Medium term Plans for Summer Reception/Year 1 Mixed age Range
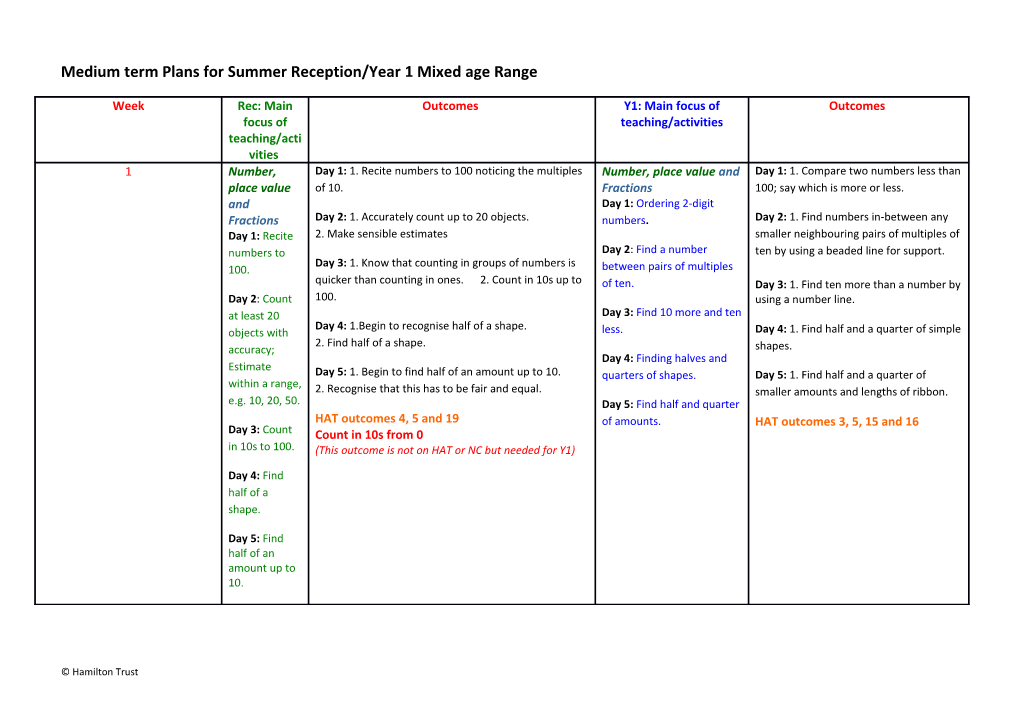
Week Rec: Main Outcomes Y1: Main focus of Outcomes focus of teaching/activities teaching/acti vities 1 Number, Day 1: 1. Recite numbers to 100 noticing the multiples Number, place value and Day 1: 1. Compare two numbers less than place value of 10. Fractions 100; say which is more or less. and Day 1: Ordering 2-digit Fractions Day 2: 1. Accurately count up to 20 objects. numbers. Day 2: 1. Find numbers in-between any Day 1: Recite 2. Make sensible estimates smaller neighbouring pairs of multiples of numbers to Day 2: Find a number ten by using a beaded line for support. Day 3: 1. Know that counting in groups of numbers is 100. between pairs of multiples quicker than counting in ones. 2. Count in 10s up to of ten. Day 3: 1. Find ten more than a number by Day 2: Count 100. using a number line. at least 20 Day 3: Find 10 more and ten Day 4: 1.Begin to recognise half of a shape. objects with less. Day 4: 1. Find half and a quarter of simple 2. Find half of a shape. accuracy; shapes. Day 4: Finding halves and Estimate Day 5: 1. Begin to find half of an amount up to 10. quarters of shapes. Day 5: 1. Find half and a quarter of within a range, 2. Recognise that this has to be fair and equal. smaller amounts and lengths of ribbon. e.g. 10, 20, 50. Day 5: Find half and quarter HAT outcomes 4, 5 and 19 of amounts. HAT outcomes 3, 5, 15 and 16 Day 3: Count Count in 10s from 0 in 10s to 100. (This outcome is not on HAT or NC but needed for Y1)
Day 4: Find half of a shape.
