WHS Risk Assessment & Control Form
Activity / Task / Location: “Servicing of automatic aerosol dispensers” Approved By: Peter Vrachas Signature and Date: Developed by: Mark Gordon & Jonathan Stanley Date: 22/05/07 Last review July 2012
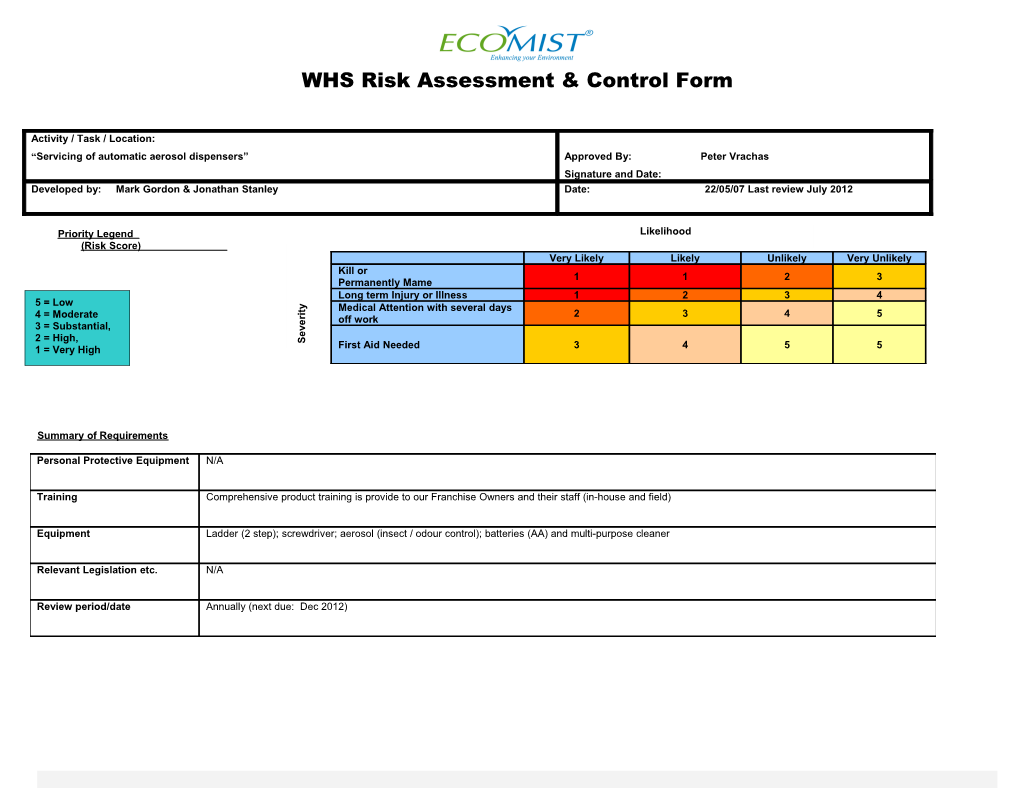
Priority Legend Likelihood (Risk Score) Very Likely Likely Unlikely Very Unlikely Kill or 1 1 2 3 Permanently Mame Long term Injury or Illness 1 2 3 4 5 = Low y
t Medical Attention with several days i 2 3 4 5 4 = Moderate r off work e
3 = Substantial, v 2 = High, e S 1 = Very High First Aid Needed 3 4 5 5
Summary of Requirements
Personal Protective Equipment N/A
Training Comprehensive product training is provide to our Franchise Owners and their staff (in-house and field)
Equipment Ladder (2 step); screwdriver; aerosol (insect / odour control); batteries (AA) and multi-purpose cleaner
Relevant Legislation etc. N/A
Review period/date Annually (next due: Dec 2012) WHS Risk Assessment & Control Form
Hazard Identification Risk Assessment Control
L W s b W ( P R e e i r k h h i i v
s o e t a a e h k r
l Who is responsible t t r i i e
h
What are the steps of t i i c S
t What methods can be used to reduce the likelihood y s
What are the o y o c the activity / items of to implement the Date Finalised o t u o
potential hazards h d l
r and/or the severity equipment e d e
changes )
Remove aerosol Fall from ladder 5 5 5 The dispenser is not to be positioned higher than 2 Franchise Owner 21/05/2012 dispenser from wall metres. Ladder must be fit for purpose ( minimum 100kg capacity) and opened fully on dry level floor. Ladder to be maintained in good condition with non-slip feet on legs
Unscrew aerosol Leaking aerosol 5 5 5 Maintain dispenser and point away from eyes. Refer Franchise Owner 22/05/07 MSDS sheet. Wipe up any spillage and wear shoes with non-slip soles,
Replace aerosol Leaking aerosol 5 5 5 Insert aerosol carefully – remove immediately if signs of Franchise Owner 21/05/2012 leaking. Refer usage instructions on can. Refer MSDS sheet. Wipe up any spillage and wear shoes with non-slip soles,
Test functionality of Aerosol spray in 5 5 5 Point dispenser away from face and eyes when testing. Franchise Owner 21/05/2012 dispenser face or eyes Refer MSDS sheets and usage instructions on can
Clean dispenser cover Cleaning solution 5 5 5 Clean and dry area immediately to remove spillage. Wipe Franchise Owner 22/05/07 leaks on floor up any spillage and wear shoes with non-slip soles.
