Chemistry Phases of Matter Unit Review
1. List all the possible phase changes, tell what two phases are involved and whether energy is absorbed or released by the system.
2. Draw and label a phase diagram for a regular substance where the liquid is more dense than the solid.
3. Draw and label a phase diagram for water.
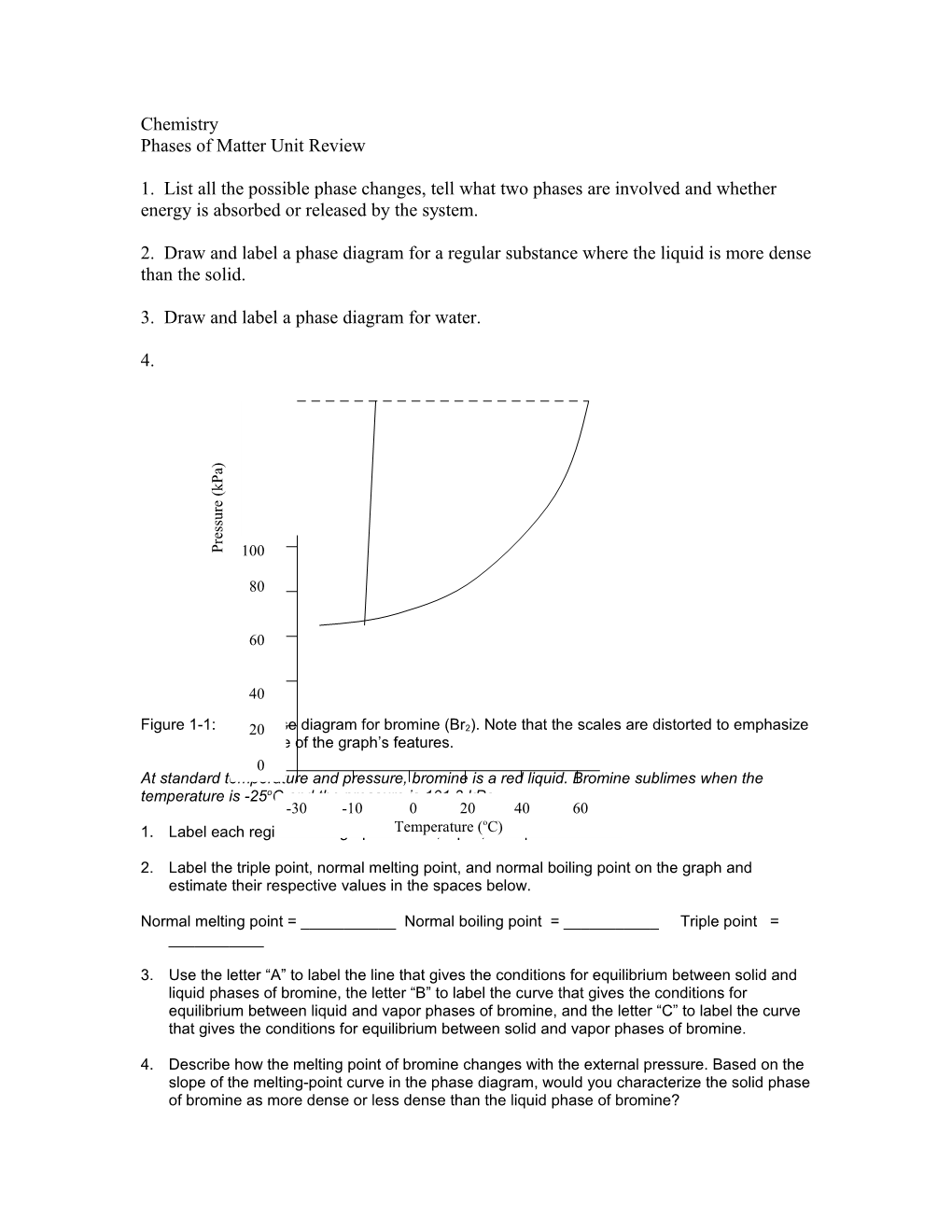
4. ) a P k (
e r u s s e r
P 100
80
60
40
Figure 1-1: 20Phase diagram for bromine (Br2). Note that the scales are distorted to emphasize some of the graph’s features. 0 At standard temperature and pressure, bromine is a red liquid. Bromine sublimes when the temperature is -25oC and the pressure is 101.3 kPa, -30 -10 0 20 40 60 o 1. Label each region of the graph asTemperature solid, liquid, ( C)or vapor.
2. Label the triple point, normal melting point, and normal boiling point on the graph and estimate their respective values in the spaces below.
Normal melting point = ______Normal boiling point = ______Triple point = ______
3. Use the letter “A” to label the line that gives the conditions for equilibrium between solid and liquid phases of bromine, the letter “B” to label the curve that gives the conditions for equilibrium between liquid and vapor phases of bromine, and the letter “C” to label the curve that gives the conditions for equilibrium between solid and vapor phases of bromine.
4. Describe how the melting point of bromine changes with the external pressure. Based on the slope of the melting-point curve in the phase diagram, would you characterize the solid phase of bromine as more dense or less dense than the liquid phase of bromine? 5. What is the boiling point of bromine when the external pressure is 75 kPa?
6. Explain the significance of the triple point.
7. Using arrows labeled “S”, “V”, and “M”, label those portions of the phase diagram where sublimation, vaporization, and melting occur, respectively.
Circle the correct word in the parentheses in each of the following sentences. 8. Bromine vapor at 15oC (condenses, sublimes) when the pressure is raised to 50 kPa.
9. Bromine liquid at 70 kPa (vaporizes, freezes) when the temperature is decreased to -15oC.
5. Use the following phase diagram to answer questions 6-8. Show your answer on the diagram.
6. Label the solid, liquid, and vapor regions. 7. What is the boiling point of the substance at 1 atm pressure? 8. What state is a substance in if its temperature is 127°C at a pressure of 1.5 atm? 9. What are intermolecular forces? How do they play a part in determining the boiling point of a substance? 10. Explain why water boils at a lower temperature here than at sea level. Include the definition of boiling point.
11. Imagine a system at the triple point. Describe what happens when: A. P and T are increased B. P and T are decreased C. P is increased and T is decreased D. P is decreased and T is increased