231/2 BIOLOGY JUNE, 2015 2 HOURS
KASSU JOINT EXAMINATION Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY Paper 2
M A R K I N G S C H E M E
SECTION A
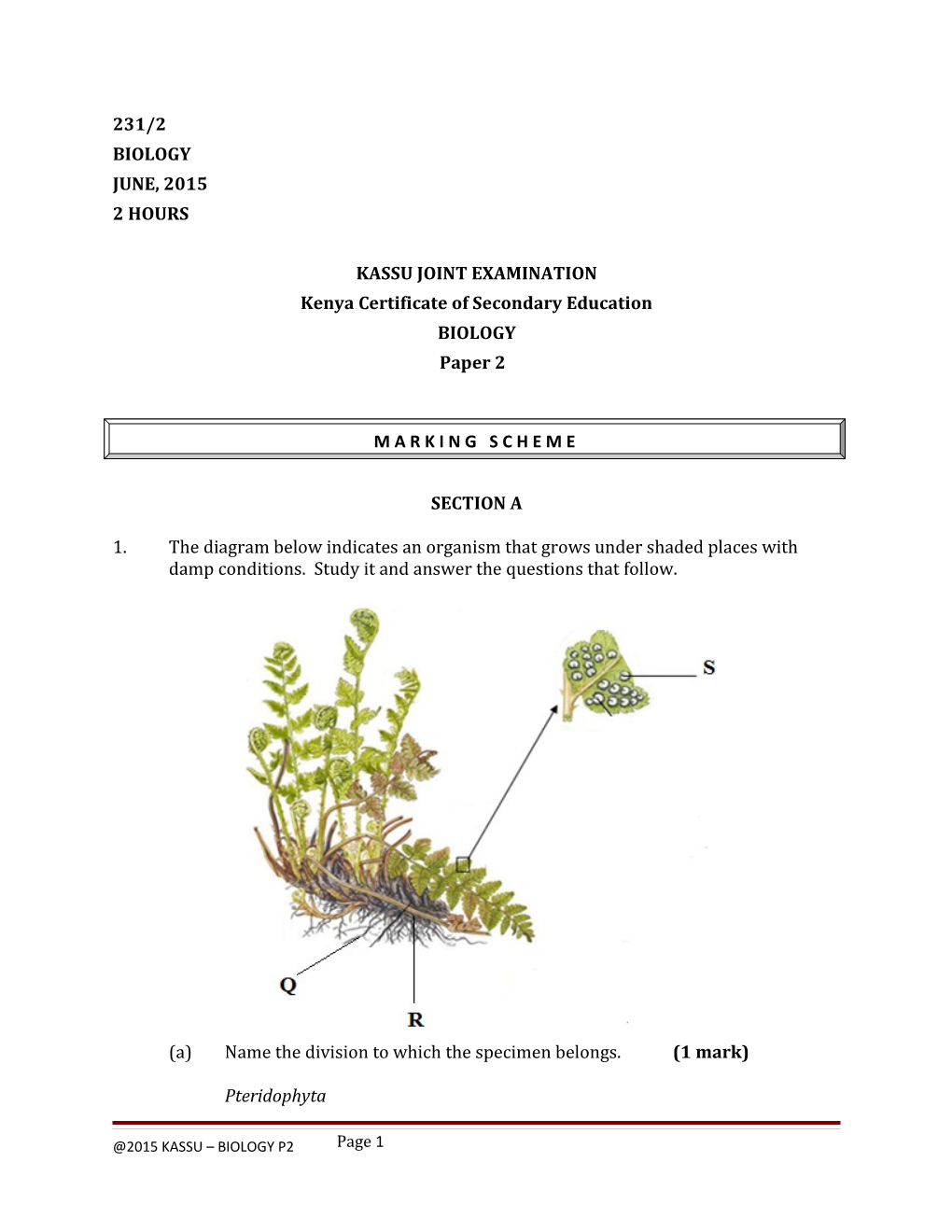
1. The diagram below indicates an organism that grows under shaded places with damp conditions. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
(a) Name the division to which the specimen belongs. (1 mark)
Pteridophyta
@2015 KASSU – BIOLOGY P2 Page 1 (b) Name and state the functions of the parts labelled Q, R and S. (6 marks)
Q Name - Adventitious root; (reject roots) – Function - Anchorage/absorption of water
R Name - Rhizome (underground stem) Function - For storage of food and water
S Name - Sorus Function - Contains (Sporangium with a sexually reproductive)spores
(c) Name the two body forms of the organism in its alternation of generation. (2 marks) . Gametophyte . Sporophyte
2. In cattle the gene for red colour is represented by letter R and that of white colour as W. A Red bull and a white cow were crossed and all the offspring were Roan.
