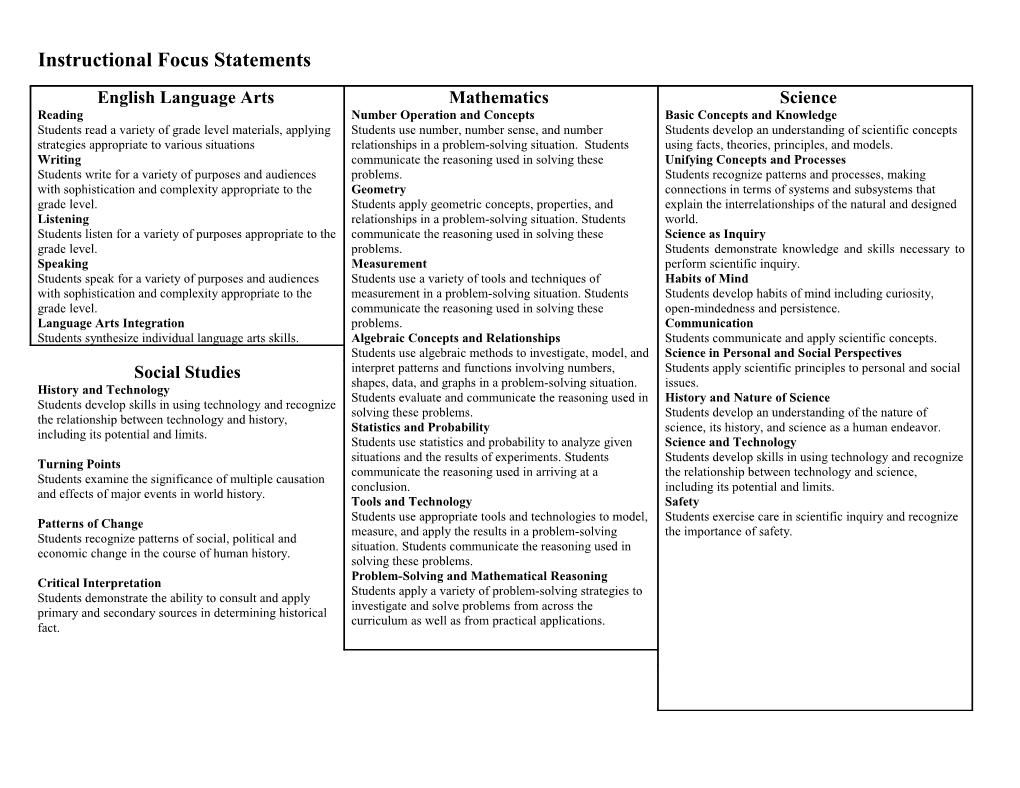
Instructional Focus Statements
English Language Arts Mathematics Science Reading Number Operation and Concepts Basic Concepts and Knowledge Students read a variety of grade level materials, applying Students use number, number sense, and number Students develop an understanding of scientific concepts strategies appropriate to various situations relationships in a problem-solving situation. Students using facts, theories, principles, and models. Writing communicate the reasoning used in solving these Unifying Concepts and Processes Students write for a variety of purposes and audiences problems. Students recognize patterns and processes, making with sophistication and complexity appropriate to the Geometry connections in terms of systems and subsystems that grade level. Students apply geometric concepts, properties, and explain the interrelationships of the natural and designed Listening relationships in a problem-solving situation. Students world. Students listen for a variety of purposes appropriate to the communicate the reasoning used in solving these Science as Inquiry grade level. problems. Students demonstrate knowledge and skills necessary to Speaking Measurement perform scientific inquiry. Students speak for a variety of purposes and audiences Students use a variety of tools and techniques of Habits of Mind with sophistication and complexity appropriate to the measurement in a problem-solving situation. Students Students develop habits of mind including curiosity, grade level. communicate the reasoning used in solving these open-mindedness and persistence. Language Arts Integration problems. Communication Students synthesize individual language arts skills. Algebraic Concepts and Relationships Students communicate and apply scientific concepts. Students use algebraic methods to investigate, model, and Science in Personal and Social Perspectives Social Studies interpret patterns and functions involving numbers, Students apply scientific principles to personal and social shapes, data, and graphs in a problem-solving situation. issues. History and Technology Students evaluate and communicate the reasoning used in History and Nature of Science Students develop skills in using technology and recognize solving these problems. Students develop an understanding of the nature of the relationship between technology and history, Statistics and Probability science, its history, and science as a human endeavor. including its potential and limits. Students use statistics and probability to analyze given Science and Technology
situations and the results of experiments. Students Students develop skills in using technology and recognize Turning Points communicate the reasoning used in arriving at a the relationship between technology and science, Students examine the significance of multiple causation conclusion. including its potential and limits. and effects of major events in world history. Tools and Technology Safety
Students use appropriate tools and technologies to model, Students exercise care in scientific inquiry and recognize Patterns of Change measure, and apply the results in a problem-solving the importance of safety. Students recognize patterns of social, political and situation. Students communicate the reasoning used in economic change in the course of human history. solving these problems.
Problem-Solving and Mathematical Reasoning Critical Interpretation Students apply a variety of problem-solving strategies to Students demonstrate the ability to consult and apply investigate and solve problems from across the primary and secondary sources in determining historical curriculum as well as from practical applications. fact.