O’Dwyer AP Biology
Name:______Date:______AP 3 5 Cells Alive! Webquest Purpose: After this webquest, you will be able to model how prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are structured. You will also be able to model how eukaryotic cells maintain internal membranes that partition the cell into specialized regions called organelles. Lastly, you will be able to relate the structure to the function of subcellular components, and their interactions, to the essential cellular emergent properties. Procedure: 1. To begin go to www.cellsalive.com 2. Select “Cell Biology” from the left hand menu
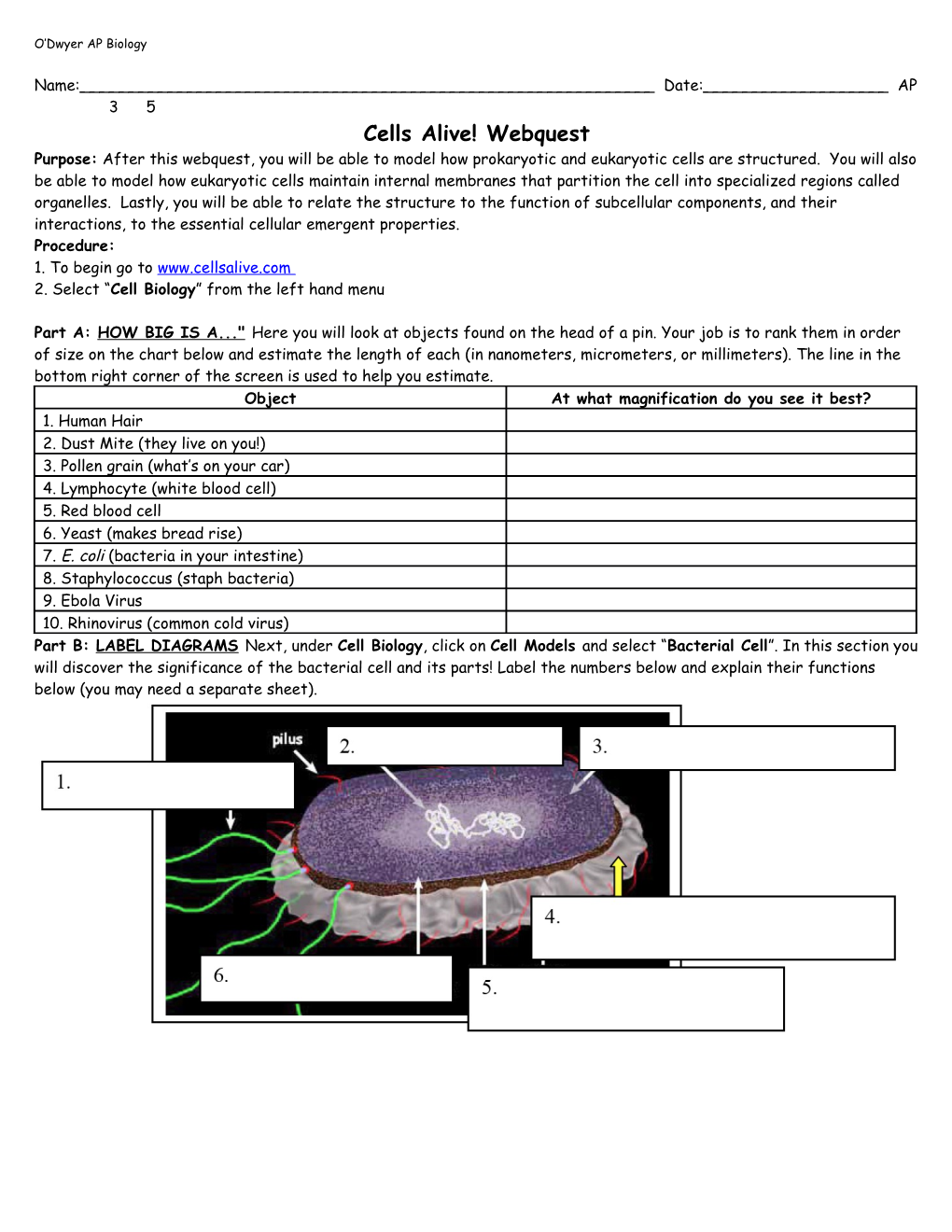
Part A: HOW BIG IS A..." Here you will look at objects found on the head of a pin. Your job is to rank them in order of size on the chart below and estimate the length of each (in nanometers, micrometers, or millimeters). The line in the bottom right corner of the screen is used to help you estimate. Object At what magnification do you see it best? 1. Human Hair 2. Dust Mite (they live on you!) 3. Pollen grain (what’s on your car) 4. Lymphocyte (white blood cell) 5. Red blood cell 6. Yeast (makes bread rise) 7. E. coli (bacteria in your intestine) 8. Staphylococcus (staph bacteria) 9. Ebola Virus 10. Rhinovirus (common cold virus) Part B: LABEL DIAGRAMS Next, under Cell Biology, click on Cell Models and select “Bacterial Cell”. In this section you will discover the significance of the bacterial cell and its parts! Label the numbers below and explain their functions below (you may need a separate sheet). Now select the “Plant and Animal Cell Animation” link from the top of the page. Once there, click on the Animal Cell and label the following parts below.
7. After looking at the bacteria cell and the animal cell, which is more complex? Circle. 8. Is the animal cell a prokaryote or a eukaryote? Circle.
Part C: ANIMAL CELL MODEL For this model, you will need to click on the various parts of the cell to go to a screen that tells you about the parts. Answers to the following questions are found there. Questions Sketches 1. What do mitochondria do? Mitochondria
2. How big are mitochondria?
3. What is the difference between the smooth and rough Rough ER ER?
4. Where specifically is the nucleolus found? Nucleus/Nucleolus 5. What does the cytoskeleton do?
6. Cytosol goes by what other name?
7. How does the golgi work? Golgi Apparatus
8. What is the main function of the plasma membrane? Plasma Membrane
Part D: PLANT CELL MODEL (you will need to return to the "Cell Biology" link to access this page, or hit your back button) Questions Sketches What specifically makes plant cells green? Chloroplast
Where does photosynthesis take place?
In plant cells, what is the function of the vacuole? Vacuole
Part E: OVERVIEW For the chart below, place a check in the box if the cell has that component. You will need to view the plant cell as well in order to do this. Cell Structure Plant Animal Plasma Membrane Vacuole Large, central vacuole Mitochondria DNA Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell Wall Golgi Apparatus Nucleus Chloroplast Ribosome Flagellum/Cilia Lysosomes Peroxisomes
Part F: ANALYSIS Click on “penicillin” in the MICROBIOLOGY navigation bar to construct a free response that explains antibiotic resistant bacteria. Include the following: What are antibiotic resistant bacteria? Why has there been an increase in antibiotic resistant bacteria? How could it be reduced?