Day 5: Find half of an amount up to 10.
© Hamilton Trust Week Rec: Main Outcomes Y1: Main focus of Outcomes focus of teaching/activities teaching/acti vities 2 Addition and Day 1: 1 Begin to know what one more is than a Addition and subtraction Day 1: 1. Add tens to 2-digit numbers. subtraction number up to 20. 2. Use Day 1: Adding ten to a 2- Day 1: Say one counting on to find the answer digit number. Day 2: 1. Add 10 to a 2-digit number. more than a 2. Add 11 to a 2-digit number number up to Day 2: 1. Work out what 2 more than a given number is Day 2: Adding 11 to 2-digit Day 3: 1. Subtract tens from 2-digit 20. by counting on. numbers. numbers. Day 2: Add 2 Day 3: 1 Add 2 or 3 to a given number up to 17. Day 3: Subtracting tens Day 4: 1. Subtract 10 from a 2-digit by counting 2. Use counting on to help work this out. from a 2-digit number. on. number. Day 4: 1. Add 2 or 3 to a given number up to 17 by Day 4: Subtracting 11 from 2. Subtract 11 from a 2-digit number. Day 3: Add 2 counting on. 2-digit numbers. or 3 by Day 5: 1. Add and subtract 10 to/from a counting on. Day 5: 1. Begin to add 2 or 3 to a given number up to Day 5: Adding /subtracting 2-digit number. 17 by using a number track and ‘jumping on.’ 11. 2. Add or subtract 11 to/from a 2-digit Day 4: Add 2 number or 3 by HAT outcomes 7, 10 (count on), 11, 12, 13 (add), counting on. 14 and 16 HAT outcomes 3, 10 and 12
Day 5: Add 2 / (plenaries) 3, counting on using a number track.
© Hamilton Trust Week Rec: Main Outcomes Y1: Main focus of Outcomes focus of teaching/activities teaching/acti vities 3 Addition and Day 1: 1.Explore and find different ways of partitioning Addition and subtraction Day 1: 1. Know number bonds to 10. subtraction 5 and 6. 2. Begin to record Day 1: Adding to the next 2. Use pairs to ten to add to the next tens Day 1: Find these in addition number sentences. ten. number. different ways to partition 5 Day 2: 1. Explore and find different ways of partitioning Day 2: Adding, bridging ten, Day 2: 1. Use number bonds to add, and 6 into two 6 and 7 into two sets. 2. Record these in deciding whether an bridging ten. sets; write addition number sentences. addition will bridge ten or 2. Recognise whether two numbers matching not. added together will bridge 10. additions. Day 3: 1. Find different ways of partitioning 6 and 7. 2. Record these as subtraction number sentences. Day 3: Subtracting bridging Day 3: 1. Use bonds to ten to bridge ten Day 2: Find ten. when subtracting (12 – 2, 12 – 3, 12 – 4, different ways Day 4: 1. Find different ways of partitioning 10. …) with visual support. to partition 6 2. Record these in matching addition number Day 4: Subtracting bridging and 7 into two sentences. 3. Begin to ten. Day 4: 1. Use pairs to ten to bridge ten sets, write spot if any other ways of partitioning 10. when subtracting (12 – 2, 12 – 3, 12 – 4, matching Day 5: Sort calculations …). additions. Day 5: 1. Begin to solve practical addition problems according to whether they 2. Record the steps on a beaded line. that involve pairs to 10. will bridge ten or not. Day 3: Find Day 5: 1. Use pairs to ten to bridge ten different ways HAT outcomes 12, 13, 16 and 17 when subtracting (12 – 2, 12 – 3, 12 – 4, to partition 6 …) and record the steps on a beaded line. and 7, write 2. Sort calculations according to whether matching they will bridge ten or not. subtractions. HAT outcomes 7, 9, 10, 11 and 12 Day 4: Find different ways to partition 10 into two sets; write matching additions.
