Microeconomics
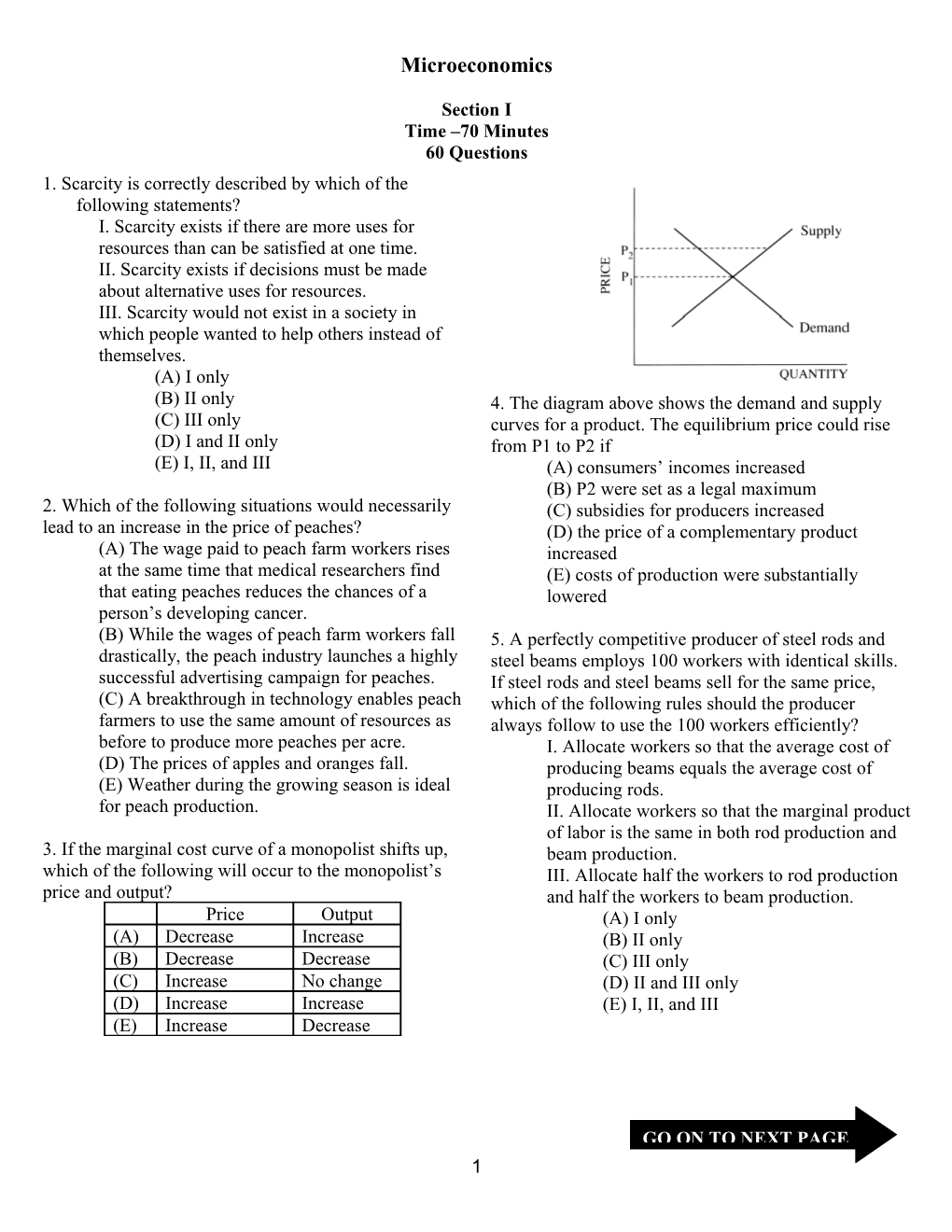
Section I Time –70 Minutes 60 Questions 1. Scarcity is correctly described by which of the following statements? I. Scarcity exists if there are more uses for resources than can be satisfied at one time. II. Scarcity exists if decisions must be made about alternative uses for resources. III. Scarcity would not exist in a society in which people wanted to help others instead of themselves. (A) I only (B) II only 4. The diagram above shows the demand and supply (C) III only curves for a product. The equilibrium price could rise (D) I and II only from P1 to P2 if (E) I, II, and III (A) consumers’ incomes increased (B) P2 were set as a legal maximum 2. Which of the following situations would necessarily (C) subsidies for producers increased lead to an increase in the price of peaches? (D) the price of a complementary product (A) The wage paid to peach farm workers rises increased at the same time that medical researchers find (E) costs of production were substantially that eating peaches reduces the chances of a lowered person’s developing cancer. (B) While the wages of peach farm workers fall 5. A perfectly competitive producer of steel rods and drastically, the peach industry launches a highly steel beams employs 100 workers with identical skills. successful advertising campaign for peaches. If steel rods and steel beams sell for the same price, (C) A breakthrough in technology enables peach which of the following rules should the producer farmers to use the same amount of resources as always follow to use the 100 workers efficiently? before to produce more peaches per acre. I. Allocate workers so that the average cost of (D) The prices of apples and oranges fall. producing beams equals the average cost of (E) Weather during the growing season is ideal producing rods. for peach production. II. Allocate workers so that the marginal product of labor is the same in both rod production and 3. If the marginal cost curve of a monopolist shifts up, beam production. which of the following will occur to the monopolist’s III. Allocate half the workers to rod production price and output? and half the workers to beam production. Price Output (A) I only (A) Decrease Increase (B) II only (B) Decrease Decrease (C) III only (C) Increase No change (D) II and III only (D) Increase Increase (E) I, II, and III (E) Increase Decrease
GO ON TO NEXT PAGE 1 6. Assume a consumer finds that his total expenditure Questions 10-11 refer to the following diagram and on compact disks stays the same after the price of assume a perfectly competitive market structure. compact disks declines, other things being equal. Which of the following is true for this price change? (A) Compact disks are inferior goods to this consumer. (B) The consumer’s demand for compact disks increased in response to the price change. (C) The consumer’s demand for compact disks is perfectly price elastic. (D) The consumer’s demand for compact disks is perfectly price inelastic. (E) The consumer’s demand for compact disks is unit price elastic. 