT, Historical Skills (ACHHS (ACHHS067) LIT, (ACHHS068) LIT, CCT, P&S, ICU, ATSI (ACHHS071) LIT, ICT 066) LIT, CCT ICT, CCT ICU, ATSI Australian Curriculum – English
Links with Term 1 Term 2 Term 3 Term 4 other Year 3 Curriculum Areas (continued):
GEOGRAPHY How and why are places similar and What How do people’s feelings about places influence their views about the Place Environment Change Sustainability different? woul protection of places? (national, regional & (national, regional & global scale) d it global scale) be like to Inquiry Questions live Key Concepts in a neig hbou ring coun try? The representation of Australia The The location of Australia’s neighbouring countries and their diverse The main climate types of the world and the The similarities and differences in individuals’ and The similarities and differences between many groups’ feelings and perceptions about places, and places in terms of their type of settlement, as states and territories, and characteristics (ACHGK016) LIT, NUM, CCT, ICU, ASIA similarities and differences between the Countr how they influence views about the protection of demographic characteristics and the lives of Australia’s major natural and human ies/Pla climates of different places (ACHGK017) these places (ACHGK018) LIT, CCT, P&S, ICU, the people who live there (ACHGK019) features (ACHGK014) NUM, ces of LIT, NUM, CCU, ICU ATSI, ASIA, SUS LIT, NUM, CCT, P&S, ATSI, ASIA LIT, CCT Aborigi nal and Torres Strait Islande r Geographical People Knowledge & s Understanding throug hout Austral ia (AC HGK 015) LIT, NUM, CCT, ICU, ATSI Develop Collect and record Represent data by constructing tables and Represent the location of places and their features Interpret geographical data to Reflect on their learning to propose individual action in response to a geographical relevant geographical contemporary geographical challenge and identify the expected effects of the by constructing large-scale maps that conform to identify distributions and patterns questions to graphs (ACHGS021) LIT, NUM, CCT data and information, and draw conclusions proposal (ACHGS025) LIT, CCT, P&S, ETH, SUS investigate cartographic conventions including scale, legend, title for example, by observing and north point, and describe their location using simple (ACHGS023) LIT, NUM, CCT (ACHGS019) by interviewing, grid references, compass direction and distance SUS LIT, CCT conducting surveys, Geographical Skills measuring, or from (ACHGS022) LIT, NUM, CCT sources such as maps, photographs, satellite images, the media and the internet (ACHGS020) LIT, NUM, ICT, CCT, ASIA THE ARTS Improvise and structure movement ideas for dance sequences Perform dances using expressive skills to communicate ideas, including telling cultural or community stories Identify how the elements of dance and production elements express using the elements of dance and choreographic Dance (ACADAM007) LIT, NUM, CCT, P&S, ICU, ATSI, ASIA, SUS ideas in dance they make, perform and experience as audience, including devices (ACADAM005) LIT, NUM, CCT, P&S exploration of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander dance (ACADAR008) LIT, CCT, P&S, ICU, ATSI, ASIA, SUS Identify intended purposes and meaning of drama, starting with Australian drama, Drama Explore ideas and narrative structures through roles and Shape and perform dramatic action using narrative structures and tension in devised and scripted drama, including including drama of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Peoples, using the situations and use empathy in their own improvisations and exploration of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander drama (ACADRM033) LIT, CCT, P&S, ICU, ATSI, ASIA, SUS elements of drama to make comparisons (ACADRR034) LIT, CCT, devised drama (ACADRM031) LIT, CCT, P&S, ETH, P&S, ICU, ATSI, ASIA, SUS SUS Develop aural skills by exploring, imitating and Create, perform and record compositions by selecting and organising sounds, silence, tempo and volume (ACAMUM086) LIT, Identify intended purposes and meanings as they listen to music using the elements of music to make comparisons, starting with Australian music, recognising elements of music including NUM, CCT, P&S, SUS Music including music of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Peoples dynamics, pitch and rhythm patterns (ACAMUR087) LIT, NUM, CCT, P&S, ICU, ATSI, ASIA, SUS (ACAMUM084) LIT, NUM, CCT, P&S, SUS Investigate and devise representations of people in their community, Plan, create and present media artworks for specific purposes with awareness of responsible media practice Identify intended purposes and meanings of media artworks, using media arts key including themselves, through settings, ideas and story structure in concepts, starting with media artworks in Australia including media artworks of Media Arts (ACAMAM060) LIT, ICT, CCT, ETH, ATSI, ASIA, SUS images, sounds and text (ACAMAM058) LIT, CCT, P&S, ATSI, ASIA Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Peoples (ACAMAR061) LIT, CCT, P&S, ICU, ATSI, ASIA Explore ideas and artworks from different cultures and times, including Present artworks and describe how they have used visual conventions to represent their ideas Identify intended purposes and meanings of artworks using visual arts artwork by Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander artists, to use as terminology to compare artworks, starting with visual artworks in Australia Visual Arts (ACAVAM112) LIT, CCT, SUS including visual artworks of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Peoples inspiration for their own representations (ACAVAM110) LIT, CCT, (ACAVAR113) LIT, CCT, P&S, ICU, ATSI, ASIA, SUS P&S, ICU, ATSI, ASIA, SUS TECHNOLOGIES Recognise the role of people in Investigate how forces Investigate food Investigate the Critique needs or Generate, develop, Select and use Evaluate design ideas, Plan a sequence of design and technologies and the properties of suitability of opportunities for and communicate materials, processes and production steps when and fibre designing and explore design ideas and solutions based on occupations and explore materials affect materials, components, tools making designed and test a variety of decisions using criteria for success factors, including sustainability the behaviour of a production and and equipment systems, appropriate technical developed with solutions that impact on the design of food materials, using safe work product or system components, tools and terms and guidance and individually and products, services and components, tools and practices to make Design & Knowledge & technologies equipment for a range including care for the collaboratively environments to meet (ACTDEK011) Processes & Skills equipment and the graphical Understanding used in modern and of purposes designed Technologies community needs LIT, NUM, ICT, CCT, techniques needed to environment (ACTDEP018) traditional societies representation ATSI, ASIA (ACTDEK013) solutions LIT, NUM, CCT, P&S (ACTDEK010) LIT, ITC, LIT, NUM, ICT, CCT, produce designed (ACTDEP017) LIT, NUM, ICT, CCT, techniques CCT, P&S, ETH, ASIA, SUS P&S, ICU, ATSI, ASIA (ACTDEP016) LIT, CCT, P&S, ETH, SUS solutions (ACTDEP015) LIT, CCT, P&S, ETH, SUS (ACTDEP014) LIT, LIT, NUM, CCT SUS CCT, ATSI, ASIA, SUS Explore and use a range of Recognise different Collect, access and present Define Implement simple digital solutions as visual Explain how developed solutions Work with others to plan the digital systems with types of data and different types of data using simple and existing information creation and communication of problems, programs with algorithms involving branching ideas and information safely, explore how the same simple software to create peripheral devices for and describe systems meet common applying agreed ethical and information and solve problems (decisions) and user input (ACTDIP011) LIT, different purposes, and transmit data can be and follow a personal, school or community NUM, ICU, CCT, ASIA social protocols (ACTDIP009) LIT, NUM, sequence of different types of data represented in needs, and envisage new ways steps and (ACTDIP013) LIT, ICU, CCT, different ways ICU, CCT of using them (ACTDIP012) Knowledge & (ACTDIK007) LIT, NUM, decisions P&S, ETH Digital Technologies (ACTDIK008) Processes & Skills LIT, ICU, CCT, P&S, ATSI, ASIA, Understanding ICU, CCT (algorithms) LIT, NUM, ICU, CCT, SUS needed to ATSI solve them (ACTDIP 010) LIT, NUM, ICU, CCT HEALTH & PHYSICAL EDUCATION
Examine how Explore strategies to Describe and Identify and Describe how Investigate how Discuss and Describe Participate in outdoor Research own heritage and cultural manage physical, games and activities to success, challenge practise strategies to respect, empathy and emotional responses strategies to make the identities, and explore strategies to respect social and emotional apply strategies interpret health and failure strengthen promote health, safety valuing difference can vary in depth and classroom and examine how change that can be used in information and and value diversity (ACPPS042) LIT, CCT, personal positively influence strength playground healthy, participation promotes situations that make and wellbeing messages in the P&S, ETH, ICU, ATSI, ASIA, SUS (ACPPS034) LIT, relationships safe and active spaces a connection between identities them feel (ACPPS038) LIT, media and on the Personal, Social & CCT, P&S (ACPPS036) LIT, the community, uncomfortable or (ACPPS037) LIT, CCT, P&S Internet (ACPPS040) LIT, (ACPPS033) LIT, CCT, P&S natural and built Community Health unsafe CCT, P&S, ETH, ICU CCT, P&S, SUS, SUS, CCT, P&S (ACPPS039) LIT, environments, and (ACPPS035) LIT, ICU, CCT, P&S health and