Day 5: Solve © Hamilton Trust Week Rec: Main Outcomes Y1: Main focus of Outcomes focus of teaching/activities teaching/acti vities 4 Measures Day 1: 1. Compare two capacities by pouring in water Measures and data Day 1: 1. Compare and discuss capacities, and data and making observations. Day 1: Compare capacities, by direct comparison. Day 1: 2. Begin to use vocabulary half empty, full etc. by direct comparison. 2. Understand the vocabulary relating to Compare two capacity. capacities Day 2: 1. Compare two capacities. Day 2: Estimate, measure using direct 2. Discuss shapes of bottles when thinking about and compare capacities, Day 2: 1. Estimate, measure and compare comparison; capacity. using cups; use a uniform, capacities, using cups. Use language non-standard unit to 2. Use a uniform, non-standard unit to of full and Day 3: 1. Use uniform and non-standard units (cups) to measure capacity. empty. measure capacity. measure capacity. 2. Order 3. Order capacities from least to greater. Day 3: Estimate, measure, Day 2: containers according to their capacity. Compare two compare capacities, using Day 3: 1. Estimate, measure and compare Day 4: 1. Use uniform and non-standard units (cups) to capacities cups. capacities, using cups. using direct measure capacity. 2. 2. Use a uniform, non-standard unit to Day 4: Draw pictograms and comparison; Order containers according to their capacity. measure capacity. discuss what they show. Use language 3. Find containers that hold a greater of full/empty. Day 5: 1. Compare two containers to a third container. capacity and order different capacities. 2. Use non-standard units of measurement. Day 5: Present data in a Day 3: Use block graph. Day 4: 1. Understand how to read a non-standard HAT outcomes 26 and 27 pictogram. units (cups) to 2. Create a pictogram and write a measure sentence describing what it shows. capacities. Day 5: 1. Create a block graph and Day 4: Use analyse the results. uniform non- standard units HAT outcomes 17 (capacity) and 18 (cups) to (capacity) measure capacities (jugs).
Day 5: Compare the © Hamilton Trust Week Rec: Main Outcomes Y1: Main focus of Outcomes focus of teaching/activities teaching/acti vities 5 Number and Day 1: 1. Begin to recognise odd and even numbers. Number and Day 1: 1. Count in 2s, 5s and 10s. Multiplicatio 2. Count in 2s whispering the odd numbers. Multiplication and 2. Record counting on a beaded line with n division hops. Day 1: Count Day 2: 1. Count sets of objects in 2s. 2. Day 1: Count in 5s and 10s – to in 2s to 20. Count in 2s up to 20. multiplication. Day 2: 1. Count in 2s, 5s and 10s. 2. Use repeated addition to work out Day 2: Count Day 3: 1. Count in 2s using 2p coins. Day 2: Count in 2s, 5s, 10s multiplication problems. in 2s in (multiplication). practical Day 4: 1. Begin to recognise repeating patterns. Day 3: 1. Work out simple multiplications context. 2. Spot missing shapes within a pattern. 3. Discuss Day 3: Multiplication using by counting ‘sets of’. a pattern and continue it. penny number line. 2. Begin to use a penny number line to Day 3: Count ring sets. in 2s using 2p Day 5: 1. Recognise repeating sound patterns. Day 4: Divide by finding coins. 2. Spot a pattern and continue the sequence. how many sets in a total Day 4: 1. Work out simple division (inverse of multiplication). problems by working out how many sets Day 4: HAT outcomes 22 and 32 in a given number. Recognise and Day 5: Divide by finding continue a how any sets in a total Day 5: 1. Work out division problems by repeating (inverse of multiplication). grouping objects. pattern of 2. Begin to use a beaded line to group. objects or shapes. HAT outcomes 2 and 14
Day 5: Recognise and continue a repeating pattern of sounds or shapes.
