Sixth Grade CMP2 Correlations to the Alabama Course of Study
Compiled by Cathey Ritter
Secondary Math Specialist AMSTI—UM
CMP2 Unit Alabama Course of Study Objective
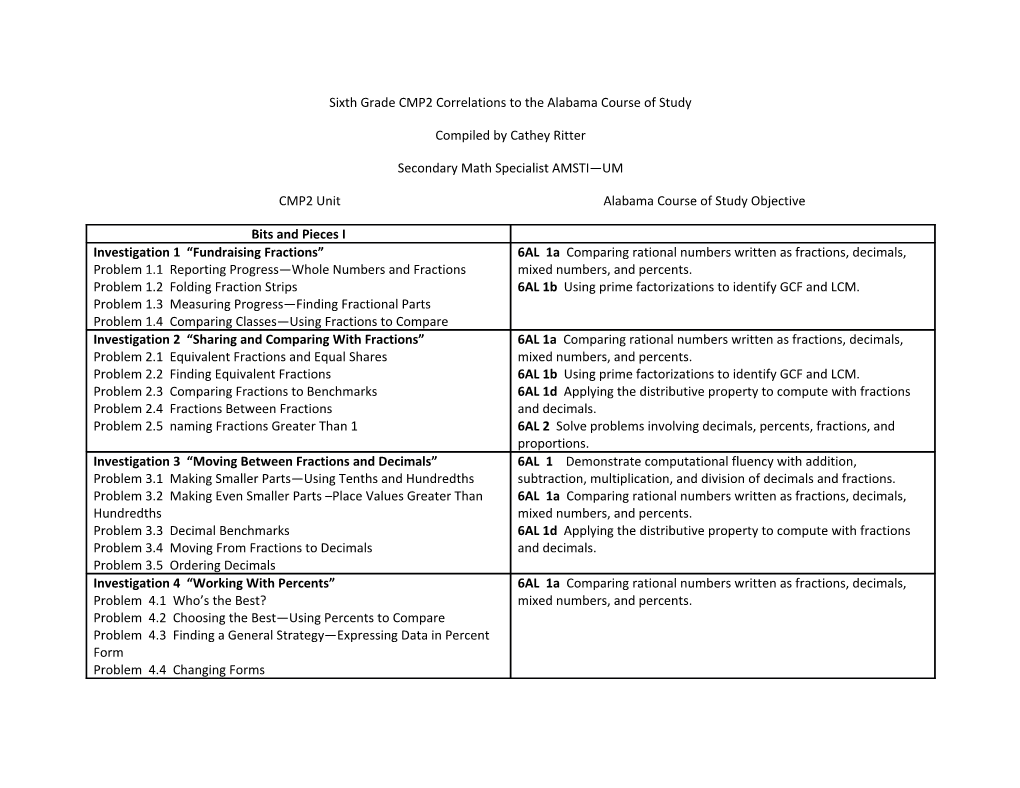
Bits and Pieces I Investigation 1 “Fundraising Fractions” 6AL 1a Comparing rational numbers written as fractions, decimals, Problem 1.1 Reporting Progress—Whole Numbers and Fractions mixed numbers, and percents. Problem 1.2 Folding Fraction Strips 6AL 1b Using prime factorizations to identify GCF and LCM. Problem 1.3 Measuring Progress—Finding Fractional Parts Problem 1.4 Comparing Classes—Using Fractions to Compare Investigation 2 “Sharing and Comparing With Fractions” 6AL 1a Comparing rational numbers written as fractions, decimals, Problem 2.1 Equivalent Fractions and Equal Shares mixed numbers, and percents. Problem 2.2 Finding Equivalent Fractions 6AL 1b Using prime factorizations to identify GCF and LCM. Problem 2.3 Comparing Fractions to Benchmarks 6AL 1d Applying the distributive property to compute with fractions Problem 2.4 Fractions Between Fractions and decimals. Problem 2.5 naming Fractions Greater Than 1 6AL 2 Solve problems involving decimals, percents, fractions, and proportions. Investigation 3 “Moving Between Fractions and Decimals” 6AL 1 Demonstrate computational fluency with addition, Problem 3.1 Making Smaller Parts—Using Tenths and Hundredths subtraction, multiplication, and division of decimals and fractions. Problem 3.2 Making Even Smaller Parts –Place Values Greater Than 6AL 1a Comparing rational numbers written as fractions, decimals, Hundredths mixed numbers, and percents. Problem 3.3 Decimal Benchmarks 6AL 1d Applying the distributive property to compute with fractions Problem 3.4 Moving From Fractions to Decimals and decimals. Problem 3.5 Ordering Decimals Investigation 4 “Working With Percents” 6AL 1a Comparing rational numbers written as fractions, decimals, Problem 4.1 Who’s the Best? mixed numbers, and percents. Problem 4.2 Choosing the Best—Using Percents to Compare Problem 4.3 Finding a General Strategy—Expressing Data in Percent Form Problem 4.4 Changing Forms Bits and Pieces II Investigation 1 “Estimating with Fractions” 6AL 2a Estimating solutions of problems involving fractions and Problem 1 Getting Close—Using Benchmarks decimals. Problem 2 Estimating Sums Investigation 2 “Adding and Subtracting Fractions 6AL 1 Demonstrate computational fluency with addition, subtraction, Problem 1 Land Sections: Writing Addition and Subtraction Sentences multiplication, and division of decimals and fractions. Problem 2 Visiting the Spice Shop: Using Addition and Subtraction 6AL 2 Solve problems involving decimals, percents, fractions, and Problem 3 Just the Facts—Fact Families proportions. Problem 4 Designing Algorithms for Addition and Subtraction 6AL 1c Formulating algorithms using basic operations on fractions and decimals. Investigation 3 “Multiplying With Fractions” 6AL 1 Demonstrate computational fluency with addition, subtraction, Problem 1 How Much of the Pan Have We Sold? A Model for multiplication, and division of decimals