HONORS UNIT 3B : AIRBAGS
Below are the class objectives, correlated to the NC Essential Standards and page numbers within your textbook. In the far right column you will see the required vocabulary of the unit as well. At the end of each unit, you should be able to define and apply all the required vocabulary words in order to be successful on the unit test.
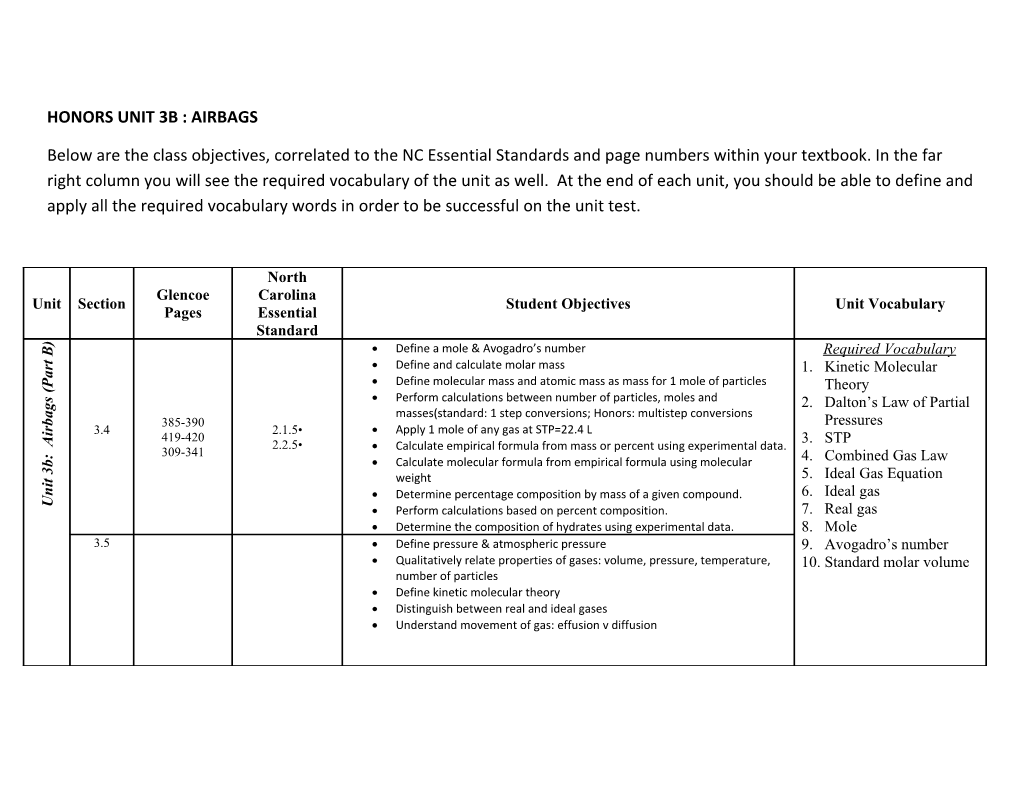
North Glencoe Carolina Unit Section Student Objectives Unit Vocabulary Pages Essential Standard ) Define a mole & Avogadro’s number B Required Vocabulary
t
r Define and calculate molar mass 1. Kinetic Molecular a
P Define molecular mass and atomic mass as mass for 1 mole of particles Theory (
s Perform calculations between number of particles, moles and 2. Dalton’s Law of Partial g
a masses(standard: 1 step conversions; Honors: multistep conversions
b 385-390 Pressures r
i 3.4 2.1.5• Apply 1 mole of any gas at STP=22.4 L 419-420 3. STP A
2.2.5• Calculate empirical formula from mass or percent using experimental data. 309-341 : 4. Combined Gas Law
b Calculate molecular formula from empirical formula using molecular 3
5. Ideal Gas Equation t weight i
n Determine percentage composition by mass of a given compound. 6. Ideal gas U Perform calculations based on percent composition. 7. Real gas Determine the composition of hydrates using experimental data. 8. Mole 3.5 Define pressure & atmospheric pressure 9. Avogadro’s number Qualitatively relate properties of gases: volume, pressure, temperature, 10. Standard molar volume number of particles Define kinetic molecular theory Distinguish between real and ideal gases Understand movement of gas: effusion v diffusion HONORS UNIT 3B : AIRBAGS
Below are the class objectives, correlated to the NC Essential Standards and page numbers within your textbook. In the far right column you will see the required vocabulary of the unit as well. At the end of each unit, you should be able to define and apply all the required vocabulary words in order to be successful on the unit test.
Apply formulas and concepts of kinetic molecular theory: 2. Ideal gas equation (PV=nRT), Combined gas law (P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2) and applications holding one variable constant: for PV=k, P1V1 = P2V2; for V/T=k, V1/T1= V2/T2; for P/T=k, P1/T1 = P2/T2. Note: Students should be able to derive and use these gas laws, but are not necessarily expected to memorize their names. Other Vocabulary Apply formulas and concepts of kinetic molecular theory: 3. Avogadro’s 11. Pressure 3.6 421-438 2.1.5• law (n/V=k), n1/V1 = n1/V2 12. Absolute temperature Apply formulas and concepts of kinetic molecular theory: 4. Dalton’s 13. Boyle’s Law law (Pt=P1+P2+P3 …) 14. Charles’ Law 15. Gay-Lussac’s Law 16. Avogadro’s Law
Use the concept of calorimetry to measure heat changes in constant pressure system for chemical and physical changes. 3.7 Understand the difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions, using reaction pathway graphs and chemical equations