© Hamilton Trust Week Rec: Main Outcomes Y1: Main focus of Outcomes focus of teaching/activities teaching/acti vities 6 Money, Day 1: 1. Recognise different coins and their values. Addition and subtraction Day 1: 1. Work out totals to 20p by using Addition and 2. Describe what these coins look like. Day 1: Find totals to 20p. number bonds to ten and twenty. subtraction Day 1: Day 2: 1. Recognise that there are 100 pennies in a Day 2: Find totals using Day 2: 1. Find totals of amounts by using Recognise pound. 2. Use pound coins number facts. different number facts to help. coins and to buy different items that cost whole pounds up to Day 3: Find totals adding 10 notes up to £10. Day 3: 1. Find totals by adding ten or £20. or 20 pence. twenty to a number. Day 3: 1. Recognise that 2 £1 coins are the same value Day 4: Find change by Day 2: Use as a £2 coin. 2. Count £2 Day 4: 1. Find change from 20p by finding the difference and pound coins to coins in 2s. counting on and finding the difference. buy different counting on. objects. Day 4: 1. Compare two amounts of money in pounds. Day 5: 1. Find the difference between Day 5: Find differences by two amounts by counting on. 2. Describe each amount is higher or lower and order counting on. Day 3: Use £2 different amounts. coins and HAT outcomes 3, 7, 8, 10, 12 (money count in 2s; Day 5: 1. Pay for different items using £1 and £2 coins. stories) and 22 (coins) Create 2. Recognise that amounts can be paid for in different Also: Begin to understand the concept of amounts with £2 coins. ways e.g. £3 with 3 x £1 coins or 1 x £2 coin and 1 x £1 difference and find a difference between pound coin. two numbers. Day 4: Comparing HAT outcomes 12, 30 and 31 two amounts of money in pounds.
Day 5: Paying for items in pounds using £1 and £2 coins.
© Hamilton Trust Week Rec: Main Outcomes Y1: Main focus of Outcomes focus of teaching/activities teaching/acti vities 7 Addition and Day 1: 1. Begin to recall the number bonds to 10. Addition and subtraction Day 1: 1. Use pairs to ten to find the subtraction 2. Find different ways of partitioning 10. Day 1: Use pairs to ten to complement to the next multiple of ten, Day 1: Find find the complement to the using a bead string for support. Day 2: 1. Find different ways of partitioning 10. ways to next multiple of ten. 2. Begin to write these as addition number sentences. Day 2: 1. Use pairs to ten to find the partition 10 Day 2: Use pairs to ten to complement to the next multiple of ten, things in a Day 3: 1. Know bonds to 5. 2. find the complement to the using a beaded number line for support. practical Begin to recall number bonds to 6. 3. Write next multiple of ten, using a context. addition number sentences. beaded number line. Day 3: 1. Add 1-digit numbers to 2-digit numbers using patterns, e.g. 2 + 4 and 12 Day 2: Find Day 4: 1. Begin to recall number bonds to 7. Day 3: Add 1-digit numbers ways to + 4. 2. Work out how many are ‘hidden’ from a set of 7. to 2-digit numbers using partition 10 3. Record these as addition number sentences. things in a patterns. Day 4: 1. Adding 1-digit numbers to 2- practical digit numbers using number facts and Day 5: 1. Recall number bonds to 5, 6 and 7. Day 4: Add 1-digit numbers context. patterns. to 2-digit numbers. 2. Begin to recognise which number bonds they can Day 3: use to work out different additions. Day 5: 1. Adding 1-digit numbers to 2- Day 5: Add 1-digit numbers Rehearse digit numbers using number facts such as to 2-digit numbers using bonds to 5 and HAT outcomes 12, 13, 16 and 17 pairs to 10 and doubles. number facts. 6. 2. Find numbers that are easier to add together and explain why. Day 4: Rehearse HAT outcomes 7, 9 and 10 bonds to 7.
