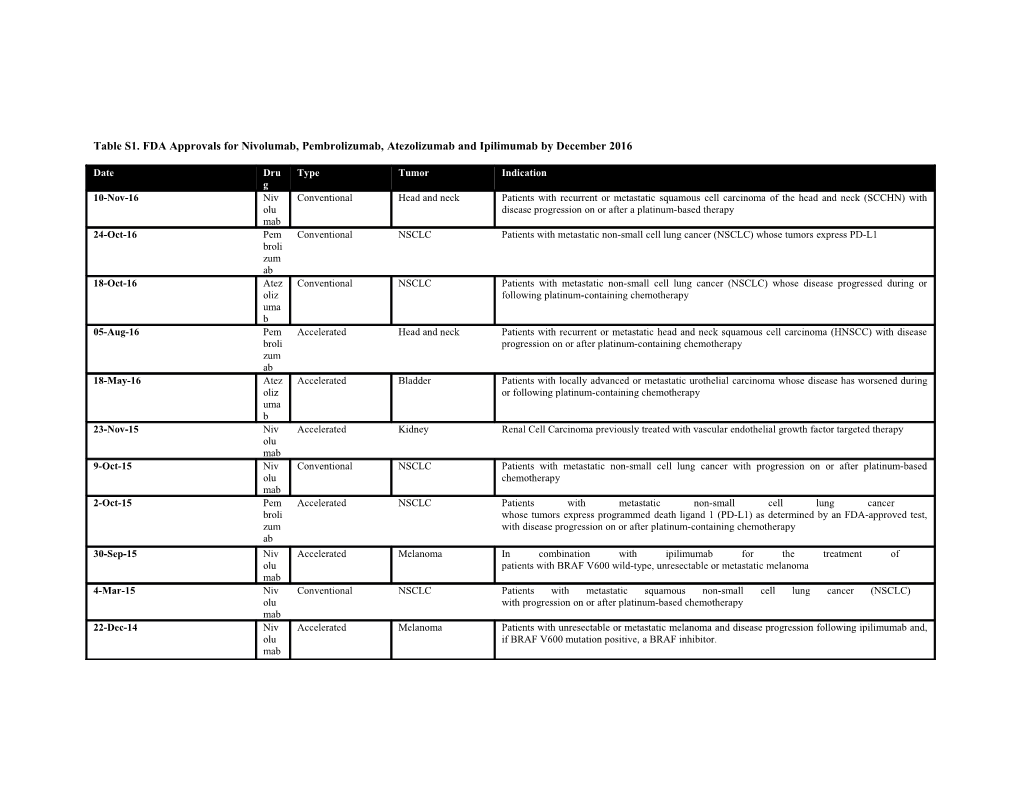
Table S1. FDA Approvals for Nivolumab, Pembrolizumab, Atezolizumab and Ipilimumab by December 2016
Date Dru Type Tumor Indication g 10-Nov-16 Niv Conventional Head and neck Patients with recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (SCCHN) with olu disease progression on or after a platinum-based therapy mab 24-Oct-16 Pem Conventional NSCLC Patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors express PD-L1 broli zum ab 18-Oct-16 Atez Conventional NSCLC Patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose disease progressed during or oliz following platinum-containing chemotherapy uma b 05-Aug-16 Pem Accelerated Head and neck Patients with recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) with disease broli progression on or after platinum-containing chemotherapy zum ab 18-May-16 Atez Accelerated Bladder Patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma whose disease has worsened during oliz or following platinum-containing chemotherapy uma b 23-Nov-15 Niv Accelerated Kidney Renal Cell Carcinoma previously treated with vascular endothelial growth factor targeted therapy olu mab 9-Oct-15 Niv Conventional NSCLC Patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer with progression on or after platinum-based olu chemotherapy mab 2-Oct-15 Pem Accelerated NSCLC Patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer broli whose tumors express programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) as determined by an FDA-approved test, zum with disease progression on or after platinum-containing chemotherapy ab 30-Sep-15 Niv Accelerated Melanoma In combination with ipilimumab for the treatment of olu patients with BRAF V600 wild-type, unresectable or metastatic melanoma mab 4-Mar-15 Niv Conventional NSCLC Patients with metastatic squamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) olu with progression on or after platinum-based chemotherapy mab 22-Dec-14 Niv Accelerated Melanoma Patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma and disease progression following ipilimumab and, olu if BRAF V600 mutation positive, a BRAF inhibitor. mab 4-Sep-14 Pem Accelerated Melanoma Patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma and disease progression following ipilimumab and, broli if BRAF V600 mutation positive, a BRAF inhibitor zum ab 25-Mar-11 Ipili Conventional Melanoma Inresectable or metastatic melanoma mu mab
Table S2. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events V4.0. for selected irAEs.