and fractions. Multiplication 6AL 1c Formulating algorithms using basic operations on fractions and Problem 2 Finding a Part of a Part: Another Model for Multiplication decimals. Problem 3 Modeling More Multiplication Situations 6AL 2 Solve problems involving decimals, percents, fractions, and Problem 4 Changing Forms: Multiplication With Mixed Numbers proportions. Problem 5 Writing a Multiplication Algorithm Investigation 4 “Dividing With Fractions” 6AL 1 Demonstrate computational fluency with addition, subtraction, Problem 1 Preparing Food—Dividing a Whole Number by a Fraction multiplication, and division of decimals and fractions. Problem 2 Fundraising continues—Dividing a Fraction by a Whole 6AL 1c Formulating algorithms using basic operations on fractions and Number decimals. Problem 3 Summer Work—Dividing a Fraction by a Fraction 6AL 2 Solve problems involving decimals, percents, fractions, and Problem 4 Writing a Division Algorithm proportions. Bits and Pieces III Investigation 1 “Decimals—More or Less” 6AL 1 Demonstrate computational fluency with addition, subtraction, Problem 1 About How Much? multiplication, and division of decimals and fractions. Problem 2 Adding and Subtracting Decimals 6AL 1a Comparing rational numbers written as fractions, decimals, Problem 3 Using Fractions to Add and Subtract Decimals mixed numbers, and percents. Problem 4 Decimal Sum and Difference Algorithms 6AL 1c Formulating algorithms using basic operations on fractions and decimals. 6AL 2 Solve problems involving decimals, percents, fractions, and proportions. 6AL 2a Estimating solutions of problems involving fractions and decimals.
Investigation 2 “Decimal Times” 6AL 2 Solve problems involving decimals, percents, fractions, and Problem 1 Relating Fraction and Decimal Multiplication proportions. Problem 2 Missing Factors Problem 3 Finding Decimal Products Problem 4 Factor—Product Relationships Investigation 3 “The Decimal Divide” 6AL 1a Comparing rational numbers written as fractions, decimals, Problem 1 Deciphering Decimal Situations mixed numbers, and percents. Problem 2 The Great Equalizer—Using common Denominators to 6AL 1c Formulating algorithms using basic operations on fractions and Divide Decimals decimals. Problem 3 Exploring Dividing Decimals 6AL 1d Applying the distributive property to compute with fractions Problem 4 Representing Fractions as Decimals and decimals. 6AL 7a Verifying formulas for determining perimeter and area of parallelograms and rectangles. 6AL 3a Determine a verbal rule for a function given the input and output. Investigation 4 “Using Percents” 6AL 1a Comparing rational numbers written as fractions, decimals, Problem 1 Determining Tax mixed numbers, and percents. Problem 2 Computing Tips 6AL 2 Solve problems involving decimals, percents, fractions, and Problem 3 Finding Bargains—Using Discounts proportions. 6AL 2b Computing Simple Interest 6AL 2c Converting terminating decimals, repeating decimals, and percents to fractions and mixed numbers. 6AL 7a Verifying formulas for determining perimeter and area of parallelograms and rectangles.