Day 5: Rehearse bonds to 5, 6 & 7.
© Hamilton Trust Week Rec: Main Outcomes Y1: Main focus of Outcomes focus of teaching/activities teaching/acti vities 8 Shape and Day 1: 1. Know the days of the week in order. Shape and Measures Day 1: 1. Know the order of days of the Measures 2. Begin to remember the months of the year. Day 1: Know days of the week and months of the year. Day 1: Know 3. Recognise that the year is broken into different week and the months of the 2. Say the next month/day that comes the days of the seasons. year. after any given month/day. week and Day 2: 1. Recognise that there are two types of clocks; Day 2: Tell the time to the Day 2: 1. Tell the time to the nearest half begin to know analogue and digital. 2. Recognise nearest half hour. hour with confidence. the months of what an o’ clock time looks like on both of these. 2. Work out times half an hour later. the year. 3. Understand what events might be happening at Day 3: Tell time to the nearest 1/2 hour. Day 3: 1. Tell the time to the nearest half Day 2: Begin different times of the day. hour with confidence. to recognise Day 3: 1. Recognise different 3-D shapes. 2. Day 4: Recognise 3D 2. Work out time problems involving half o’clock times. Describe some of the properties of 3-D shapes. shapes; understand ¼, ½ hour time intervals. and ¾ turns. Day 3: Name 3. Sort 3-D shapes into two hoops according to their Day 4: 1. Recognise 3D shapes and and describe properties. Day 5: Recognise 3D shapes describe some of their properties. cube, cuboid, and describe their position. Day 4: 1. Recognise different 3-D shapes. 2. 2. Describe how a 3D object has been sphere, cone, Recognise a pyramid and how they can have different turned. cylinder. faces on the bottom. 3. Sort 3-D 3. Understand ¼, ½ and ¾ turns. Day 4: Name shapes into two hoops according to their properties. Day 5: 1. Recognise 3D shapes and and describe Day 5: 1. Understand instructions involving direction. describe some of their properties. cube, cuboid, 2. Remember which side is left and which is right. 2. Describe the position of a 3D shape sphere, cone, 3. Give instructions to other children. using directional language. cylinder and pyramid. HAT outcomes 21, 28, 29, 33 and 34 HAT outcomes 19, 20, 24 (3D) and 25 Day 5: Revise common 3-D shapes; follow directions.
© Hamilton Trust Week Rec: Main Outcomes Y1: Main focus of Outcomes focus of teaching/activities teaching/acti vities 9 Number and Day 1: 1. Count reliably to 20. 2. Number and place Day 1: 1. Double a number up to 20 by place value Read and write numbers to 20. 3. value/Multiplication and doubling the tens and then doubling the Day 1: Fill in Recognise missing numbers up to 20. division ones. missing Day 1: Doubling numbers numbers on a Day 2: 1. Recognise numbers up to 20. 2. <20. Day 2: 1. Understand what halving a 1-20 track. Read and write numbers from 10-20. number means. Day 2: Halving numbers 2. Halving even numbers up to 20. Day 2: Read Day 3: 1. Read 2-digit numbers and find on a 1-100 (even to 40). and write number grid. 2. Recognise that Day 3: 1. Understand multiplication as numbers to in each row on a 1-100 grid the numbers have the Day 3: Multiply using ‘sets ‘sets of’ in a practical context. 20. same amount of tens. of’. 2. Begin to record ‘sets of’ as a multiplication number sentence.1. Find Day 4: Understand Day 3: Day 4: 1. Count to 100. 2. doubles to double 6. multiplication as ‘sets of’ & Recognise and Understand how many ones are in 2-digit numbers and 3. Use these facts to work out near division as ‘how many sets?’ read numbers show on hands. doubles. to 100. Day 5: Begin to multiply and Day 5: 1. Count to 100. 2. Day 4: 1. Work out multiplication as sets divide. Day 4: Work out missing numbers on a 1-100 grid. of 5 and 10 using towers of cubes. Recognise and 3. Begin to read and write numbers to 100. read numbers Day 5: 1. Work out practical HAT outcomes 5, 7 and 8 to 100. multiplication problems involving money. 2. Begin to work out practical division Day 5: Begin problems as grouping. to fill in missing HAT outcomes 13, 14 and 15 numbers on a 1-100 grid.
