Power SystemAnalysis and Control (EET 408) Laboratory Module
EXPERIMENT 4
OPTIMAL POWER FLOW
1. OBJECTIVE:
To analyze the optimal power flow by means of MiPower soft ware
2. EQUIPMENT:
MiPower software
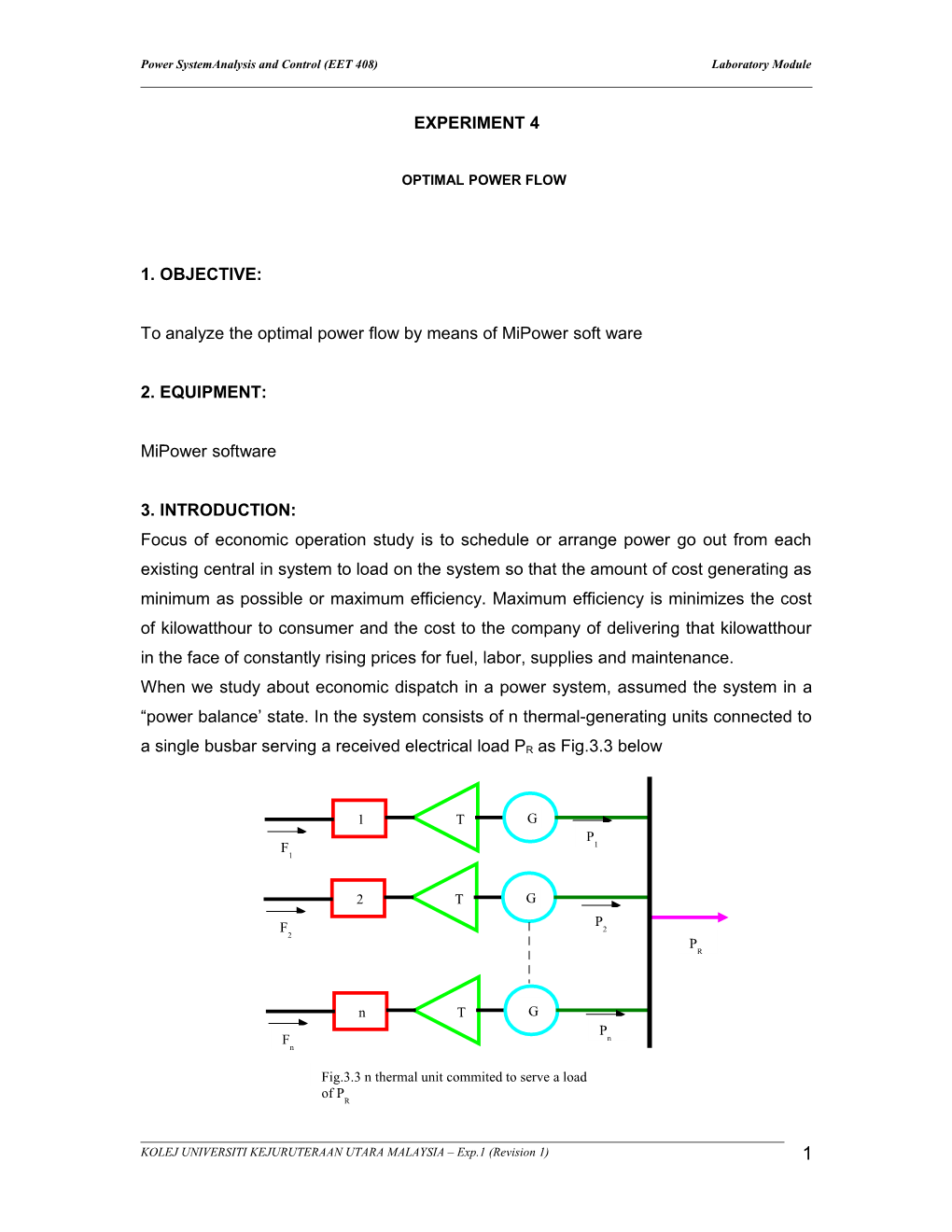
3. INTRODUCTION: Focus of economic operation study is to schedule or arrange power go out from each existing central in system to load on the system so that the amount of cost generating as minimum as possible or maximum efficiency. Maximum efficiency is minimizes the cost of kilowatthour to consumer and the cost to the company of delivering that kilowatthour in the face of constantly rising prices for fuel, labor, supplies and maintenance. When we study about economic dispatch in a power system, assumed the system in a “power balance’ state. In the system consists of n thermal-generating units connected to a single busbar serving a received electrical load PR as Fig.3.3 below
1 T G P F 1 1
2 T G P F 2 2 P R
n T G P F n n
Fig.3.3 n thermal unit commited to serve a load of P R
KOLEJ UNIVERSITI KEJURUTERAAN UTARA MALAYSIA – Exp.1 (Revision 1) 1 Power SystemAnalysis and Control (EET 408) Laboratory Module
So, total system generated equal to the total system load plus losses in the transmission line including tie line flows out of the system
n PG Pi PR PL i1 1 where:
PG = total output generated electrical power
Pi = output-generated electrical power for the ith generating unit [per- unit] on a common power base
PR = total system load, including tie line flows,[per-unit]
PL = total system transmission losses [per-unit] n = number of generators in service in the system A basic constraint is that for each generator:
P P P mini Gi max 2 To determine economic dispatch in the power plants, we can divided to two categories: a) System without transmission losses
n PG Pi PR i1 3 The operating cost of a unit includes fuel cost, labor, supplies and maintenance in expressed as C F P i i ini 4 where:
Ci = operating cost of unit i [$/H]
Fi = operating unit i [$/ M Btu]
Pin i = input unit i power [M Btu/H]
The curve Ci can be represented by a second-order expression
KOLEJ UNIVERSITI KEJURUTERAAN UTARA MALAYSIA – Exp.1 (Revision 1) 2 Power SystemAnalysis and Control (EET 408) Laboratory Module
2 Ci i i Pi i Pi 5 where: i = generator i, one of n units
Ci = operating cost of generator i[$H]
Pi = electrical power output of generator i [per-unit] on a common power base , and are in units of $/H
dFi for Pi,min Pi Pi,max dPi
dFi for Pi Pi,max dPi 6
dFi for Pi Pi,min dPi
This is the requisite to minimize cost of the system. A general solution is called the method of Lagrangian multipliers. If without losses and no generator limits, the most economic operation
k k i Pi k 2 i Bii 7 is called Coordination Equation and
KOLEJ UNIVERSITI KEJURUTERAAN UTARA MALAYSIA – Exp.1 (Revision 1) 3 Power SystemAnalysis and Control (EET 408) Laboratory Module
ng i PD i1 2 i ng 1 i1 2 i 8
b) System with transmission losses
4. PROCEDURE: PART A
Cost equation and loss co-efficient of different units in a plant are given in Table 1.0. Determined economic generation for a total load demand of 240 MW. Unit No Cost of Fuel in RM/hour Pschedule