Grad Colitis AST Rash Pneumonitis Hypothyroidism e elevation 1 Asymptomatic, >ULN - Papules and/or pustules Asymptomatic, Asymptomatic, pathologic or 3.0 x covering radiographic intervention not radiographic ULN findings only indicated findings only 2 Abdominal pain; >3.0 - Rash covering 10-30% Symptomatic; Symptomatic, not mucus or blood in 5.0 x BSA, which may or may medical interfering with ADL; stool ULN not be associated with intervention thyroid replacement symptoms of pruritus or indicated; limiting indicated tenderness; associated with instrumental ADL psychosocial impact; limiting instrumental ADL 3 Severe abdominal >5.0 – Rash covering >30% BSA, Severe symptoms; Symptoms interfering pain; change in 20.0 x which may or may not be limiting self care with ADL; bowel habits; ULN associated with symptoms ADL; oxygen hospitalization medical of pruritus or tenderness; indicated indicated intervention limiting self-care ADL; indicated; associated with local peritoneal signs superinfection with oral antibiotics indicated 4 Life-threatening >20.0 x any % BSA, which may or Life-threatening Life-threatening consequences; ULN may not be associated with respiratory myxedema coma urgent intervention symptoms of pruritus or compromise; urgent indicated tenderness and are intervention associated with extensive indicated (e.g., superinfection with IV tracheotomy or antibiotics indicated; intubation) lifethreatening consequence 5 Death — Death Death Death
Differences between CTCAE version 3 and version 4 in grade 1/2 AST elevation does not vary the final data and rash for grade 3 which decreases the area covered to 30% instead of 50%. Table S3. Subgroup analyses stratified by type of control-arm. The control-arm: Chemotherapy (DTIC, Docetaxel, CP, CPem, VP16+Plt, and ChT: N=15) vs. Biological Therapy (Hodi et al.; Motzer et al.: N=2) vs. Placebo (Kwon et al.; Eggermont et al.; Beer et al.: N=3)
Immune- Biological Chemotherapy Placebo related Therapy P for difference RR (95% CI) RR (95% CI) toxicity RR (95% CI) All- grade P for chemo vs. bio = 0.53 Colitis 3.71 (1.44-9.58) 7.75 (1.07-56.3) 10.7 (5.61-20.3) P for chemo vs. placebo = 0.10 P for bio vs. placebo = 0.77 P for chemo vs. bio = 0.39 AST 1.78 (0.96-3.30) 0.65 (0.13-3.29) 2.49 (1.32-4.67) P for chemo vs. placebo = 0.63 P for bio vs. placebo = 0.30 P for chemo vs. bio = 0.21 Rash 2.62 (1.76-3.91) 1.37 (0.18-10.3) 3.52 (2.48-4.98) P for chemo vs. placebo = 0.69 P for bio vs. placebo = 0.17 P for chemo vs. bio = 0.04 Hypothyroidism 7.63 (4.14-14.1) 1.03 (0.22-4.81) 10.3 (4.12-25.5) P for chemo vs. placebo = 0.61 P for bio vs. placebo = 0.03 P for chemo vs. bio = <.001 Pneumonitis 3.75 (2.02-6.96) 0.27 (0.16-0.46) 11.1 (2.09-58.7) P for chemo vs. placebo = 0.26 P for bio vs. placebo = 0.002 Grade 3/4 P for chemo vs. bio = 0.40 Colitis 2.63 (0.96-7.18) 10.1 (0.62-166.7) 25.0 (6.05-103.6) P for chemo vs. placebo = 0.03 P for bio vs. placebo = 0.59 P for chemo vs. bio = 0.59 AST 2.50 (0.92-6.83) 0.78 (0.03-19.0) 7.23 (0.45-117.2) P for chemo vs. placebo = 0.48 P for bio vs. placebo = 0.39 P for chemo vs. bio = 0.64 Rash 1.56 (0.70-3.47) 1.03 (0.23-4.69) 3.32 (0.53-2.09) P for chemo vs. placebo = 0.48 P for bio vs. placebo = 0.39 P for chemo vs. bio = 0.95 Hypothyroidism 0.86 (0.27-2.73) 0.78 (0.03-19.0) 3.95 (0.44-35.7) P for chemo vs. placebo = 0.26 P for bio vs. placebo = 0.43 P for chemo vs. bio = 0.04 Pneumonitis 2.63 (1.13-6.10) 0.53 (0.20-1.43) 6.81 (0.80-57.6) P for chemo vs. placebo = 0.44 P for bio vs. placebo = 0.06 Table S4. Subgroup analyses stratified by type of tumor (melanoma vs. lung vs. others)
Immune- Melanoma Lung CA Other CA related Relative Risk Relative Risk (95% Relative Risk P for difference toxicity (95% CI) CI) (95% CI) All- grade P for melanoma vs. lung = 0.45 Colitis 9.53 (4.94-18.4) 4.96 (1.10-22.3) 3.24 (0.46-22.8) P for melanoma vs. others = 0.41 P for lung vs. others = 0.89 P for melanoma vs. lung = 0.37 AST 2.35 (0.98-5.64) 1.42 (0.89-2.25) 1.26 (0.43-3.68) P for melanoma vs. others = 0.32 P for lung vs. others = 0.70 P for melanoma vs. lung = 0.84 Rash 2.96 (1.94-4.51) 2.70 (1.52-4.79) 1.70 (0.54-5.35) P for melanoma vs. others = 0.30 P for lung vs. others = 0.40 P for melanoma vs. lung = 0.54 Hypothyroidism 5.93 (2.33-15.1) 7.83 (3.66-16.8) 6.19 (1.44-26.5) P for melanoma vs. others = 0.97 P for lung vs. others = 0.71 P for melanoma vs. lung >0.99 Pneumonitis 5.66 (1.06-30.3) 3.67 (1.83-7.39) 2.45 (0.26-23.0) P for melanoma vs. others = 0.39 P for lung vs. others = 0.27 Grade3/4 P for melanoma vs. lung = 0.60 Colitis 6.18 (1.82-21.0) 3.63 (0.78-16.9) 6.81 (0.68-68.5) P for melanoma vs. others = 0.88 P for lung vs. others = 0.58 P for melanoma vs. lung = 0.23 AST 5.29 (0.78-35.8) 1.66 (0.57-4.80) 1.99 (0.65-6.11) P for melanoma vs. others = 0.29 P for lung vs. others = 0.97 P for melanoma vs. lung = 0.41 Rash 3.40 (0.95-12.1) 1.70 (0.65-4.44) 1.01 (0.25-4.08) P for melanoma vs. others = 0.15 P for lung vs. others = 0.43 P for melanoma vs. lung = 0.88 Hypothyroidism 0.94 (0.22-4.15) 1.12 (0.24-5.19) 2.07 (0.19-22.8) P for melanoma vs. others = 0.60 P for lung vs. others = 0.68 P for melanoma vs. lung = 0.40 Pneumonitis 1.15 (0.15-8.84) 3.21 (1.22-8.46) 1.73 (0.36-8.20) P for melanoma vs. others = 0.93 P for lung vs. others = 0.15