10. At the price 0A, economic profits are 7. A firm uses workers and seed to grow lettuce. Its (A) ABJG (B) ABKH (C) ABLI (D) ACMG (E) C0FM output rises from 100 tons to 200 tons when the number of workers increases from 25 to 75. Its production 11. In the short run, the firm will stop production when process shows the price falls below A. decreasing returns to scale (A) 0A (B) 0B (C) 0C (D) 0D (E) 0E B. diminishing returns to labor C. increasing returns to scale 12. If the chemical industry in an area has been D. increasing returns to labor dumping its toxic waste free of charge into a river, E. increasing long-run average cost government action to ensure a more efficient use of resources would have which of the following effects on 8. For a firm buying labor in a perfectly competitive the industry’s output and product price? labor market, the marginal revenue product curve Output Price slopes downward after some point because as more of a (A) Decrease Decrease factor is employed, which of the following declines? (B) Decrease Increase (A) Marginal product (C) Increase Decrease (B) Marginal factor cost (D) Increase Increase (C) Marginal cost (D) Total output (E) Increase No change (E) Wage rates 13. A market is clearly not perfectly competitive if 9. Which of the following is always true of the which of the following is true in equilibrium? relationship between average and marginal costs? (A) Price exceeds marginal cost. (A) Average total costs are increasing when (B) Price exceeds average variable cost. marginal costs are increasing. (C) Price exceeds average fixed cost. (B) Marginal costs are increasing when average (D) Price equals opportunity cost. variable costs are higher than marginal costs. (E) Accounting profits are positive. (C) Average variable costs are increasing when marginal costs are increasing. (D) Average variable costs are increasing when marginal costs are higher than average variable costs. (E) Average total costs are constant when marginal costs are constant. GO ON TO NEXT PAGE 2 Questions 14–15 are based on the following information and diagram. 17. If a perfectly competitive industry is in long-run Assume that the original supply and demand curves of a equilibrium, which of the following is most likely to be commodity are S and D, respectively. Also assume that true? the government imposes an excise tax (per unit tax) of t (A) Some firms can be expected to leave the dollars on the commodity, which shifts the supply curve industry. to Sl. (B) Individual firms are not operating at the minimum points on their average total cost curves. (C) Firms are earning a return on investment that is equal to their opportunity costs. (D) Some factors are not receiving a return equal to their opportunity costs. (E) Consumers can anticipate price increases.
