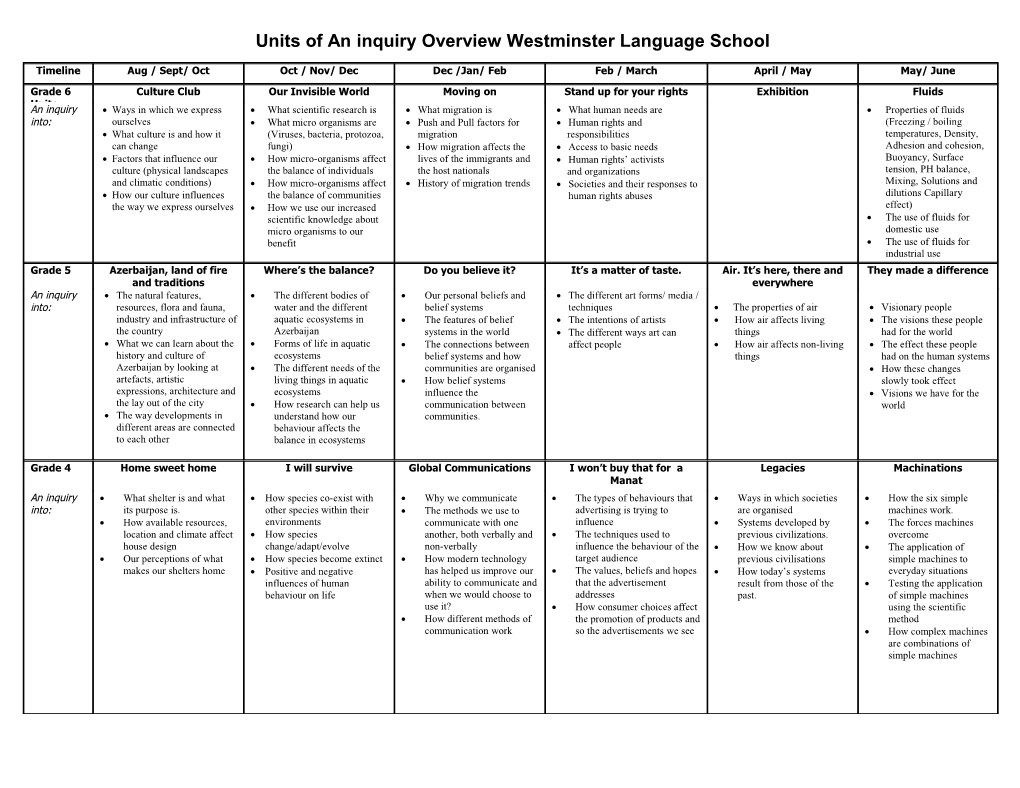
Units of An inquiry Overview Westminster Language School
Timeline Aug / Sept/ Oct Oct / Nov/ Dec Dec /Jan/ Feb Feb / March April / May May/ June
Grade 6 Culture Club Our Invisible World Moving on Stand up for your rights Exhibition Fluids Units An inquiry Ways in which we express What scientific research is What migration is What human needs are Properties of fluids into: ourselves What micro organisms are Push and Pull factors for Human rights and (Freezing / boiling What culture is and how it (Viruses, bacteria, protozoa, migration responsibilities temperatures, Density, can change fungi) How migration affects the Access to basic needs Adhesion and cohesion, Factors that influence our How micro-organisms affect lives of the immigrants and Human rights’ activists Buoyancy, Surface culture (physical landscapes the balance of individuals the host nationals and organizations tension, PH balance, and climatic conditions) How micro-organisms affect History of migration trends Societies and their responses to Mixing, Solutions and How our culture influences the balance of communities human rights abuses dilutions Capillary the way we express ourselves How we use our increased effect) scientific knowledge about The use of fluids for micro organisms to our domestic use benefit The use of fluids for industrial use Grade 5 Azerbaijan, land of fire Where’s the balance? Do you believe it? It’s a matter of taste. Air. It’s here, there and They made a difference and traditions everywhere An inquiry The natural features, The different bodies of Our personal beliefs and The different art forms/ media / into: resources, flora and fauna, water and the different belief systems techniques The properties of air Visionary people industry and infrastructure of aquatic ecosystems in The features of belief The intentions of artists How air affects living The visions these people the country Azerbaijan systems in the world The different ways art can things had for the world What we can learn about the Forms of life in aquatic The connections between affect people How air affects non-living The effect these people history and culture of ecosystems belief systems and how things had on the human systems Azerbaijan by looking at The different needs of the communities are organised How these changes artefacts, artistic living things in aquatic How belief systems slowly took effect expressions, architecture and ecosystems influence the Visions we have for the the lay out of the city How research can help us communication between world The way developments in understand how our communities. different areas are connected behaviour affects the to each other balance in ecosystems
Grade 4 Home sweet home I will survive Global Communications I won’t buy that for a Legacies Machinations Manat An inquiry What shelter is and what How species co-exist with Why we communicate The types of behaviours that Ways in which societies How the six simple into: its purpose is. other species within their The methods we use to advertising is trying to are organised machines work. How available resources, environments communicate with one influence Systems developed by The forces machines location and climate affect How species another, both verbally and The techniques used to previous civilizations. overcome house design change/adapt/evolve non-verbally influence the behaviour of the How we know about The application of Our perceptions of what How species become extinct How modern technology target audience previous civilisations simple machines to makes our shelters home Positive and negative has helped us improve our The values, beliefs and hopes How today’s systems everyday situations influences of human ability to communicate and that the advertisement result from those of the Testing the application behaviour on life when we would choose to addresses past. of simple machines use it? How consumer choices affect using the scientific How different methods of the promotion of products and method communication work so the advertisements we see How complex machines are combinations of simple machines Grade 3 Express Yourself Here Today, Gone It’s About Time Science in the kitchen How does my body work Communities Tomorrow An inquiry Expressing feelings, What resources are The orbit and rotation of Our kitchen set up The main organs of the Basic needs of people into: moods and ideas How living things share the earth Processes that cause changes body Different types of The artistic mediums resources and depend on each The different time cycles to food How my body systems communities people use to express other How time and weather are Changes to food work Facilities and themselves. The balance between affected by the earth’ s How the systems work infrastructures of Interpreting artistic consumption and regeneration movement together communities expressions Possible ways of managing Keeping my body healthy How working together available resources can help in meeting the needs of individuals and the community as a whole