(a) Give a reason for the appearance of roan cattle in F1 generation. (1 mark) Incomplete/co-dominance (b) Using a punnet square work out the F2 generation. (4 marks)
R W; Gametes
R RR; RW; All off springs
Correct crossing W RW WW;
(c) State the genotypic and phenotypic ratio of the F2 offspring above. (2 marks) Phenotypic ratio ; 1 Red : 2 Roan : 1 white Genotypic ratio ;1RR : 2RW :1WW
@2015 KASSU – BIOLOGY P2 Page 2 (d) Name the molecule that carries genetic information in eukaryotic cells. (1 mark) Deoxyribon nucleic acid
3. Study the diagram of the organism shown below then answer the questions that follow.
(a) State the phylum to which the organism belongs. (1mark)
Arthropoda (b) With reasons state the class to which the organism belongs. Class Insecta (1 mark) Reasons : Three body parts/Head, thorax and abdomen Three pairs of legs/six legs A pair of antennae (3 marks)
(c) Name two human diseases of which the organism is a vector. (2 marks)
- Cholera - Typhoid - Amoebic dysentry
(d) What type of metamorphis does the organism show? (1 mark)
Complete metamorphosis
@2015 KASSU – BIOLOGY P2 Page 3 4. The epidermis of a leaf is adapted to have the specialized cells known as the guard cell such as shown below.
Guard cell ●
● X ●
Epidermal cell ●
(a) (i) Name the structure labelled X on the diagram. (1 mark)
Stoma Reject Stomata
(ii) State three adaptations of the guard cell to its function of opening and closing of stomata in plants. (3 marks)
The was of the guard cell is differentially thickened with the inner membrane to open the stoma when turgid. The cell is rich in mitochondria for photosynthesis which creates sugar for high osmotic gradient of the cell which draws in water from adjacent cells. Bean and sauge shaped to create a pore/aperture/stomata for gaseous exchange.
(iii) Describe the photosynthetic mechanism of opening and closing of stomata. (4 marks)
During day time. The guard cell traps light for photosynthesis; which results into sugar that is a osmotically active; the sugars draw in water by osmosis; from epidermal cells making it turgid and opening stomata/converse is correct.
(b) The mammalian lung is known to have adapted the mammal to terrestrial habitat by having a pleural membrane.
(i) State two functions of a pleural membrane that gives the mammal advantage over other organisms. (2 marks)
Secretes pleural fluids; Holds the lungs in pleural cavity Protection of lungs
@2015 KASSU – BIOLOGY P2 Page 4 (ii) Name two diseases of the respiratory system. (2 marks) Lung cancer Asthma Bronchitis
5. The human ear has the following structures; (i) Auditory meatus (ii) ear drum (iii) eustachian tube (iv) ear ossicles and (v) cochlea.
(a) Name two function of the mammalian ear. (2 marks) Hearing Body balance and posture
(b) For each of the structures above, state its function. (5 marks)
(i) Auditory meatus
Transmission of sound waves into the eardrum
(ii) Eardrum
Vibrates and amplify soundwaves
(iii) Eustachian tube
Balancing the pressure (iv) Ear ossicles
Regulates the position of the head and body posture (v) Cochlea
Contains perilymph which moves on detecting vibration transmitting stimulus to the receptor cells.
(c) Name a defect caused by damage of the cochlea. (1mark) Permanent deafness
@2015 KASSU – BIOLOGY P2 Page 5 6. A physiologist working to determine the amount of glucose levels in the iliac artery and hepatic vein per hour after a heavy carbohydrate meal in mg/100ml of blood collected and recorded the following data in a 24 hour period. Study the data and use it to answer the questions that follow.