Bits and Pieces III Investigation 5 “More About Percents” 6AL 1a Comparing rational numbers written as fractions, decimals, Problem 1 Clipping Coupons—Finding Percent Discounts mixed numbers, and percents. Problem 2 How Much Can We Spend? 6AL 2 Solve problems involving decimals, percents, fractions, and Problem 3 Making Circle Graphs proportions. 6AL 10 Interpret information from bar graphs, line graphs, and circle graphs. Prime Time Investigation 1 “Factors and Products” 6AL 1b Using prime factorizations to identify GCF and LCM. Problem 1 Playing the Factor Game—Finding Proper Factors Problem 2 Playing to Win the Factor Game—Prime and Composite Numbers Problem 3 Playing the Product Game—Finding Multiples Investigation 2 “Whole-Number Patterns and Relationships” 6AL 1b Using prime factorizations to identify GCF and LCM. Problem 1 Finding Patterns—Rectangles and Factor Pairs 6AL 3 Solve problems using numeric and geometric patterns. Problem 2 Reasoning With Even and Odd Numbers 6AL 3a Determine a verbal rule for a function given the input and Problem 3 Classifying Numbers output. Investigation 3 “Common Multiples and Common Factors” 6AL 1b Using prime factorizations to identify GCF and LCM. Problem 1 Riding Ferris Wheels—Choosing Common Multiples or 6AL 3 Solve problems using numeric and geometric patterns. Common Factors Problem 2 Looking at Cicada Cycles—Choosing Common Multiples or Common Factors Problem 3 Bagging Snacks—Choosing Common Multiples or Common Factors Problem 4 Planning a Picnic— Choosing Common Multiples or Common Factors
Investigation 4 “Factorizations: Searching for Factor Strings” 6AL 1b Using prime factorizations to identify GCF and LCM. Problem 1 The Product Puzzle—Finding Factor Strings 6AL 3 Solve problems using numeric and geometric patterns. Problem 2 Finding the Longest Factor String 6AL 3a Determine a verbal rule for a function given the input and Problem 3 Using Prime Factorizations output. Investigation 5 “Putting It All Together” 6AL 1b Using prime factorizations to identify GCF and LCM. Problem 1 Unraveling the Locker Problem—Using Multiples and Factors
Covering and Surrounding Investigation 1 “Designing Bumper Cars” 6AL 7 Solve problems involving perimeter and area of parallelograms Problem 1 Designing Bumper-Car Rides—Understanding Area and and rectangles. Perimeter 6AL 7a Verifying formulas for determining perimeter and area of Problem 2 Pricing Bumper-Car rides—Finding Area and Perimeter parallelograms and rectangles. Problem 3 Decoding Designs—Finding Area and Perimeter of 6AL 7b Estimating perimeter and area of parallelograms and Rectangles rectangles. Investigation 2 “Changing Area, Changing Perimeter 6AL 4 Identify two-dimensional shapes and three dimensional figures Problem 1 Building Storm Shelters—Constant Area, Changing based on their attributes, properties and component parts. Perimeter 6AL 7 Solve problems involving perimeter and area of parallelograms Problem 2 Stretching the Perimeter—Perimeters and Irregular Shapes and rectangles. Problem 3 Fencing in Spaces—Constant Perimeter, Changing Area 6AL 7a Verifying formulas for determining perimeter and area of Problem 4 Adding tiles to Pentominos—Increasing Area and Perimeter parallelograms and rectangles. 6AL 7b Estimating perimeter and area of parallelograms and rectangles. Investigation 3 “Measuring Triangles” 6AL 4b Classifying triangles as right, obtuse, or acute. Problem 1 Triangles on Grids—finding Area and Perimeter 6AL 5 Plot points on grids, graphs, and maps using coordinates. Problem 2 More Triangles—Identifying Base and Height 6AL 7 Solve problems involving perimeter and area of parallelograms Problem 3 What’s the Area?—Triangle Families and rectangles. Problem 4 Designing Triangles Under Constraints 6AL 7a Verifying formulas for determining perimeter and area of parallelograms and rectangles. 6AL 7b Estimating perimeter and area of parallelograms and rectangles. Investigation 4 “Measuring Parallelograms” 6AL 6 Classify angles as acute, obtuse, right or straight. Problem 1 Finding Measures of Parallelograms 6AL 7 Solve problems involving perimeter and area of parallelograms Problem 2 Parallelograms From Triangles and rectangles. Problem 3 Designing Parallelograms Under Constraints 6AL 7a Verifying formulas for determining perimeter and area of Problem 4 Parks, Hotels, and Quilts—finding Areas and Perimeters parallelograms and rectangles. 6AL 7b Estimating perimeter and area of parallelograms and rectangles.