© Hamilton Trust Week Rec: Main Outcomes Y1: Main focus of Outcomes focus of teaching/activities teaching/acti vities 10 Money/Addi Day 1: 1. Count reliably to 20. 2. Money/Addition and Day 1: 1. Adding 1-digit numbers to 2- tion and Add and subtract from a number up to 20 by counting subtraction digit numbers using facts and patterns. subtraction on or back using a number track. Day 1: Adding 1-digit Day 1: Add by numbers to 2-digit numbers Day 2: 1. Subtracting 1-digit numbers counting on 2 Day 2: 1. Count reliably to 20. 2. using facts. from 2-digit numbers using facts and or 3 from any Add and subtract from a number up to 20 by counting patterns. number up to on or back using a number track. Day 2: Subtracting 1-digit Day 3: 1. Use the correct operation to 20. numbers to 2-digit numbers Day 3: 1. Use repeated addition or subtractions to find using facts. work out number sentences. Day 2: an answer to a problem. 2. Work out addition and subtraction Subtract by 2. Begin to recognise how to write repeated Day 3: Adding and number sentences using facts and counting back addition/subtraction as a number sentence. subtracting 1-digit numbers patterns to help. 2 or 3 from to 2-digit numbers using Day 4: 1. Recognise coin values up to 50p. 2. Day 4: 1. Find totals of money amounts any number < facts. Begin to understand the value of each coin. using number facts. 20. 3. Begin to work out small totals of different coins. Day 4: Finding totals of 2. Find the best order for adding money money. Day 3: Carry amounts. Day 5: 1. Understand how many pennies each coin is out repeated 3. Use pairs to ten to bridge ten with the worth. 2. Begin to Day 5: Give change by additions or support of beaded lines. understand that coins can be exchanged for other finding the difference. subtractions; numbers of coins, e.g. 5p could be given as 5 pennies Day 5: 1. Find change from 30p by finding find an or two 2p coins and one 1p coin. the difference. answer. HAT outcomes 7, 8, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 17, 30 and HAT outcomes 9, 10, 11, 12 (money Day 4: Find totals of small 31 stories) and 22 (coins) numbers of Also: Begin to understand the concept of coins. change and find a difference between two amounts. Day 5: Exchange higher denomination coins for © Hamilton Trust Week Rec: Main Outcomes Y1: Main focus of Outcomes focus of teaching/activities teaching/acti vities 11 Measures Day 1: 1. Begin to understand what a minute is and Measures and data Day 1: 1. Understand that time can be and data what can be done in that time. Day 1: Understand that measures in hours, minutes and seconds Day 1: Begin 2. Understand that a minute is 60 seconds. time can be measures in Day 2: 1. Read o’clock and half-past times to understand 3. Begin to time events using a minute sand timer. hours, minutes and seconds on analogue and digital clocks. how we can Day 2: 1. Revise the days of the week. 2. Day 2: Order times from 2. Convert digital times to analogue time short Say what day comes before/after a given day. earliest to latest. times. events in 3. Order times from earliest to latest. seconds and Day 3: 1. Know the days of the week and answer Day 3: Learning the months minutes; questions about them. 2. of the year. Day 3: 1. Know the days of the week and recognise that Understand what the day will be after ‘1 or 2 sleeps’. months of the year in order. there are 60 3. Begin to use correct language to describe time. Day 4: Draw, read and 2. Say the month that comes before or seconds in a understand block graphs. after a given month. minute. Day 4: 1. Understand what the day will be after ‘1 or 2 sleeps’. 2. Use the Day 5: Read, understand Day 4: 1. Show data in block graphs. Day 2: Revise correct language to describe time. and draw pictograms. 2. Answer questions about their block days of the graphs. week. Day 5: 1. Begin to learn the months of the year. 2. Know important times of the year relating to months Day 5: 1. Present data in pictograms. Day 3: Revise e.g. special festivals, their birthday, etc. 2. Compare data from two pictograms. days of the 3. Know the different seasons of the year and begin to week; Use the identify the months that form these. HAT outcomes 19, 20 and 21 language of time to HAT outcomes 28 and 29 (seconds, minutes, understand days, week, months) what day it is ‘after 1 or 2 sleeps’.
