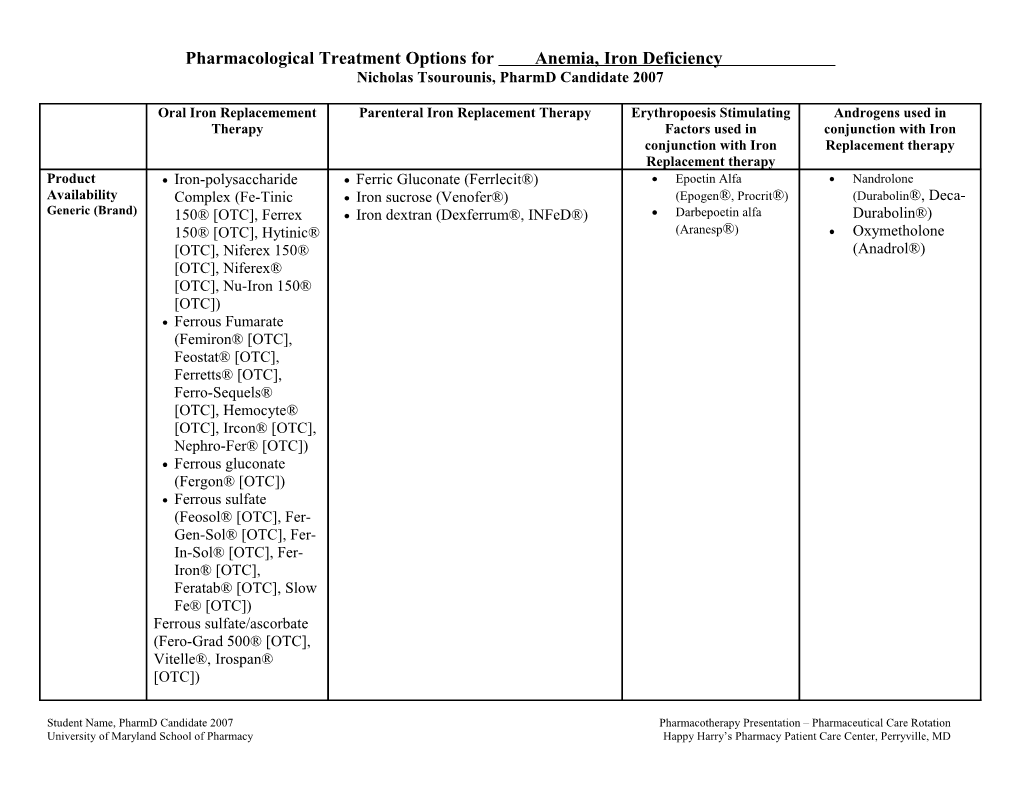
Pharmacological Treatment Options for Anemia, Iron Deficiency Nicholas Tsourounis, PharmD Candidate 2007
Oral Iron Replacemement Parenteral Iron Replacement Therapy Erythropoesis Stimulating Androgens used in Therapy Factors used in conjunction with Iron conjunction with Iron Replacement therapy Replacement therapy Product Iron-polysaccharide Ferric Gluconate (Ferrlecit®) Epoetin Alfa Nandrolone Availability Complex (Fe-Tinic Iron sucrose (Venofer®) (Epogen®, Procrit®) (Durabolin®, Deca- Generic (Brand) 150® [OTC], Ferrex Iron dextran (Dexferrum®, INFeD®) Darbepoetin alfa Durabolin®) 150® [OTC], Hytinic® (Aranesp®) Oxymetholone [OTC], Niferex 150® (Anadrol®) [OTC], Niferex® [OTC], Nu-Iron 150® [OTC]) Ferrous Fumarate (Femiron® [OTC], Feostat® [OTC], Ferretts® [OTC], Ferro-Sequels® [OTC], Hemocyte® [OTC], Ircon® [OTC], Nephro-Fer® [OTC]) Ferrous gluconate (Fergon® [OTC]) Ferrous sulfate (Feosol® [OTC], Fer- Gen-Sol® [OTC], Fer- In-Sol® [OTC], Fer- Iron® [OTC], Feratab® [OTC], Slow Fe® [OTC]) Ferrous sulfate/ascorbate (Fero-Grad 500® [OTC], Vitelle®, Irospan® [OTC])
Student Name, PharmD Candidate 2007 Pharmacotherapy Presentation – Pharmaceutical Care Rotation University of Maryland School of Pharmacy Happy Harry’s Pharmacy Patient Care Center, Perryville, MD Mechanism All aforementioned products are All aforementioned products are iron salts, which get Both Epoetin-alfa and Both Nandrolone and of Action iron salts, which get incorporated into hemoglobin and increase the Darbepoetin-alfa cause Oxymetholone promote incorporated into hemoglobin oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood. erythropoesis by stimulating anabolism, and promote the and increase the oxygen- the division and differentiation production of erythropoetin and carrying capacity of the blood. of erythroid progenitor cells IGF1. The end result is an increase in hemoglobin and RBC volume. EFFICACY Both Epoetin-alfa and Both Nandrolone and These products are indicated for All these products are inidcated for use in Darbepoetin-alfa are indicated Oxymetholone are indicated for (Indication/Use, use in the prevention and the treatment of microcytic, hypochromic for use in the treatment of use in the treatment of anemia Clinical Data treatment of iron-deficiency anemia in patients with CRF, in of renal insufficiency, with or Support) anemias. anemia due to iron deficiency or blood loss, with or without dialysis. These without dialysis. These drugs when oral therapy for these conditions drugs are being included since are being included since there proves ineffective, or in dialysis patients. there drugs are usually given in drugs are usually given in conjunction with iron conjunction with iron replacement therapy if serum replacement therapy. ferritin is <100mcg/mL and transferrin saturation <20% SAFETY Interactions: Interactions: Interactions: Interactions: False positive on fecal Chloramphenicol may delay response to iron EtOH consumption may increase the effects of (Major Drug occult blood test therapy decreases the effect of oral anticoagulants Interactions, Increased these drugs may increase the effects of Pre-cautions, absorption/effect when Precautions: insulin and oral