18. From the point of view of economic efficiency, a monopolist produces (A) too much of a good and charges too low a price 14. The total amount of tax collected by the government (B) too much of a good and charges too high a is equal to price (A) t x Q0 (C) too little of a good and charges too low a (B) t x Ql price (C) P0P1JK (D) too little of a good and charges too high a (D) P0P1GH price (E) P0P2IH (E) the socially optimal amount of a good
15. Which of the following bears the total tax burden? Questions 19–21 are based on the chart below, which (A) The consumers bear it. gives a firm’s total cost of producing different levels of (B) The producers bear it. output. (C) The consumers and the producers each bear Output Total Cost a part of it. 0 $13 (D) The group that legally pays the tax bears it. 1 20 (E) The government bears it. 2 25 3 28 16. A President’s claim that the United States could 4 32 increase its defense budget without sacrificing any of its 5 43 domestic programs would be correct if 6 60 (A) the United States economy were producing at its full potential 19. The marginal cost of producing the fourth unit of (B) the United States economy were operating output is on its production possibilities frontier (A) $ 4 (C) the United States economy were centrally (B) $11 planned (C) $19 (D) some resources were not being fully (D) $32 employed (E) impossible to determine from the (E) the production possibilities frontier for the information given U.S. economy would shift to the left. GO ON TO NEXT PAGE 3 20. The total variable cost of producing five units of A. firms behave strategically output is B. output is produced at minimum average total (A) $ 6 cost (B) $11 C. firms make price and output decisions without (C) $30 regard to the responses of their rivals (D) $43 D. high profits will attract many new entrants to the (E) impossible to determine from the industry information given E. firms don’t have the ability to collude
21. The profit-maximizing level of output for this firm is (A) 2 (B) 3 (C) 4 (D) 5 (E) impossible to determine from the information given
22. Compared to perfect competition, monopolistic competition: A. provides greater product differentiation at the cost of some excess capacity. B. offers less product differentiation but attains equal productive efficiency. C. provides greater product differentiation and achieves greater productive efficiency. 25. Refer to the diagrams. Zero long-run economic D. offers less product differentiation and lower profits are most likely to occur in markets illustrated productive efficiency. by: E. is more efficient in the long-run A. Figure A only B. Figure B only 23. The table given below shows how many tons can C. Figures B and C be produced in India and Canada with one unit of input. D. Figures C and D To achieve gains from specialization: E. Figures B and D
Uranium (ton) Coal (ton) 26. Increasing the tax rate for the poor without India 10 10 changing the taxes the rich pay will: Canada 40 20 A. Cause the Lorenz Curve to move closer to the 45-degree line. A. India should export Coal to Canada and import B. Cause the Lorenz Curve to move further away Canadian Uranium. from the 45-degree line. B. India should export Uranium to Canada and C. It will not have any affect on the Lorenz Curve. import Canadian Coal. D. It will insure that the Lorenz Curve is on the 45- C. Canada should produce both Uranium and Coal degree line. and not trade with India. E. Decrease the demand for inferior goods D. India should produce both Uranium and Coal and not trade with Canada. E. They should not trade.
24. In an oligopolistic industry: GO ON TO NEXT PAGE 4 27. A production possibility frontier that is represented by a straight line rather than the usual bowed shape would indicate; A. Increasing opportunity cost B. Decreasing opportunity cost C. Constant opportunity cost D. Absolute and Comparative Advantage E. Comparative but not absolute advantage
Figure 3 30. Chasey Company Inc. is the only producer in a small town. Cost and revenue information for the Chasey Company are shown in Figure 3. Chasey Company would set the price of its product at; A. $7.50 B. $6.00 C. $4.50 D. $3.75 E. $3.00
