Ex ercise 6 (Transimission of electricity) Suggested Answers
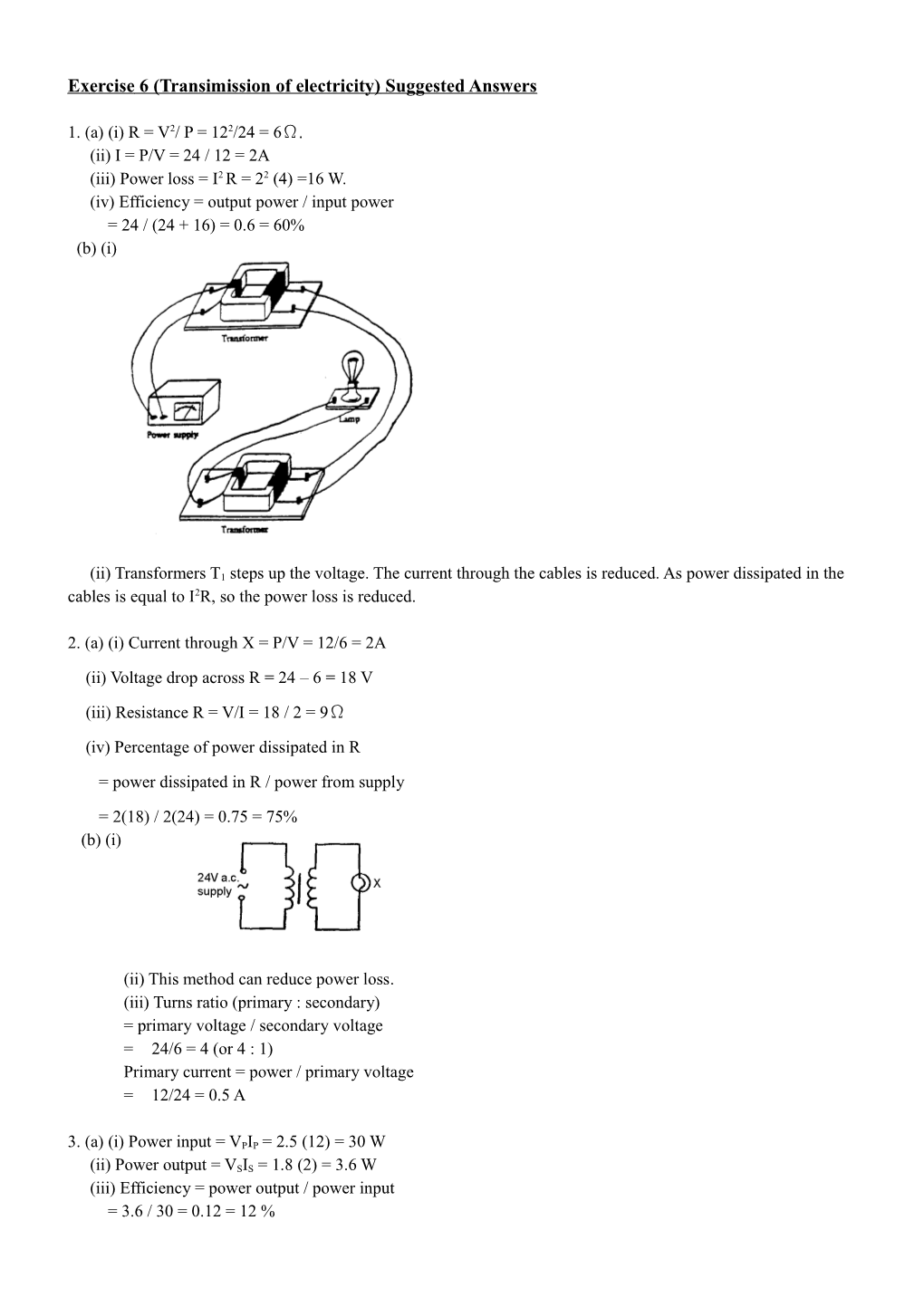
1. (a) (i) R = V2/ P = 122/24 = 6Ω. (ii) I = P/V = 24 / 12 = 2A (iii) Power loss = I2 R = 22 (4) =16 W. (iv) Efficiency = output power / input power = 24 / (24 + 16) = 0.6 = 60% (b) (i)
(ii) Transformers T1 steps up the voltage. The current through the cables is reduced. As power dissipated in the cables is equal to I2R, so the power loss is reduced.
