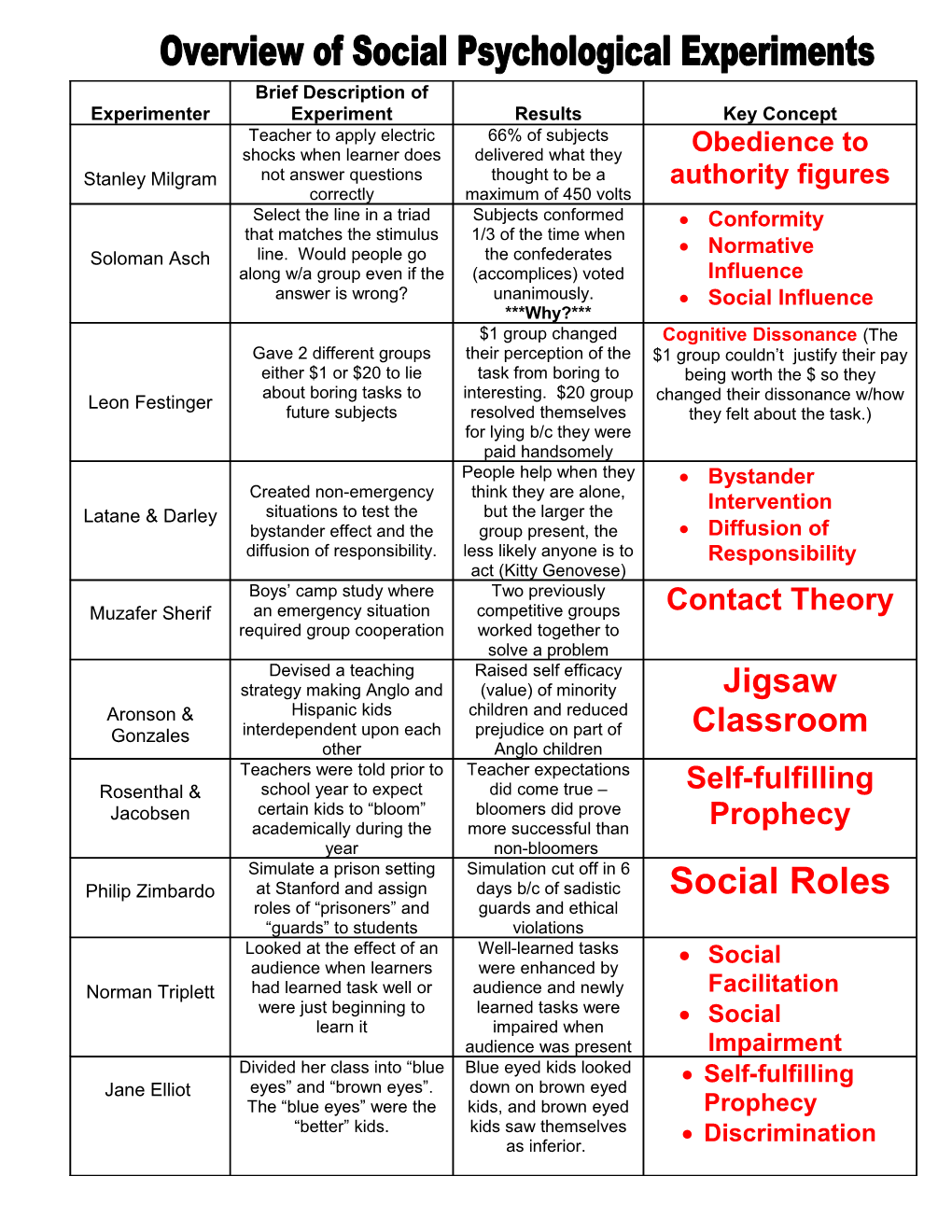
Brief Description of Experimenter Experiment Results Key Concept Teacher to apply electric 66% of subjects shocks when learner does delivered what they Obedience to Stanley Milgram not answer questions thought to be a authority figures correctly maximum of 450 volts Select the line in a triad Subjects conformed Conformity that matches the stimulus 1/3 of the time when Normative Soloman Asch line. Would people go the confederates along w/a group even if the (accomplices) voted Influence answer is wrong? unanimously. Social Influence ***Why?*** $1 group changed Cognitive Dissonance (The Gave 2 different groups their perception of the $1 group couldn’t justify their pay either $1 or $20 to lie task from boring to being worth the $ so they about boring tasks to interesting. $20 group Leon Festinger changed their dissonance w/how future subjects resolved themselves they felt about the task.) for lying b/c they were paid handsomely People help when they Bystander Created non-emergency think they are alone, Intervention Latane & Darley situations to test the but the larger the bystander effect and the group present, the Diffusion of diffusion of responsibility. less likely anyone is to Responsibility act (Kitty Genovese) Boys’ camp study where Two previously Muzafer Sherif an emergency situation competitive groups Contact Theory required group cooperation worked together to solve a problem Devised a teaching Raised self efficacy strategy making Anglo and (value) of minority Jigsaw Aronson & Hispanic kids children and reduced Gonzales interdependent upon each prejudice on part of Classroom other Anglo children Teachers were told prior to Teacher expectations Rosenthal & school year to expect did come true – Self-fulfilling Jacobsen certain kids to “bloom” bloomers did prove academically during the more successful than Prophecy year non-bloomers Simulate a prison setting Simulation cut off in 6 Philip Zimbardo at Stanford and assign days b/c of sadistic Social Roles roles of “prisoners” and guards and ethical “guards” to students violations Looked at the effect of an Well-learned tasks Social audience when learners were enhanced by Norman Triplett had learned task well or audience and newly Facilitation were just beginning to learned tasks were Social learn it impaired when audience was present Impairment Divided her class into “blue Blue eyed kids looked Self-fulfilling Jane Elliot eyes” and “brown eyes”. down on brown eyed The “blue eyes” were the kids, and brown eyed Prophecy “better” kids. kids saw themselves Discrimination as inferior.
Overview of Social Psychological Experiments
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Recommended publications