31. In Figure 3 the Chasey Company would maximize Figure 1 profits by producing a quantity of; 28. If the current price for the perfectly competitive A. 60 firm represented in Figure 1 is $10.00, what would be B. 100 the result of an increase in fixed cost on the firm’s C. 120 profit maximizing price and quantity? D. 140 A. Price increase and Quantity increase E. 170 B. Price increase and Quantity decrease C. Price constant and Quantity constant 32. In Figure 3 the Chasey Company will make a profit D. Price decrease and Quantity decrease of ______; E. Price decrease and Quantity increase A. $750 B. $450 29. If a legal price ceiling is established on a good C. $300 above the existing equilibrium price, the effect would D. $150 be to: E. $150 loss A. Raise the price of the good and lower the quantity purchased B. Have no effect on the price or quantity of the good C. Lower the price of the good and lower the quantity purchased D. Raise the price of the good and raise the quantity purchased E. Lower the price of the good and increase the quantity purchased GO ON TO NEXT PAGE 5 Figure 4 Number of workers Output 0 0 1 5 2 11 3 19 4 25 5 29 6 31 7 31 8 30
33. In Figure 4 the law of diminishing returns sets in with the addition of the _____ worker. A. 1 B. 2 Figure 5 37. The profit-maximizing price for a perfectly C. 4 competitive firm like the one shown in Figure 5 in the D. 7 long run would be; E. 8 A. A B. B 34 Using the data in Figure 4, if workers are paid $35 C. C and the product being produced sells for $10, how D. D many workers would the Chasey Company hire? E. E A. 1 B. 4 38. In Figure 5 at a market price of A, the profit- C. 5 maximizing output for a perfectly competitive firm is D. 7 A. 0 E. 8. B. 1 C. 2 35. Other things equal, the demand for labor will be D. 3 more elastic: E. 4 A. the greater the demand for the product B. the more substitutable labor is with other inputs 39. If a natural disaster occurs that adversely affects C. the higher the price of capital production and shipping, D. the smaller the elasticity of product demand A. the firm’s supply curve will shift to the right E. the higher the interest rate B. the firm’s demand curve will shift to the right C. 36. Suppose you consume two goods, a and b, such that the firm’s demand curve will shift to the left D. the firm’s supply curve will shift to the left MUa/Pa < MUb/Pb, then you: A. can never maximize utility. E. Neither curve will shift, but instead movement B. have maximized total utility. will be along each curve C. can increase utility by buying more of b and less of a. D. can increase utility by buying more of a and less of b. E. are experiencing the law of diminishing marginal utility
GO ON TO NEXT PAGE 6 40. The government has imposed a tax on the producers 43. If supply and demand both increase, we can of good X and has subsidized the consumers of good Y. correctly conclude that If these policies result in the production of the efficient amounts of both goods, it is likely the government is I. Equilibrium price will rise correcting for: II. Equilibrium price is indeterminate A. Good X is being produced by a monopoly III. Equilibrium quantity will rise whereas good Y is being produced in a perfectly IV. Equilibrium quantity is indeterminate competitive firm B. spillover costs in producing X and spillover A. I only benefits in consuming Y B. I and III only C. spillover benefits in producing X and spillover C. II and IV only costs in consuming Y D. II and III only D. spillover benefits in producing X and E. I and IV only consuming Y E. spillover costs in producing X and consuming Y 44. For a firm that both sells its output and buys its inputs in purely competitive markets, the labor demand Figure 7 curve: Assume that the following information is for Good A. A. slopes downward and the labor supply curve is perfectly elastic Income of Quantity Price of Good B. slopes downward and the labor supply curve is Consumers of demanded of A upward sloping Good A Good A C. is perfectly inelastic and their labor supply is $5.00 $200 20 downward sloping $4.00 $175 40 D. is perfectly elastic and the labor supply curve is $3.00 $150 60 upward sloping $2.00 $125 90 E. is perfectly elastic and the labor supply curve is $1.00 $100 100 perfectly inelastic
41. What would be the effect on total revenue of 45. If an increase in the price of one good increases the changing the price from $5.00 to $4.00, based on the demand for another good, then these two goods are information in Figure 7? A. regular goods A. Increase by $160 B. substitute goods B. Increase by $100 C. public goods C. Increase by $60 D. complementary goods D. Decrease by $700 E. independent goods E. Decrease by $300 46. The necessity for a monopoly to lower its price in 42. Based on the information in Figure 7 it can be order to sell more units of its product explains why correctly concluded that good A is A. monopolies are common among public utilities A. A normal good B. the marginal revenue curve is below the demand B. An inferior good curve for a monopoly C. A exterior good C the marginal cost curve for a monopoly slopes D. A good with a positive externality upward E. A good with a negative externality D. monopolies are able to maintain market power E. monopolies differ from monopolistically competitive firms.
