ME 362 Compressible Flow with Shock Wave Page 1 of 4
Solution:
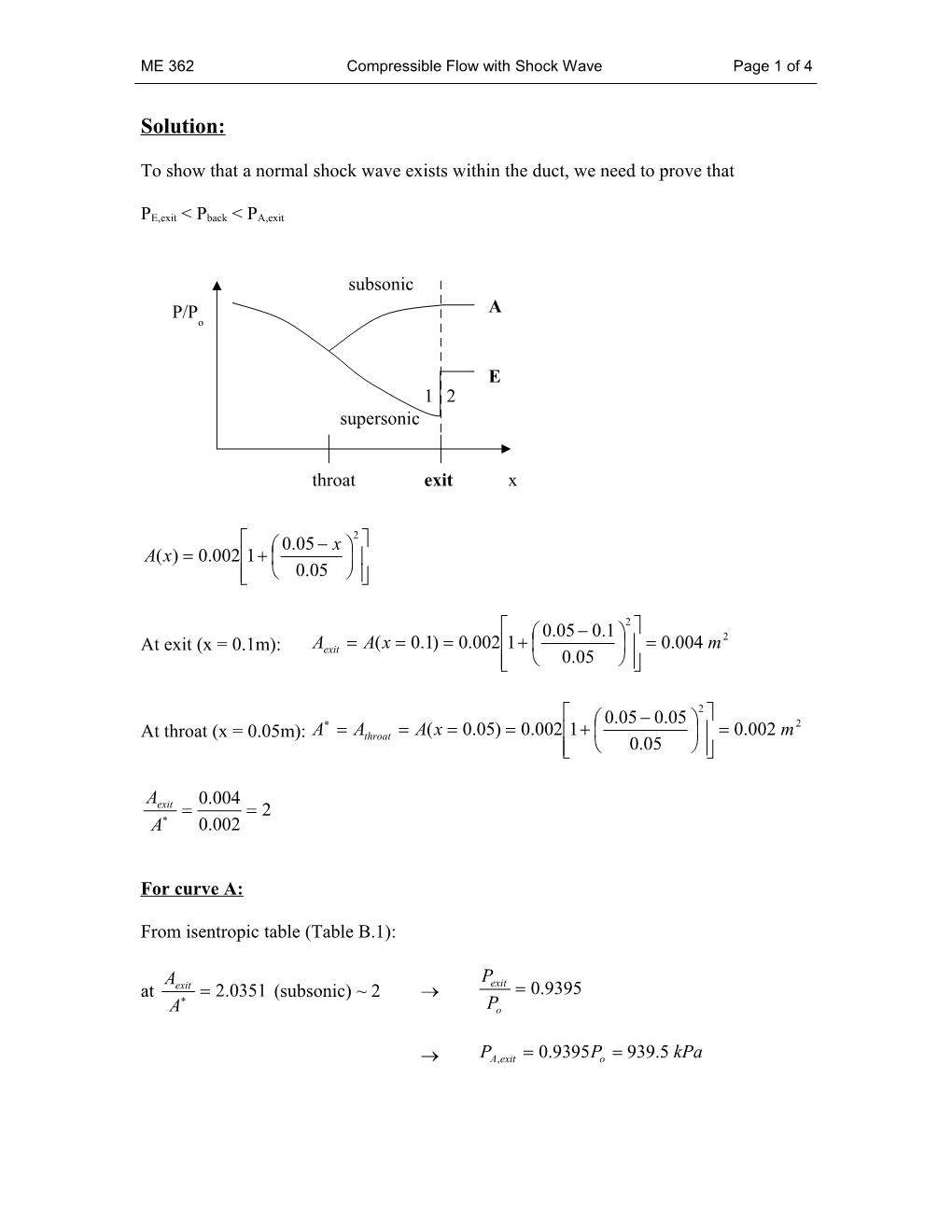
To show that a normal shock wave exists within the duct, we need to prove that
PE,exit < Pback < PA,exit
subsonic P/P A o
E 1 2 supersonic
throat exit x
2 0.05 x A(x) 0.0021 0.05
2 0.05 0.1 2 At exit (x = 0.1m): Aexit A(x 0.1) 0.0021 0.004 m 0.05
2 0.05 0.05 2 At throat (x = 0.05m): A Athroat A(x 0.05) 0.0021 0.002 m 0.05
A 0.004 exit 2 A 0.002
For curve A:
From isentropic table (Table B.1):
A P exit exit 0.9395 at 2.0351 (subsonic) ~ 2 A Po
PA,exit 0.9395Po 939.5 kPa ME 362 Compressible Flow with Shock Wave Page 2 of 4
For curve E:
Before shock (isentropic, supersonic):
From isentropic table (Table B.1):
A at exit 2.0050 (supersonic) ~ 2 Ma 2.2 A 1
Across shock (nonisentropic):
From shock table (Table B.2):
P A o2 0.6281 2 at Ma1 2.2 and 1.5920 Po1 A1
2 A1 Athroat 0.002 m
2 A21.5920 A 1 1.5920 0.002 0.003184 m
After shock (isentropic, subsonic):
Aexit 0.004 1.2563 A2 0.003184
From isentropic table (Table B.1):
Aexit Pexit at 1.2403 (subsonic) 0.8082 A2 Po2 ~ 1.2563 P P P exit exit o2 0.8082 0.6281 0.5076 Po Po2 Po1
PE,exit 0.5076Po 507.6 kPa
PE,exit 507.6 kPa < Pback 650 kPa < PA,exit 939.5 kPa
Normal shock exists within the nozzle [Ans.] ME 362 Compressible Flow with Shock Wave Page 3 of 4
Iterative procedure for locating normal shock wave:
sonic subsonic 1 2 supersonic
throat x exit x shock
Before shock (isentropic, supersonic): at x = 0.075m:
2 0.05 0.075 2 A1 Ashock A(x 0.075) 0.0021 0.0025 m 0.05
A 0.0025 1 1.25 A 0.002
From isentropic table (Table B.1):
A at 1 1.2502 (supersonic) ~ 1.25 Ma 1.6 A 1
Across shock (nonisentropic):
From shock table (Table B.2):
P A o2 0.8952 2 at Ma1 1.6 and 1.1171 Po1 A1
2 A21.1171 A 1 1.1171 0.002 0.00223 m ME 362 Compressible Flow with Shock Wave Page 4 of 4
After shock (isentropic, subsonic):
Aexit 0.004 1.7937 A2 0.00223
From isentropic table (Table B.1):
Aexit Pexit at 1.8229 (subsonic) ~ 1.7937 0.9231 A2 Po2
Pexit Pexit Po2 0.9231 0.8952 0.8264 Pexit 0.8264Po 826.4 kPa [Ans.] Po Po2 Po1
Determine if correct shock position is upstream or downstream of x = 0.075 m:
Pexit826.4 kPa P back 650 kPa correct shock position > x = 0.075 m
correct shock position is further downstream [Ans.]
P /P P > P back o exit back sonic P = P P exit back back shock
x x x x throat shock exit x = 0.075m