Grade 2 Peace begins with us What’s in the bin? It Keeps on changing Journeys Movements, movements Say it in another way everywhere An inquiry The communities we’re part of What waste is When , How & why the school The types of journeys people How familiar things move The different art forms into: What people do in How we waste was built and how it has make and why and why The different artistic communities (work, play, The effect of waste on our changed & grown How we organise ourselves, and Different kinds of forces elements used in each art share) environment How children & staff have the choices we make when we How forces effect the form The problems that can come How we can cut down waste changed since the school was want to travel movement or shape of an Differences and similarities up with in or between by reusing, reducing and built How maps are used to plan object between the different art communities. recycling How we can find out about journeys What energy is and how forms How we can make Our responsibilities in changes that have taken place forces and energy are Examples of stories that communities work together keeping our environment safe How the school might develop connected. integrate the different art and solve problems and clean and improve What the forces in Nature are forms How the properties of The connections between the How we design things to materials affect reusing and changes in the school and other make them speed up or slow recycling changes around us down more easily Grade 1 How do I know? Food, Glorious food Water, water, Learning about the past Let’s celebrate Colour me a rainbow everywhere (throughout the year) An inquiry What our senses are and Different types of food How older people can share How nature uses colour for into: how we use them How food spoils Where we find water with us about life in the past Why we celebrate many different purposes How our senses help us Different ways to pack, store What we use water for How artefacts, personal records What we celebrate How people use colour for stay safe and healthy and preserve food How we process and save and photos can tell us about life The traditional aspects of many different purposes How we use our senses to How these techniques help water for consumption in the past celebrations How we can use colours learn about new things keep food longer The different journeys that How places can tell us about The reasons why different that nature has made How our senses change our water can make the past cultures celebrate similar How we can make and perceptions of things Different states of water How the past was different events in different ways change colours by mixing and separating
Kindergart Let’s play! Make it move Plants in our life Tell me a story en different kinds of toys and games Different types of transport and their uses Natural and manmade environments Stories with puppets or pictures, plays, poetry or songs An inquiry who do we play with Why different forms of transport are suitable Life cycles of plants and trees for different jobs How imagination helps us to create stories into: what we need to do to play together What they need to grow how toys work How transport moves What do we like to have in a garden How we need words and pictures to express why we play How forces affect forms of transport our imagination what we learn when we play Structure of stories why and how stories are created and told stories from different cultures
Pre-K All about me Our School We make Art All about animals The school buildings and the school ground An inquiry Our Physical differences What we can say about our art How animals look Who works in the school, what job they do, into: Our feelings What makes our art special Where animals live what tools help them to do their jobs Our friends and Families Ways to show our art to others What animals need and have in their homes Routines and systems that help us learn