1 2 90 C1=0.05 P1 + 20 P1 + 800 0<= P1 <=100
2 2 90 C2=0.06 P2 + 15 P2 + 1000 0<= P2 <=100
3 2 90 C3=0.07 P3 + 18 P3 + 900 0<= P3 <=100
TABLE 1.0
B11= 0.0005; B12= 0.00005; B13= 0.0002;
B22=0.0004; B23=0.00018; B33= 0.0005;
B21=B12; B23 = B32; B13 = B31;
1. Invoke MiPower Tools in MiPower main screen and select “Economic Dispatch by B- Coefficient”.
KOLEJ UNIVERSITI KEJURUTERAAN UTARA MALAYSIA – Exp.1 (Revision 1) 4 Power SystemAnalysis and Control (EET 408) Laboratory Module
2. Click button to create new file. 3. After given a file name and specify the directory in MiPower directory, save it. The following windows will appear.
4. Figure above shows how to enter data for generator no 1. To input data for gen 2 and
3, simply click and input all necessary data based on the data given in Table 1.0.
KOLEJ UNIVERSITI KEJURUTERAAN UTARA MALAYSIA – Exp.1 (Revision 1) 5 Power SystemAnalysis and Control (EET 408) Laboratory Module
5. To input the B-coefficient data of B11, follow the procedure as shown in windows
below. Then click the button. 6. Similarly enter the values if B12 to B31.
7. Click the main button to save all the input data.
8. After, click button to run the program. 9. After saving the output in a notepad, print it(Print only the last part of the display output).
Click here to save every B-coefficient data
Select 1 to enter data of B11
Enter 0.0005 as B11
Click here to save all data Click execute button after saving all data
10. What is Initial Total generation cost of the system? 11. What is the final cost of generation of every generator and total generation? 12. What is the final value of lambda?
KOLEJ UNIVERSITI KEJURUTERAAN UTARA MALAYSIA – Exp.1 (Revision 1) 6 Power SystemAnalysis and Control (EET 408) Laboratory Module
13. Repeat the procedure 1-9 with initial lambda of 30. How many iterations required to get the same result? 14. Repeat the procedure 1-9 for Pschedule of 100MW. Answer the procedure 10- 13m for this case.
QUESTION
1. The fuel-cost functions for three thermal plants in $/h are given by:
2 C1 350 7.20P1 0.0040P1
2 C2 500 7.30P2 0.0025P2
2 C3 600 6.74P3 0.0030P3
where P1 , P2, and P3 in MW. The governors are set such that generators share the load equally. Neglecting line losses and generator limits, find the total cost in $/h when the total load is:
(i) PD = 750 MW
(ii) PD = 1335 MW.
2. What is the difference between economic dispatch and unit commitment? 3. Solve problem 1, if the governor not share the load equally for load 450 MW
KOLEJ UNIVERSITI KEJURUTERAAN UTARA MALAYSIA – Exp.1 (Revision 1) 7 Power SystemAnalysis and Control (EET 408) Laboratory Module
Name: ______Matrix No:______Experiment No:______Date: ______
RESULTS: 10. Initial Total generation ______
11. Generator 1 ______Generator 2 ______Generator 3 ______
12. Final Value of Lambda ______
13. No of iterations ______
14.
KOLEJ UNIVERSITI KEJURUTERAAN UTARA MALAYSIA – Exp.1 (Revision 1) 8 Power SystemAnalysis and Control (EET 408) Laboratory Module
PART B
1.
DISCUSSION
CONCLUSION
KOLEJ UNIVERSITI KEJURUTERAAN UTARA MALAYSIA – Exp.1 (Revision 1) 9 Power SystemAnalysis and Control (EET 408) Laboratory Module
KOLEJ UNIVERSITI KEJURUTERAAN UTARA MALAYSIA – Exp.1 (Revision 1) 10