Contra- co-administered with Use with caution in asthmatics, people with Precautions: antidiabetics indications, >200mg vitamin C per hepatic impairment, or rheumatoid arthritis Use with caution in may increase the effects of Adverse Effects, 30 mg elemental iron Not recommended for children <4months old patients with a history ACTH and other adrenal Pregnancy Risk Co-administration of Anaphylaxis can occur following of seizures, HTN, steroids Category) iron and tetracyclines administration, possibly resulting in death angina, or CHF increased hepatotoxicity of decreases absorption of A test dose is needed to determine whether Use with caution in cyclosporine both drugs anaphylaxis will occur patients with Iron decreases the porphyria Precautions: absorption of Contraindications: Discontinue use monitor DM patients fluoroquinolones, Hypersensitivity to any component of the within 2 weeks of a closely levodopa, methyldopa, formulation successful renal may cause peliosis and penecillamine Hemochromatosis allograft hepatitis, Concurrent Hemolytic anemia Use with caution in hepatocellular administration of Anemias that are not due to iron deficiency patients at risk for carcinoma, changes in antacids, dairy thrombosis blood lipids, and products, H2 blockers, Adverse Effects: Iron stores must be increase the risk of and PPI’s may Flushing monitored during atherosclerosis decrease iron Dizziness therapy use in caution in absorption Fever elderly patients, they Chloramphenicol may N/V Contraindications: may be at a greater risk delay response to iron Hypersensitivity to of prostatic hyperplasia Student Name, PharmD Candidate 2007 Pharmacotherapy Presentation – Pharmaceutical Care Rotation University of Maryland School of Pharmacy Happy Harry’s Pharmacy Patient Care Center, Perryville, MD therapy Metallic taste human albumin, use with caution in HA mammalian cell- patients with epilepsy Precautions: Staining of skin at site of injection derived products, or or cardiac, renal, or Avoid in patients with chills polysorbate 80 hepatic disease peptic ulcer disease, Diaphoresis (Darbepoetin) may accelerate bone ulcerative colitis, or Athralgia Uncontrolled HTN maturation, decreasing enteritis Urticaria height potential Avoid administering -these last 6 effects may be delayed up to 48 hours Adverse Effects: continuously for >6 after IV administration, or 3-4 days after IM HTN Contraindications: months unless patient administration HA Those who have a is continuously Anaphylaxis Fever hypersensitivity to the bleeding Fatigue drug or any component Avoid using in patients Nausea of the formulation receiving frequent Pregnancy Risk category: C Athralgia Pregnant women blood transfusions Chest pain Infants Avoid use in Asthenia Those with carcinoma premature infants until Injection site pain of the breast or vitamin E stores are MI prostate repleted to avoid CVA Patients with nephrosis increase hemolysis TIA Contraindications Epoetin-alfa - seizure Adverse Effects: Hypersensitivity to any Darbepoetin – Acne active or inactive Gynocomastia ingredient in the preipheral edema, fluid overload, Priapism formualtion Nausea Hemochromatosis Pregnancy Risk category: C Diarrhea Hemolytic anemia Virilism Prostatic hyperplasia Adverse