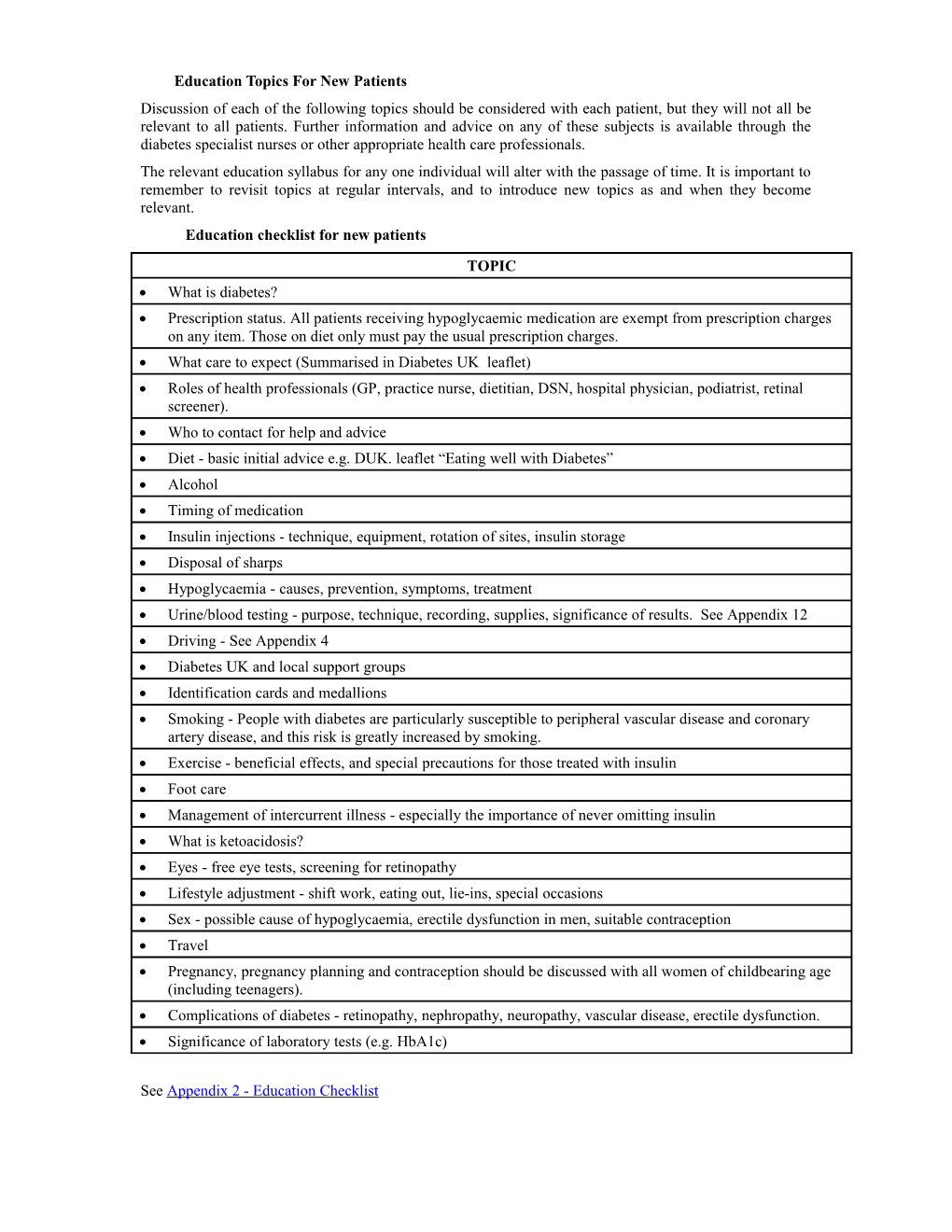
Education Topics For New Patients Discussion of each of the following topics should be considered with each patient, but they will not all be relevant to all patients. Further information and advice on any of these subjects is available through the diabetes specialist nurses or other appropriate health care professionals. The relevant education syllabus for any one individual will alter with the passage of time. It is important to remember to revisit topics at regular intervals, and to introduce new topics as and when they become relevant. Education checklist for new patients TOPIC What is diabetes? Prescription status. All patients receiving hypoglycaemic medication are exempt from prescription charges on any item. Those on diet only must pay the usual prescription charges. What care to expect (Summarised in Diabetes UK leaflet) Roles of health professionals (GP, practice nurse, dietitian, DSN, hospital physician, podiatrist, retinal screener). Who to contact for help and advice Diet - basic initial advice e.g. DUK. leaflet “Eating well with Diabetes” Alcohol Timing of medication Insulin injections - technique, equipment, rotation of sites, insulin storage Disposal of sharps Hypoglycaemia - causes, prevention, symptoms, treatment Urine/blood testing - purpose, technique, recording, supplies, significance of results. See Appendix 12 Driving - See Appendix 4 Diabetes UK and local support groups Identification cards and medallions Smoking - People with diabetes are particularly susceptible to peripheral vascular disease and coronary artery disease, and this risk is greatly increased by smoking. Exercise - beneficial effects, and special precautions for those treated with insulin Foot care Management of intercurrent illness - especially the importance of never omitting insulin What is ketoacidosis? Eyes - free eye tests, screening for retinopathy Lifestyle adjustment - shift work, eating out, lie-ins, special occasions Sex - possible cause of hypoglycaemia, erectile dysfunction in men, suitable contraception Travel Pregnancy, pregnancy planning and contraception should be discussed with all women of childbearing age (including teenagers). Complications of diabetes - retinopathy, nephropathy, neuropathy, vascular disease, erectile dysfunction. Significance of laboratory tests (e.g. HbA1c)
See Appendix 2 - Education Checklist