Replace dispenser on Fall from ladder 5 5 5 The dispenser is not to be positioned higher than 2 Franchise Owner 21/05/2012 wall metres. Ladder must be fit for purpose ( minimum 100kg capacity) and opened fully on dry level floor. Ladder to be maintained in good condition with non-slip feet on legs
Placement of Children or 5 5 5 Equipment to be kept in close proximity to service Franchise Owners 06/12/2011 equipment on site aged/infirm person at all times WHS Risk Assessment & Control Form accessing maintenance tools Tool box obstacles 5 5 5 Ensure tool box is not placed in thoroughfares. Franchise Owners 22/05/07 WHS Risk Assessment & Control Form
What is a hazard?
A Could people be injured or made sick by things such as: B What could go wrong? Noise What if equipment is misused? Light What might people do that they shouldn’t Radiation How could someone be killed? Toxicity How could people be injured? Infection What may make people ill? High or low temperatures Are there any special emergency procedures required? Electricity Moving or falling things (or people) Flammable or explosive materials Things under tension or pressure (compressed gas or liquid; springs) Any other energy sources or stresses Biohazardous material Laser C Can workplace practices cause injury or sickness? D How might these injuries happen to people? Are there heavy or awkward lifting jobs? Broken bones Can people work in a comfortable posture? Eye damage If the work is repetitive, can people take breaks? Hearing problems Are people properly trained? Strains or sprains Do people follow correct work practices? Cuts or abrasions Are there adequate facilities for the work being performed? Bruises Are universal safety precautions for biohazards followed? Burns Is there poor housekeeping? Look out for clutter Lung problems including inhalation injury/ infection Torn or slippery flooring Skin contact Sharp objects sticking out Poisoning Obstacles Needle-stick injury E Imagine that a child was to enter your work area F What are the special hazards? What would you warn them to be extra careful of? What occurs only occasionally-for example during maintenance and other irregular work? What would do to reduce the harm to them? WHS Risk Assessment & Control Form
How to Assess Risk
Step 3 – Calculate the Risk Step 1 – Consider the Consequences Step 2 – Consider the Likelihood A. Take Step 1 rating and select the correct column. What are the consequences of this incident occurring? What is the likelihood of the consequence identified in step 1 Consider what could reasonably have happened as well as what happening? Consider this without new or interim controls in B. Take Step 2 Rating and select the correct line. actually happened. place. Look at the descriptions and choose the most suitable Look at the descriptions and choose the most suitable C. The calculated risk score is where the two Consequence. Likelihood. ratings cross on the matrix below. SEVERITY LIKELIHOOD Process Environ- LIKELIHOOD Personal Consequence $ Damage Interruptio mental Description Damage Likelihood Very Likely Unlikely Very n Impact Likely Unlikely
Very The event is expected to occur in most circumstances Y Major Extensive >$100K > 1 week Communit T Likely I Maj 1 1 2 3 (Maj) injury or y alarm R E
death V Likely The event could occur at some time E Moderate Medical $50 – $100K 1 day- 1 Off site S Mod 1 2 4 (Mod) treatment week impact 3 Unlikely The event could occur, but only rarely Minor First aid $5 – 50K 1 hour – 1 On site Min 2 3 4 5 (Min) treatment day impact Very The event may occur, but probably never will. Insignificant No <5K <1 hour Potential Ins 3 4 5 5 (Ins) treatment impact unlikely
* -” The magnitude of consequences of any event, should it occur, and the likelihood of the event and its associated consequences, are assessed in the context of the effectiveness of existing strategies and controls.” Section 3.4.3 AS/NZS 4360:2004, Risk Management
Risk Control Risk control is a method of managing the risk with the primary emphasis on controlling the hazards at source. For a risk that is assessed as “high”, steps should be taken immediately to minimize risk of injury. The method of ensuring that risks are controlled effectively is by using the “hierarchy of controls”. The Hierarchy of Controls are:
Order No. Control Example Firstly Eliminate Removing the hazard, eg taking a hazardous piece of equipment out of service. Secondly Substitute Replacing a hazardous substance or process with a less hazardous one, eg substituting a hazardous substance with a non-hazardous substance. Thirdly Isolation Isolating the hazard from the person at risk, eg using a guard or barrier. Fourthly Engineering Redesign a process or piece of equipment to make it less hazardous. Fifthly Administrative Adopting safe work practices or providing appropriate training, instruction or information. Sixthly Personal Protective Equipment The use of personal protective equipment could include using gloves, glasses, earmuffs, aprons, safety footwear, dust masks.