Day 4: Revise days of the week; Use the language of time. © Hamilton Trust Title of topic – colour code (see below)
GREEN – Place Value or number ORANGE – Addition or subtraction PURPLE – Multiplication or division (inc. scaling or square/cube numbers or multiples and factors...) GREY – Fractions or decimals or percentages or ratio BLUE – shape or measures or data BROWN – Algebra
The Hamilton plans do provide resources for practice of the relevant algorithms, skills and the reinforcement of crucial understandings. However, some teachers may prefer to use textbooks as an additional source of practice. We have agreed with Pearson, the publisher of Abacus, that we can reference the Abacus textbooks and that they will do a special deal if any Hamilton users wish to purchase a set of these textbooks. These are new books, written specifically to match the new National Curriculum. Any schools wishing to follow this up should go to this webpage: http://www.pearsonschoolsandfecolleges.co.uk/Primary/GlobalPages/AbacusFriendsofHamiltonTrust/SpecialOfferforFriend sofHamiltonTrust.aspx
Reception Outcomes
1. Recognise numerals 1-5 and some of personal significance; select the correct numeral to represent up to 10 objects. N 2. Count up to 5, then 10 objects, including in an irregular arrangement, match one-to-one; count actions, images, objects which cannot be moved. N 3. Count out a set of up to 6 objects from a larger group. N 4. Estimate how many objects they can see and check by counting them. N 5. ELG: Count reliably using numbers 1 to 20 and place the numbers in order. N 6. Compare two numbers up to 20, and find numbers in between. N 7. ELG: Say the number after a given number up to 20. N 8. ELG: Say the number before a given number up to 20. N 9. Use the language of ‘greater’ and ‘less than’ and ‘more’ and ‘fewer’ to compare two sets of objects. N 10. Find the total number of items in two groups by counting all of them; begin to find the total by counting on from the larger number. AS 11. Find one more than a group of up to 5 objects and then up to 10 objects. AS 12. In practical activities, perform additions and subtractions and use the appropriate and relevant vocabulary. AS 13. Use appropriate marks to record numbers and operations: begin to use +, – , and = to record additions and subtractions. AS 14. ELG: Say the number one more than a given number up to 20. AS 15. ELG: Say the number one less than a given number up to 20. AS © Hamilton Trust 16. ELG: Add numbers (<10) of objects, images and quantities, counting on to find the answer, including counting on along a number track or line. AS 17. ELG: Subtract one single digit number from another in the context of a practical activity, including counting back along a number track or line. AS 18. Identify and begin to solve mathematical problems in the context of their own activity or interest. AS 19. ELG: Solve problems including doubling and halving or sharing. MD 20. Explore 2D shapes, begin to use mathematical names for these ‘flat’ shapes; select a named shape: circle, square, rectangle, triangle. G 21. Explore 3D shapes, begin to use mathematical names for ‘solid’ shapes; select a given named shape: sphere, cube, cuboid, pyramid, cone, cylinder. G 22. Use familiar objects and common shapes to create and recreate patterns and build models. G 23. Order/sequence everyday events, begin to understand that we can tell the time; recognise analogue/digital o’clock times; measure short times in simple ways. MS 24. ELG: Use everyday language to compare and order two or three items by length or height. MS 25. ELG: Begin to