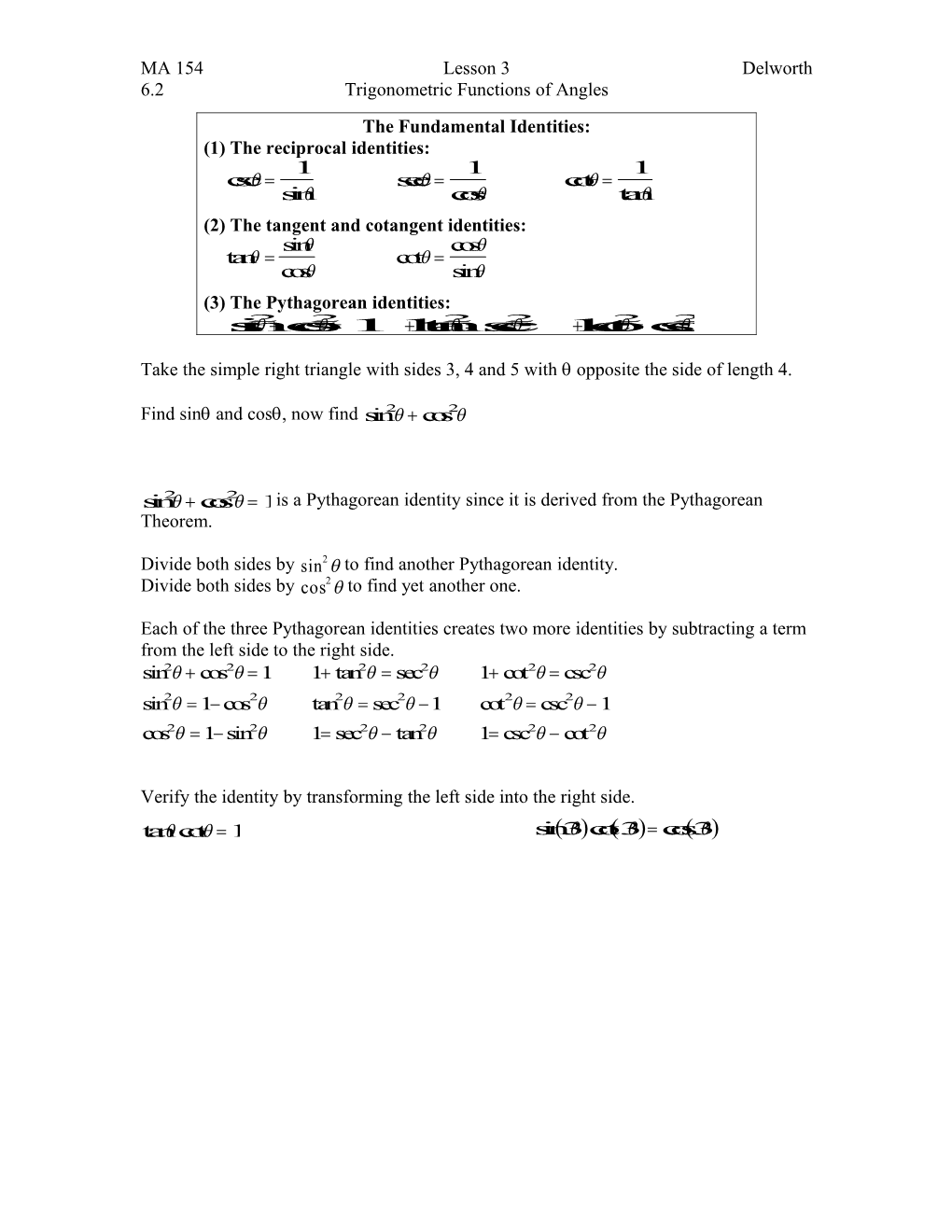
MA 154 Lesson 3 Delworth 6.2 Trigonometric Functions of Angles The Fundamental Identities: (1) The reciprocal identities: 1 1 1 csc sec cot sin cos tan (2) The tangent and cotangent identities: sin cos tan cot cos sin (3) The Pythagorean identities: sin2 cos2 11 tan2 sec2 1 cot2 csc2
Take the simple right triangle with sides 3, 4 and 5 with opposite the side of length 4.
Find sin and cos, now find sin2 cos2
sin2 cos2 1 is a Pythagorean identity since it is derived from the Pythagorean Theorem.
Divide both sides by sin2 to find another Pythagorean identity. Divide both sides by cos2 to find yet another one.
Each of the three Pythagorean identities creates two more identities by subtracting a term from the left side to the right side. sin2 cos2 1 1 tan2 sec2 1 cot2 csc2 sin2 1 cos2 tan2 sec2 1 cot2 csc2 1 cos2 1 sin2 1 sec2 tan2 1 csc2 cot2
Verify the identity by transforming the left side into the right side. tan cot 1 sin3cot3 cos3
MA 154 Lesson 3 Delworth 6.2 Trigonometric Functions of Angles sin c o s sec 2 2 csc 1 c o t tan 2 sin 2
2 2 2 (1 cos)(1 cos) sin2 cossec 1 sin
2 2 1 sin1 tan 1 cot tan csc sec
MA 154 Lesson 3 Delworth 6.2 Trigonometric Functions of Angles Using the coordinate system,
Notice that the adjacent side corresponds to the x-value of the coordinate and the opposite side corresponds the y-value of the coordinate (x, y) The idea that the cosine of corresponds to the x-axis and the sine of corresponds to the y-axis is one that you need to get use to.
If is an angle in standard position on a rectangular coordinate system and if P(-5, 12) is on the terminal side of , find the values of the six trigonometric functions of .
If is an angle in standard position on a rectangular coordinate system and if P(4, 3) is on the terminal side of , find the values of the six trigonometric functions of .
Find the exact values of the six trigonometric functions of if is in standard position and the terminal side of is in the specified quadrant and satisfies the given condition.
III; on the line 4x – 3y = 0 II; parallel to the line 3x + y – 7 = 0
MA 154 Lesson 3 Delworth 6.2 Trigonometric Functions of Angles Find the quadrant containing if the given conditions are true. a) tan < 0 and cos > 0 I II sin All b) sec > 0 and tan < 0 csc
c) csc > 0 and cot < 0 III IV tan cos d) cos < 0 and csc < 0 cot sin
Use the fundamental identities to find the values of the trigonometric functions for the given conditions:
12 tan and cos 0 sec 4 and csc 0 5