Effects: Peliosis hepatitis Stomach cramps Hepatic necrosis Nausea/vomiting Hepatocellular Dark stools carcinoma Constipation Suppression of clotting Heartburn factors Discolored urine CAD Stained teeth Peripheral edema Electrolyte Pregnancy Risk category: A abnormalities Impotence Testicular atrophy/dysfunction Clitoromegaly Dyslipidemia Student Name, PharmD Candidate 2007 Pharmacotherapy Presentation – Pharmaceutical Care Rotation University of Maryland School of Pharmacy Happy Harry’s Pharmacy Patient Care Center, Perryville, MD Menstrual irregularity jaundice
Pregnancy Risk category: X
Therapeutic Class/Agents Therapeutic Class/Agents Therapeutic Class/Agents Therapeutic Class/Agents
Dosage & Iron-polysaccharide Ferric Gluconate Epoetin-alfa – IV or SQ Nandrolone Administration 1. tablets or elixir – 1. Adults – Test dose of 2mL diluted in 1. Pedicatrics – 50 1. Women, 50-100mg 50 to 100mg BID NS 50mL over 60 minutes, 125mg Units/kg 3x/week Qweek 2. Adults – 50 to 100 2. Men, 100-200mg (Include renal 2. capsules – 150 to elemental iron/10mL by IV infusion and/or hepatic Units/kg 3x/week Qweek adjustments) 300 mg QD or slow injection 3. Adjustments – 3. Pediatrics, 25-50mg Ferrous Fumarate 2. Pediatrics – 1.5mg/kg (max 125mg) Increase dose 25% if Qweek 1. prophylaxis - 60 to diluted in 25mL NS infused over 60 Hgb does not increase 100mg QDay minutes by 2g/dL within 8 Oxymetholone – 1 to 5 weeks. Decrease dose mg/kg/day in one dose, 2. In elderly – up to Iron sucrose 25% if Hgb increases max dose 100mg/Day 200mg 3-4x/Day 1. during dialysis – 100mg 1-3x/week 1g/dL within a 2 week 3. Pediatrics – 4 to 6 2. PD patients – two 300mg infusions period. mg/kg/day in 3 over 1.5 hours 14 days apart with one Darbepoetin-alfa – IV or SQ divided doses 400mg infusion 14days later 0.45mcg/kg Qweek or 0.75mcg/kg QOweek, Ferrous gluconate 3. non-dialysis – 200mg slow infusion titrate to response. 1. prophylaxis – on 5 different days during a 2 week 60mg QDay period 2. Treatment - adults Iron dextran - administered IV bolus of - 60mg BID to <1mL/min or diluted in 250-1000mL QID NS infused over 1-6 hours 3. Treatment – 1. 0.5mL test dose should be given in adults, pediatrics, severe – 0.25mL test dose in pediatrics 2. Fe Deficiency – 4 to 6 mg/kg/day in Dose=0.0476*LBW(kg)*(normal Hgb – 3 divided doses observed Hgb)+(1mL/5kgLBW up to 14mL) 4. Treatment – 3. Blood loss – Replacement Iron (mg) = blood pediatrics, mild to loss mL’s * Hct moderate – 3 4. Max dose – Pediatrics <10kg, mg/kg/day QDay 1mL.Pediatrics 10-50kg, 2mL. Adults >50kg, 2mL. or in 2 divided doses Ferrous sulfate 1. Prophylaxis – Student Name, PharmD Candidate 2007 Pharmacotherapy Presentation – Pharmaceutical Care Rotation University of Maryland School of Pharmacy Happy Harry’s Pharmacy Patient Care Center, Perryville, MD 300mg QDay 2. Treatment – 300mg BID to QID, or 250mg ER Qday to BID Ferrous sulfate/ascorbate - One 525mg FeS/500mg Vit C tablet QDay Monitoring o Efficacy – Monitor o Efficacy – Monitor Hct, Hgb, serum o Efficacy – o Efficacy – Hgb, Hct, Hgb, serum Fe, Fe, TIBC, reticulocyte count, Monitor Hct, Hgb, Hct, reticulocyte (Efficacy and TIBC, reticulocyte transferrin saturation, serum ferritin, CBC with count Q3months Toxicity