GO ON TO NEXT PAGE 7 47. Game theory, and price leadership are explanations 50. If one firm in a perfectly competitive industry for the profit-maximizing behavior of a firm under experiences a technological breakthrough that lowers which of the following market structures? only that firm’s cost of production, which of the A. Pure monopoly following correctly describes the effect on this firm’s B. Oligopoly price, quantity, and profit? C. Monopolistic competition Price Quantity Profit D. Perfect competition A. decrease decrease decrease E. All of the above market structures B. decrease increase increase C no change decrease increase D no change increase increase E increase increase increase
51. In the factor market, which of the following would happen if the workers became more productive and at the same time the price of the product fell? A. The value of the marginal product of labor would increase B. The value of the marginal product of labor would decrease C. The value of the marginal product of labor would be indeterminate D. The demand for labor would shift to the right E. The demand for labor would shift to the left
52. Which of the following would contribute to a reduction in consumer surplus? Figure 9 A. imposition of an effective price floor 48. Which graph in Figure 9 shows the long-run profit B. imposition of an effective price ceiling maximizing position for a monopolistic competitor? C. an increase in supply A. A D. a decrease in equilibrium price B. B E. all of the above would contribute to a reduction C. C in consumer surplus D. D E. E 53. Karen’s Karmel Korn produces a type of caramel corn candy. Caramel, an ingredient in caramel corn, 49. Which of the following is a progressive tax? increases in price by 10%. Which of the following A. Every taxpayer pays $10.00 correctly describes the effect that this increase will have B. Every taxpayer pays 10% of his/her income on the cost of production? C. Higher income taxpayers pay a higher percent A. only marginal cost will increase of their income in tax B. only marginal cost and average total cost will D. Higher income taxpayers pay a lower percent of increase their income in tax C. marginal cost, average variable cost, average E. None of the above correctly describes a total cost will increase progressive tax D. marginal cost, average total cost, and average fixed cost will increase E. marginal cost, average variable cost, average total cost, and average fixed cost will increase GO ON TO NEXT PAGE 8 54. The derived demand concept suggests that an increase in the demand for computers will: A. increase the demand for computer software 58. Which of the following correctly describes a B. decrease the demand for typewriters perfectly competitive firm’s short run supply curve? C. increase the price of computers A. marginal cost curve D. increase the demand for microchip design B. rising portion of the marginal cost curve engineers C. rising portion of the marginal cost curve above E. increase the supply of computer manufacturers equilibrium D. rising portion of the marginal cost curve above 55. There are two generally recognized measures of average variable cost economic efficiency; one measures efficiency from a E. rising portion of the marginal cost curve above production perspective and the other measures average total cost efficiency from an allocation perspective. Which of the following correctly states these two measures of 59. A price discriminating monopolist would differ efficiency, and in the order mentioned in the question? from a non-price discriminating monopolist in which of A. P = minimum ATC, and P = AR the following ways? B. P = minimum ATC, and P = MC Profit Consumer surplus C. P = MC, and P = minimum ATC A higher w/ price higher w/ price D. P = MC, and P = AR discrimination discrimination E. MC = MR, and MRP = VMP B higher w/ price lower w/ price discrimination discrimination Figure 14 C lower w/ price lower w/ price Quantity Average Average Marginal discrimination discrimination of Output Variable Cost Total Cost Cost D lower w/ price higher w/ price discrimination discrimination 0 - - - E the same with both the same with both - 1 50 250 50 60. Suppose the only three members of society will 2 45 145 40 receive marginal benefits from a proposed public 3 41.7 108.4 35 project equal to $300, $500, and $800, respectively. 4 40 90 35 However, each must pay taxes of $400 to pay for the 5 40 80 40 total cost. In the absence of vote trading, a majority rule 6 40.8 74.1 45 vote will: 7 42.1 70.7 50 A. pass this project and resources will be allocated 8 44.3 69.3 60 efficiently B. pass this project and resources will be 56. Refer to Figure 14. The average fixed cost of overallocated to the project producing 4 units of output is: C. defeat this project and resources will be A. 35 B. 40 C.50 D. 90 E. 200 allocated efficiently D. defeat this project and resources will be 57. Refer to Figure 14. If the product’s price is underallocated to the project constant at $47.00, to maximize profits this firm will E. not enough information to determine what produce: would happen. A. zero, the firm will lose money by producing any level of output B. zero in the short run, but 6 in the long run C. zero in the long run, but 6 in the short run D. 1 in the short run, but 7 in the long run E. 7 in the long run, but 1 in the short run GO ON TO NEXT PAGE 9 48. B Answer Key 49. C 1. D 50. D 2. A 51. C 3. E 52. A 4. A 53. C 5. B 54. D 6. E 55. B 7. B 56. E 8. A 57. C 9. D 58. D 10. B 59. B 11. D 60. A 12. B 13. A 14. B 15. C 16. D 17. C 18. D 19. A 20. C 21. E 22. A 23. A 24. A 25. E 26. B 27. C 28. C 29. B 30. A 31. B 32. C 33. C 34. C 35. B 36. C 37. D 38. A 39. D 40. B 41. C 42. B 43. D 44. A 45. B 46. B 47. B GO ON TO NEXT PAGE 10