measure using repeated uniform units, e.g. crayons or footprints. MS 26. ELG: Use everyday language to compare and order 2/3 items by weight or capacity. MS 27. ELG: Begin to measure using repeated uniform units, e.g. conkers or egg-cups. MS 28. ELG: Use everyday language to sequence events & compare durations (e.g. after two sleeps, all afternoon); understand that we can measure time. MS 29. Recognise the common units of time (minutes, hours, days, weeks, months, years). MS 30. ELG: Use everyday language to talk about money, to identify/describe coins; begin to understand that different coins have different values. MS 31. Exchange one coin for several of another and make small amounts. MS 32. ELG: Recognise, create and describe patterns. G 33. ELG: Explore characteristics of shapes and everyday objects and use mathematical language to describe them. G 34. ELG Use everyday language to describe position and direction, e.g. ‘behind’, ‘in front of’, ‘next to’, ‘underneath’, ‘on top of’. G The letters in orange indicate the strand on Hamilton Assessment Tracker to which each Outcome belongs.
Year 1 – Outcomes
1. Count on and back in ones to and from 100 and from any single-digit or 2-digit number; given a number up to 100, identify one more and one less. N 2. Count in 2s, 5s and 10s from 0. N 3. Count on and back in tens from any 1-digit or 2-digit number, e.g. 23, 33, 43, 53... Continue to just over 100. N 4. Locate any number on a 1-100 grid or a beaded line 0-100. N 5. Compare numbers to at least 20. N 6. Read and write numbers to 100 in numerals and read numbers in words to 20. N 7. Know number bonds to 10, e.g. 5 + 5, 6 + 4, etc. Also know what is left if objects are taken from 10, e.g. 10 fingers, fold down 4, leaves 6 standing. AS 8. Begin to know pairs which make 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 and 20. AS 9. Begin to be aware of unit patterns, e.g. 2 + 4 = 6, 7 + 4 = 11, 12 + 4 = 16, 17 + 4 = 21, 22 + 4 = 26 etc. 27 + 4 = 31 etc. AS 10. Recognise the + and – and = signs, and use these to read and write simple additions and subtractions. AS 11. Add small numbers by counting on and subtract small numbers by counting back. AS © Hamilton Trust 12. Solve missing number problems and addition/subtraction problems in number stories. AS 13. Recognise doubles to double 6 and find related halves (half even numbers up to 12). MD 14. Solve simple problems involving multiplication/division, find answers with support using objects, pictorial representations or arrays. MD 15. Recognise, find, name a half as 1 of 2 equal parts of an object, shape, quantity. FD 16. Recognise, find and name a quarter as one of four equal parts of an object, shape or quantity. FD 17. Compare objects according to height, length, weight, capacity, using appropriate mathematical language. MS 18. Count uniform non-standard, then simple standard units to measure length/height, weight, capacity. MS 19. Tell the time to the half hour on analogue and digital clocks. MS 20. Use the language of time including days, months, earlier, later, yesterday, minutes, hours, days, weeks and years. MS 21. Sequence events in chronological order. MS 22. Recognise and know the value of different denominations of coins and notes. MS 23. Sort items into lists or tables. MS 24. Recognise the difference between 2-D and 3-D shapes; name and describe common 2-D and 3-D shapes. G 25. Describe position, direction and movement, including whole, half, quarter and three-quarter turns. G
The letters in orange indicate the strand on Hamilton Assessment Tracker to which each Outcome belongs.
© Hamilton Trust