Metabolic effects of FGF21 in DIO mice
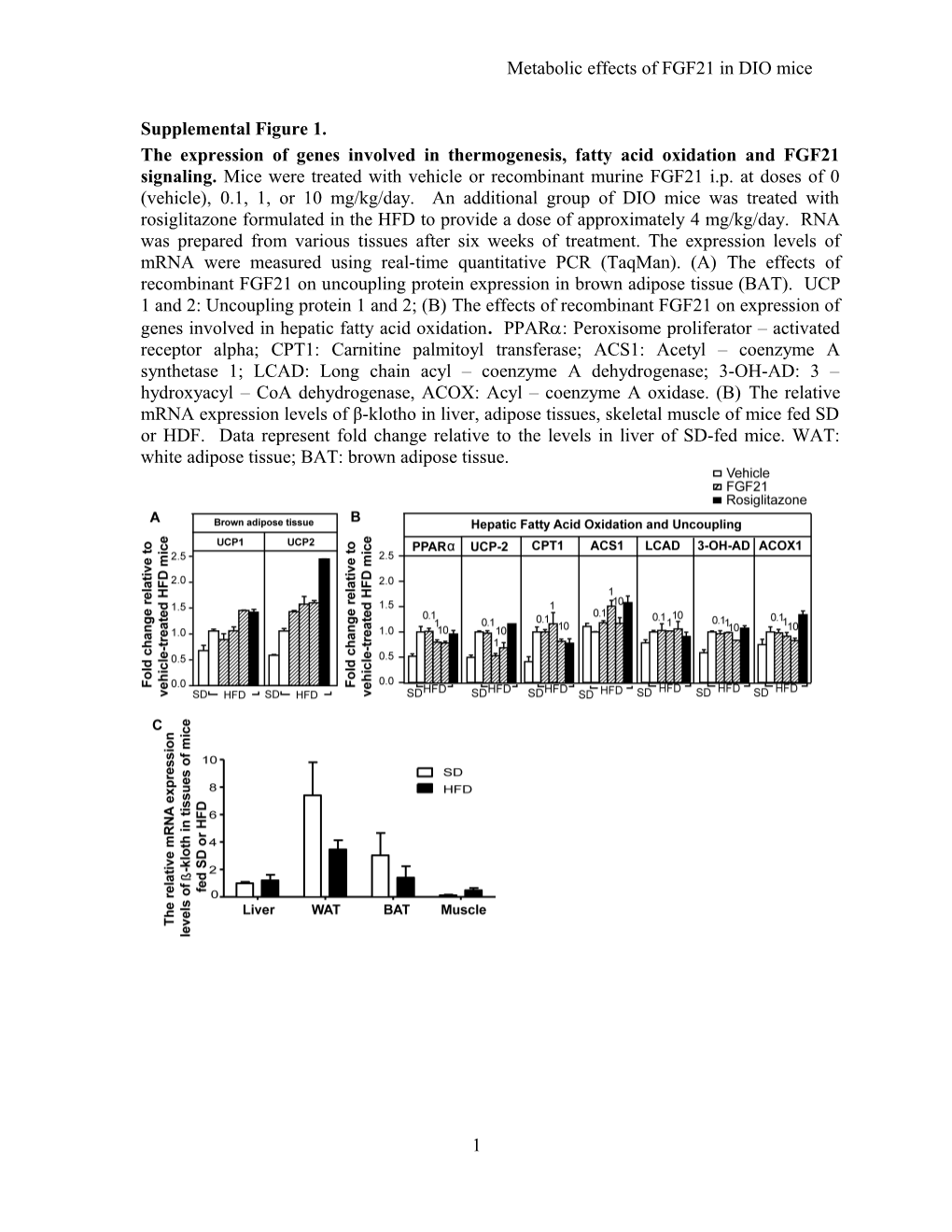
Supplemental Figure 1. The expression of genes involved in thermogenesis, fatty acid oxidation and FGF21 signaling. Mice were treated with vehicle or recombinant murine FGF21 i.p. at doses of 0 (vehicle), 0.1, 1, or 10 mg/kg/day. An additional group of DIO mice was treated with rosiglitazone formulated in the HFD to provide a dose of approximately 4 mg/kg/day. RNA was prepared from various tissues after six weeks of treatment. The expression levels of mRNA were measured using real-time quantitative PCR (TaqMan). (A) The effects of recombinant FGF21 on uncoupling protein expression in brown adipose tissue (BAT). UCP 1 and 2: Uncoupling protein 1 and 2; (B) The effects of recombinant FGF21 on expression of genes involved in hepatic fatty acid oxidation. PPAR: Peroxisome proliferator – activated receptor alpha; CPT1: Carnitine palmitoyl transferase; ACS1: Acetyl – coenzyme A synthetase 1; LCAD: Long chain acyl – coenzyme A dehydrogenase; 3-OH-AD: 3 – hydroxyacyl – CoA dehydrogenase, ACOX: Acyl – coenzyme A oxidase. (B) The relative mRNA expression levels of β-klotho in liver, adipose tissues, skeletal muscle of mice fed SD or HDF. Data represent fold change relative to the levels in liver of SD-fed mice. WAT: white adipose tissue; BAT: brown adipose tissue.
1 Metabolic effects of FGF21 in DIO mice
Supplemental Table 1
Metabolic parameters during basal (12 h fast) and hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp periods in mice chronically treated with muFGF21. Basal Clamp Body Insulin Glucose Insulin N Glucose (mg/dL) weight (g) (pM) (mg/dL) (pM) PBS 10 25 0 146 9 36 3 134 4 97 5 SD muFGF21 10 mg/kg 8 23 1* 143 9 32 4 132 6 84 7 PBS 12 43 1† 190 10‡ 139 41§ 170 11* 490 32† HFD muFGF21 0.1 mg/kg 12 43 1 151 7* 115 19 137 7║ 376 27║ muFGF21 10 mg/kg 12 35 1¶ 125 3¶ 72 17 129 7* 239 24¶ All data represent means SEM. ║ P < 0.05, * P < 0.01, ¶ P < 0.001 vs. diet-matched PBS treated mice; § P < 0.05, ‡ P < 0.01, † P < 0.001 vs. SD-fed vehicle-treated mice.
2