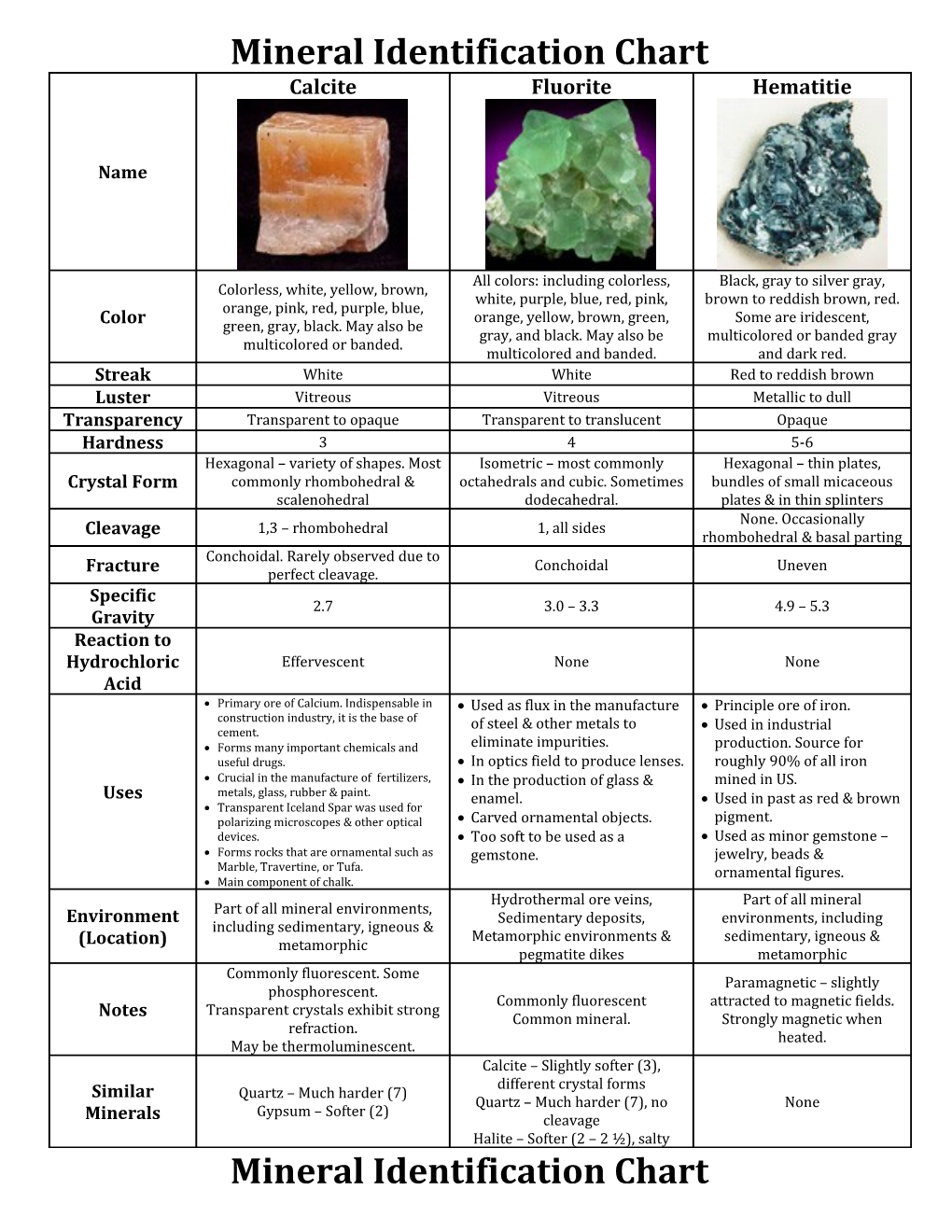
Mineral Identification Chart Calcite Fluorite Hematitie
Name
All colors: including colorless, Black, gray to silver gray, Colorless, white, yellow, brown, white, purple, blue, red, pink, brown to reddish brown, red. orange, pink, red, purple, blue, orange, yellow, brown, green, Some are iridescent, Color green, gray, black. May also be gray, and black. May also be multicolored or banded gray multicolored or banded. multicolored and banded. and dark red. Streak White White Red to reddish brown Luster Vitreous Vitreous Metallic to dull Transparency Transparent to opaque Transparent to translucent Opaque Hardness 3 4 5-6 Hexagonal – variety of shapes. Most Isometric – most commonly Hexagonal – thin plates, Crystal Form commonly rhombohedral & octahedrals and cubic. Sometimes bundles of small micaceous scalenohedral dodecahedral. plates & in thin splinters None. Occasionally 1,3 – rhombohedral 1, all sides Cleavage rhombohedral & basal parting Conchoidal. Rarely observed due to Conchoidal Uneven Fracture perfect cleavage. Specific 2.7 3.0 – 3.3 4.9 – 5.3 Gravity Reaction to Hydrochloric Effervescent None None Acid Primary ore of Calcium. Indispensable in Used as flux in the manufacture Principle ore of iron. construction industry, it is the base of of steel & other metals to Used in industrial cement. Forms many important chemicals and eliminate impurities. production. Source for useful drugs. In optics field to produce lenses. roughly 90% of all iron Crucial in the manufacture of fertilizers, In the production of glass & mined in US. Uses metals, glass, rubber & paint. enamel. Used in past as red & brown Transparent Iceland Spar was used for polarizing microscopes & other optical Carved ornamental objects. pigment. devices. Too soft to be used as a Used as minor gemstone – Forms rocks that are ornamental such as gemstone. jewelry, beads & Marble, Travertine, or Tufa. ornamental figures. Main component of chalk. Hydrothermal ore veins, Part of all mineral Part of all mineral environments, Environment Sedimentary deposits, environments, including including sedimentary, igneous & Metamorphic environments & sedimentary, igneous & (Location) metamorphic pegmatite dikes metamorphic Commonly fluorescent. Some Paramagnetic – slightly phosphorescent. Commonly fluorescent attracted to magnetic fields. Transparent crystals exhibit strong Notes Common mineral. Strongly magnetic when refraction. heated. May be thermoluminescent. Calcite – Slightly softer (3), different crystal forms Similar Quartz – Much harder (7) Quartz – Much harder (7), no None Gypsum – Softer (2) Minerals cleavage Halite – Softer (2 – 2 ½), salty Mineral Identification Chart Biotite – Mica Muscovite – Mica Talc