CCT, P&S wellbeing (ACPPS041) LIT, CCT, P&S Movement & Physical Practise and refine Perform Practise and apply movement Combine the elements of effort, Activity fundamental moveme Examine the benefits of space, time, objects and people Apply innovative and creative thinking in solving movement Apply basic rules and scoring concepts and strategies when performing and LIT, CCT, P&S systems, and movement skills in nt physical activity challenges (ACPMP049) demonstrate (ACPMP045) LIT, NUM, CCT, P&S movement to health fair play when participating different movement sequenc physical fitness sequences LIT, CCT, P&S, and (ACPMP050) situations es which wellbeing (ACPMP047) LIT, NUM, ETH link (ACPMP046) LIT, CCT (ACPMP043) LIT, NUM, CCT, P&S CCT, P&S fundame ntal moveme nt skills (ACPMP0 44) LIT, NUM, CCT, P&S, ATSI, ASIA LANGUAGES - LOTE – INDONESIAN Share with peers and Contribute to class Respond to questions, Obtain and share Present information Listen to, read and Translate using textual Produce texts such as Communicate in Interact with others teacher information activities such as instructions and information from about school and Create texts such descriptions and signs Indonesian using and noticing how view creative texts such cues such as about aspects of solving a problem, requests, and peers and texts neighbourhood using as dialogues and in both Indonesian and routine phrases and as rhymes, songs and pictures, layout and identity matters, personal world such as creating a display or participate in routine related to family, tables, lists and stories, using English for the school expressions, stories, identifying key words to predict such as in use of daily routines, home, conducting a role- exchanges home, routines and descriptions formulaic expressions community recognising that such meaning, and terms of address, who and favourite objects play/scenario [Key concepts: interests [Key concept: data; characters and and modelled [Key concepts: comment on the non- language reflects and what is included, and pastimes [Key concept: respect, sopan [Key concepts: Key processes: acting out events similarity, difference; language equivalence of words cultural practices and and what [Key concepts: collaboration; Key santun; Key routine, pastimes; Key informing, [Key concepts: Key processes: [Key concepts: due to cultural norms Communicating routine, occasion; Key processes: problem processes: interacting, processes: selecting, organising] character, plot; Key describing, captioning] language is used humour, imagination; differences [Key concepts: processes: describing, solving, participating] responding] tabulating, processes: performing, [Key concept: (ACLINC022) Key processes: [Key concepts: gist, (ACLINC026) LIT, politeness, etiquette; sharing] categorising] membership; Key (ACLINC019) (ACLINC020) LIT, CCT, P&S, ICU recounting; Key text presenting, creating; meaning; Key CCT, ICU Key processes: processes: interacting, (ACLINC018) LIT, CCT, P&S, ICU LIT, CCT, P&S, ICU (ACLINC021) types: fable, legend, processes: translating, experimenting, Key text types: play, noticing] LIT, CCT, P&S, ICU LIT, CCT, P&S, ICU song, children’s predicting] connecting] poem] (ACLINC028) television] (ACLINC025) (ACLINC027) (ACLINC024) LIT, CCT, P&S, ICU (ACLINC023) LIT, LIT, CCT, ICU LIT, CCT, P&S, ICU LIT, CCT, P&S, ICU CCT, P&S, Understanding Recognise and reproduce D Recognise that texts such as stories, games and conversations have particular features Understand that language varies Recognise that Indonesian is the official Make connections between cultural e pronunciation conventions, including [Key concept: genre; Key processes: observing patterns, distinguishing] according to age, gender and social language of Indonesia and is one of practices and language use, such as v position, such as place in the family many languages in the Asia-Pacific region specific vocabulary and expressions loan words from English and intonation e (ACLINU031) LIT, CCT, ICU [Key concept: status; Key processes: [Key concept: diversity; Key processes: for questions, statements and commands. l [Key concept: official language; Key observing, comparing] comparing, connecting] [Key concept: intonation; Key o process: understanding] p (ACLINU032) LIT, CCT, P&S, ICU (ACLINU034) LIT, CCT, P&S, ICU processes: imitating, discriminating sounds] (ACLINU033) LIT, CCT, P&S, ICU, ASIA u (ACLINU029) LIT, CCT, ICU n d e r s t a n d i n g o f w a y s t o e x p r e s s p o s s e s s i o n a n d d e s c ri b e q u a li ti e s o f p e o p l e a n d o b j e c t s , a n d e x p a n d v o c a b u l a r y r e l a t e d t o p e r s o n a l a n d s o c i a l w o rl d [ K e y c o n c e p t s : a c ti o n , s e q u e n c e ; K e y p r o c e s s e s : d e s c ri b i n g , r e l a ti n g , p r e d i c ti n g ] ( A C L I N U 0 3 0 ) L I T , N U M , C C T , P & S , I C U