Covering and Surrounding Investigation 5 “Measuring Irregular Shapes and Circles” 6AL 7 Solve problems involving perimeter and area of parallelograms Problem 1 Measuring Lakes—Estimating Perimeter and Area and rectangles. Problem 2 Surrounding a Circle—Finding Circumference 6AL 7a Verifying formulas for determining perimeter and area of Problem 3 Pricing Pizzas—Exploring Area and Circumference parallelograms and rectangles. Problem 4 “Squaring” a Circle—Finding Area 6AL 7b Estimating perimeter and area of parallelograms and rectangles. Shapes and Designs Investigation 1 “Bees and Polygons” 6AL 4 Identify two-dimensional shapes and three-dimensional figures Problem 1 Sorting Shapes—Classifying Polygons based on their attributes, properties , and component parts. Problem 2 Symmetries of Shapes—Symmetry Problem 3 Tiling a Beehive—Tiling With Regular Polygons Investigation 2 “Polygons and Angles” 6AL 4 Identify two-dimensional shapes and three-dimensional figures Problem 1 Understanding Angles based on their attributes, properties , and component parts. Problem 2 Developing Angle Benchmarks 6AL 5 Plot points on grids, graphs, and maps using coordinates. Problem 3 Using and Angle Ruler—Measuring Angles 6AL 6 Classify angles as acute, obtuse, right, or straight. Problem 4 Analyzing Measurement Errors 6AL 6a Measuring angles to the nearest degree using a protractor. Problem 5 Angles and Parallel Lines 6AL 4c Recognizing similar shapes and figures based on their attributes. Investigation 3 “Polygon Properties and Tiling” 6AL 4 Identify two-dimensional shapes and three-dimensional figures Problem 1 Angle Sums of Regular Polygons based on their attributes, properties, and component parts. Problem 2 Angle Sums of Any Polygon Problem 3 Back to the Bees—Interior Angles in Tiling Problem 4 Exterior Angles of Polygons Investigation 4 “Building Polygons” 6AL 4a Classify quadrilaterals, including trapezoids and Problem 1 Building Triangles parallelograms, based on their attributes. Problem 2 Building Quadrilaterals 6AL 4b Classify triangles as right, obtuse or acute. Problem 3 The Quadrilateral Game—Properties of Quadrilaterals 6AL 9 Converts units of length, weight, or capacity within the same customary or metric system. How Likely Is It? Investigation 1 “A First Look at Chance” 6AL 11 Determine the probability of a simple event by expressing the Problem 1 Choosing Cereal—Finding Probabilities With a Coin probability as a ratio, percent, or decimal. Problem 2 Tossing Paper Cups—Finding Probabilities With a Coin Problem 3 One More Try—finding Experimental Probabilities Problem 4 Analyzing Events—Understanding Equally Likely Events Investigation 2 “Experimental and Theoretical Probability” 6AL 11 Determine the probability of a simple event by expressing the Problem 1 Predicting to Win probability as a ratio, percent, or decimal. Problem 2 Exploring Probabilities Problem 3 Winning the Bonus Prize Problem 4 Pondering Possible and Probable Investigation 3 “Making Decisions with Probability” 6AL 11 Determine the probability of a simple event by expressing the Problem 1 Designing a Spinner—Finding Probabilities With a Spinner probability as a ratio, percent, or decimal. Problem 2 Making Decisions—Analyzing Fairness Problem 3 Scratching Spots—Using a Simulation Investigation 4 “Probability, Genetics, and Games” 6AL 11 Determine the probability of a simple event by expressing the Problem 1 Genetic Triats—Applying Experimental Probability probability as a ratio, percent, or decimal. Problem 2 Tracing Traits—Applying Theoretical Probability Problem 3 roller Derby—Analyzing a Game Data About Us Investigation 1 “Looking at Data” 6AL 8a Using different forms of notation to symbolize ratios and rates. Problem 1 Organizing and Interpreting Data 6AL 10 Interpret information from bar graphs, line graphs, and circle Problem 2 Useful Statistics graphs. Problem 3 Experimenting with the Median 6AL 11 Determine the probability of a simple event by expressing the Problem 4 Using Different Data Types probability as a ratio, percent, or decimal. Problem 5 Vertical Bar Graphs and Horizontal Bar Graphs Investigation 2 “Using Graphs to Explore Data” 6AL 8a Using different forms of notation to symbolize ratios and rates. Problem 1 Traveling to School—Making a Stem-and-Leaf Plot 6AL 10 Interpret information from bar graphs, line graphs, and circle Problem 2 Jumping Rope—Comparing Distributions graphs. Problem 3 Relating Height to Arm Span—Making and Reading 6AL 11 Determine the probability of a simple event by expressing the Coordinate Graphs probability as a ratio, percent, or decimal. Problem 4 Relating Travel Time to Distance—Using Coordinate Graphs to find Relationships Investigation 3 “What Do We Mean by Mean?” Problem 1 Finding the Mean Problem 2 Data With the Same Mean Problem 3 Using the Mean
*****I could not find evidence that the following objectives are covered in the 6th grade CMP2 materials:
6AL 7c (Determining the volume of a rectangular prism) and 6AL 8 (Determine the distance between two points on a scale drawing or map using proportional reasoning)