Amount of Iliac 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 8 12 20 24 20 24 22 28 20 glucose in artery mg/100ml
Hepatic 20 22 24 24 24 24 18 12 6 4 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 vein Time of 00 1.00 2.00 3.00 4.00 5.00 6.00 7.00 8.00 9.00 10.00 11.0 12.0 13.0 14.0 15.0 16.00 day
(a) On the same axes plot a line graph to show amount of glucose in mg/100ml of blood against time of the day in a 24hour day up to 4.00 p.m. (8 marks)
@2015 KASSU – BIOLOGY P2 Page 6 (b) At what time of day was the amount of glucose the same in the iliac artery and iliac vein? (1 mark)
8.00 a.m
(c) Account for the rise in glucose levels in the iliac artery peaks at: (3 marks)
(i) 11.00 hrs a.m.
The peak is achieved at 11.00 hrs due breakfast involving carbohydrate intake; digestion; absorbed directly into the blood stream;
(ii) 14:00 hrs p.m.
The peak at 14.00 hrs is accounted for by intake of a heavy carbohydrate meal at lunch time taken at 12.00 hrs p.m; and the peak after complete digestion; and absorption; at 14.00 hrs.
@2015 KASSU – BIOLOGY P2 Page 7 (d) Which organ and hormone is responsible for raising the sugar levels in Hepatic vein between 00.00 hrs – 2.00 hrs a.m. (2 marks)
Organ - Liver Hormone - Glucagon (e) Name the hormone responsible for the fall of glucose and the complex polysaccharide sugar that forms between 14:00 hrs p.m. and 6.00 hrs p.m.
(2 marks) Hormone - Insulin Complex polysaccharide - glycogen (f) Name a disease that would have resulted if the hormone in (e) above failed to be produced. (2 marks)
Diabetes mellitus 7. (a) Explain the role of the following factors in germination
(i) Oxygen (2marks)
Required for aerobic respiration that releases energy/ATP; for germination
(ii) Water (3 marks)
Mobilises and dissolves stored food; stimulates the (germinating) enzymes; Provides medium for transport of dissolved food; provides a medium for reaction of enzymes.
(iii) Gibberellic acid (1 mark)
Stimulates germination;
(b) (i) Describe the various modes of adaptation for the flat worm of the blood Schistosoma mansonii (8 marks)
Has two hosts to improve chances of survival; the secondary host the snail and human as the primary host; The adult worms have suckers for taking in digested food; The larvae occurs as either cercariae; redia or minacidia; The worm produces chemical substances against the hosts antibodies the female lays numerous eggs to improve chances of survival.
@2015 KASSU – BIOLOGY P2 Page 8
(ii) State the effects of Schistosoma mansonii on its primary host, the human (6 marks)
Deprives it of its food making weak bores and tears the intestine leading to bleeding; the anaemia; Causes abdominal pains; causes ulceration of the alimentary canal; cercariae causes itching or boning the skin;
8. (a) Describe how the digestion of a protein is achieved in the following portions of the alimentary canal.
(i) Stomach (4 marks)
Pepsin; acts on proteins to polypeptides; Rennin; Acts on milk protein caseinogens to casein; this occurs in acidic medium.
(ii) Duodenum (4 marks)
Trypsin; in pancreatic juice; hydrolyses polypeptides to peptides molecules; in alkaline conditions provided by bile juice.
(b) (i) Describe the process of absorption at the root hair to the xylem of the root. (8 marks)
The root hair cell sap is hypertonic to the soil water; water from the soil moves into the root hair cell sap by osmosis; this makes the cell sap hypotonic/dilute; compared to hypertonic adjacent cortex cells; water moves into the cortex cells by osmosis; till it reaches the casparian layer; which pumps water into the xylem of the root; this is called the root pressure;
(ii) Describe how temperature and light intensity affect the rate of transpiration. (4 marks)
Increase in temperature causes evaporation of water into the intercellular airspace of the leaf; this makes water vapour from adjacent cells to move into the stoma; creating diffusion gradient deficit between the atmosphere and intercellular space increased transpiration;
Increase in light intensity; increases rate of photosynthesis; leading to opening of stomata which leads to increased transpiration.
@2015 KASSU – BIOLOGY P2 Page 9