Parameters) count, transferrin and patient specific signs and differential, o Toxicity – LFT’s, saturation, serum symptoms of anemia reticulocyte count, BG, jaundice, and ferritin, and patient o Toxicity – anaphylaxis, pulmonary transferrin blood lipids specific signs and edema, convulsions, tachycardia, saturation, serum Q6months, prostate symptoms of anemia hematemesis, hepatic and renal ferritin, and patient exam Qyear o Toxicity - Gi impairment, acidosis, lethargy, coma specific signs and irritation, stomach symptoms of anemia ulcers, hematemesis, (2x weekly, then 2- lethargy, acidosis, 4x monthly) hepatic or renal o Toxicity – BP, impairment, and polycythemia, MI, coma CVA, TIA, seizures, peripheral edema, fluid overload
Patient Do not take within 2 You will need frequent blood tests while on Do not take any new Do not take any new Education hours before or 4 hours this medication medications without medications unless after taking an antacid If you have RA, you may have an increase in consulting prescriber approved by prescriber Do not take with swelling or pain in your joints If self-administering, Do not donate blood cereals, fiber- Exercise caution while driving after follow exact for at least 1 month containing foods, tea, treatment because of some side effects directions for use following use coffee, eggs, or milk Small meals, proper oral hygeine, and You will require Take as directed Take with water or lozenges or chewing gum may help with frequent blood tests to May cause nausea, juice on an empty nausea or metallic taste determine appropriate vomiting, and diarrhea stomach With any respiratory difficulty, acute GI dosage May cause a myriad of To enhance absorption, problems, rapid heartbeat, yellowing of the Do not change intake side effects (see above) try to take with a glass skin, or swelling of hands and feet, consult of dietary iron without
Student Name, PharmD Candidate 2007 Pharmacotherapy Presentation – Pharmaceutical Care Rotation University of Maryland School of Pharmacy Happy Harry’s Pharmacy Patient Care Center, Perryville, MD of orange juice physician consulting physician This medication will Report cause a false positive signs/symptoms of on a fecal occult blood edema, swollen test, which is a test extremities, used to screen for respiratory difficulty, colon cancer. Before or rapid weight gain taking an FOBT, If you experience inform your physician severe HA, acute back that you are on an iron pain, chest pain, supplement. tremors, or seizure, contact 911 Cost Iron-polysaccharide – Ferric Gluconate - $688.00 Epoetin-alfa - $2,123.88 Oxymetholone - $1,178.45 (1-month) o Capsules - $8.93 - Iron sucrose - $688.00 Darbepoetin - $3,584.36 Nandrolone - $83.96 $17.86 Iron dextran - $452.40 o Elixir – $21.91 Ferrous Fumarate – $24.99 Ferrous gluconate - $5.99 Ferrous sulfate - $18.99 Ferrous sulfate/ascorbate - all brands DC’ed References Lexicomp Lexicomp Lexicomp Lexicomp (Guidelines, Walgreens.com http://uuhsc.utah.edu/pharmacy/bulletins/venofer.html Walgreens.com Walgreens.com Drug Info Sources)
Student Name, PharmD Candidate 2007 Pharmacotherapy Presentation – Pharmaceutical Care Rotation University of Maryland School of Pharmacy Happy Harry’s Pharmacy Patient Care Center, Perryville, MD