Name
Colorless, white, beige, White, beige, gray, yellow, Black, dark brown, dark green, yellow, brown, gray, green, brown, pink, purple, blue, Color reddish black. pink, purple, red, black; green. Rarely colorless. occasionally multicolored Streak White Colorless White Luster Pearly Pearly Greasy, waxy, pearly Transparency Translucent to opaque Transparent to translucent Transparent to opaque Hardness 2.5 – 3 2 – 2 ½ 1 Monoclinic – Most often large Crystal Form Monoclinic – Thick flakes Monoclinic – thick flakes distorted masses and foliated sheets and plates. Cleavage 1,1 1, 1 1,1 Fracture Uneven Uneven Uneven Specific Gravity 2.8 – 3.4 2.7 – 3.0 Reaction to Hydrochloric None None None Acid Poor conductor of heat & electricity Poor conductor of heat & Industrial uses. and used as an insulator for electricity and used as an Crushed into a powder to form electrical products & insulator for electrical products & talcum powder. Main ingredient semiconductors. semiconductors. in cosmetics and some baby Large sheets once used for oven powders. windows. Once used as a filler to prevent slipping in latex gloves. Uses Highly resistant to heat & electricity – used as an insulator in electronics. Filler material for paints, rubber & insecticides. Ornamental stone, carved into figures, jewelry boxes, tiling & art sculptures. Common rock forming Common rock forming mineral; In metamorphic rocks, mineral. Especially found in especially in metamorphic especially Serpentine Environment granite pegmatites, rocks such as schist & gneiss. deposits. metamorphic rocks, (Location) Also in igneous rocks such as Most commonly forms the metamorphic schists, & granite & rhyolite. rock Soapstone. hydrothermal veins. Has a greasy feel. Small pieces flake or peel off Small pieces flake or peel off Notes May be lightly fluorescent. Biotite – Usually darker in color Lepidolite – difficult to tell Muscovite – Usually lighter in from pink muscovite Calcite Similar Minerals color Gypsum – Cannot be peeled into micaceous sheets, crystals usually different shapes Mineral Identification Chart
Name Color Streak Luster Transparency Hardness Crystal Form Cleavage Fracture Specific Gravity Reaction to Hydrochloric Acid Uses Environment (Location) Notes Similar Minerals