2. (a) (i) Current through X = P/V = 12/6 = 2A
(ii) Voltage drop across R = 24 – 6 = 18 V
(iii) Resistance R = V/I = 18 / 2 = 9Ω
(iv) Percentage of power dissipated in R
= power dissipated in R / power from supply
= 2(18) / 2(24) = 0.75 = 75% (b) (i)
(ii) This method can reduce power loss. (iii) Turns ratio (primary : secondary) = primary voltage / secondary voltage = 24/6 = 4 (or 4 : 1) Primary current = power / primary voltage = 12/24 = 0.5 A
3. (a) (i) Power input = VPIP = 2.5 (12) = 30 W
(ii) Power output = VSIS = 1.8 (2) = 3.6 W (iii) Efficiency = power output / power input = 3.6 / 30 = 0.12 = 12 % (b) A2 decreases because when R increases, since the secondary voltage is unchanged, so current in the secondary (= Vs/R) would decrease. Since the ratio (current in primary / current in secondary) is a constant, so current in the primary coil decreases.
(c) (1) Use thicker wires to reduce resistance, thereby reduce the heating effect. (2) Use laminated core to reduce eddy currents.
4. (a) Power wasted internally P = I V = 0.30 × 9.0 = 2.7 W (b) Input power = 2.7 / 0.9 = 3.0 W Mains current = 3 / 230 = 1.30 × 10-2 A (c) Any one from the following
1) The ac current in the primary coil magnetises, demagnetises and remagnetises the core continuously in opposite directions. Energy is required both to magnetise and to demagnetise the core and this energy is wasted because it simply heats the core. The energy wasted may be reduced by choosing a material for the core which is easily magnetised and demagnetised, ie a magnetically soft material such as iron, or a special alloy, rather than steel.
2) As the core is made of soft iron and is in a changing magnetic field, eddy currents are induced in it, and as a result, the core heats up. The energy losses due to eddy currents can be reduced by using a laminated core.
5. (a)
(b) • A.c.voltage at primary generates alternating B field • Magnetic field links with secondary coil through the core • Changing magnetic field induces emf in secondary (c)
MC answers
1-5 B D C C B 6-10 A C A D B
Explanations to selected mc 1. Power input = power output
1(4) = Is (20) + 0.8 => Is = 0.16 A 2. For statement 1, the potential difference across P and R is 10 V while that across P and Q is 5 V.
For statement 3, VP IP x 0.8 = 40 W => IP = 0.25 A 3. Let I be the required rms current. The period is 2 ms. By considering the area, we have
2 Irms = I 17 = 4.12 A
4. V2 / R = P => R = 402 / 80 = 20 Current in cables I = V / R = 40 / 20 = 2A So V = P / I = 200000 / 2 = 100000 V
V0 5 5. Rms voltageVrms = 3.536V 2 2
V 2 3.5362 Average power dissipated = 0.25W R 50
6. Statement 2. A transformer cannot work on a d.c.
7. Efficiency = output power/input power = (20 x 3) / (220 x 0.5) = 54.5%
8. Current in lamp I = P/V = 9/3 = 3A Current in PQ = 3/40 A 2 2 Power loss in cables = I R = (3/40) x 15 = 0.0844 W
2 2 9. Max power = Vmax / R = 110 / 20 = 605 W
2 2 2 (V0 / 2) V0 10. Average power = Vrms / R = R 2R
2 V0 For the square wave,