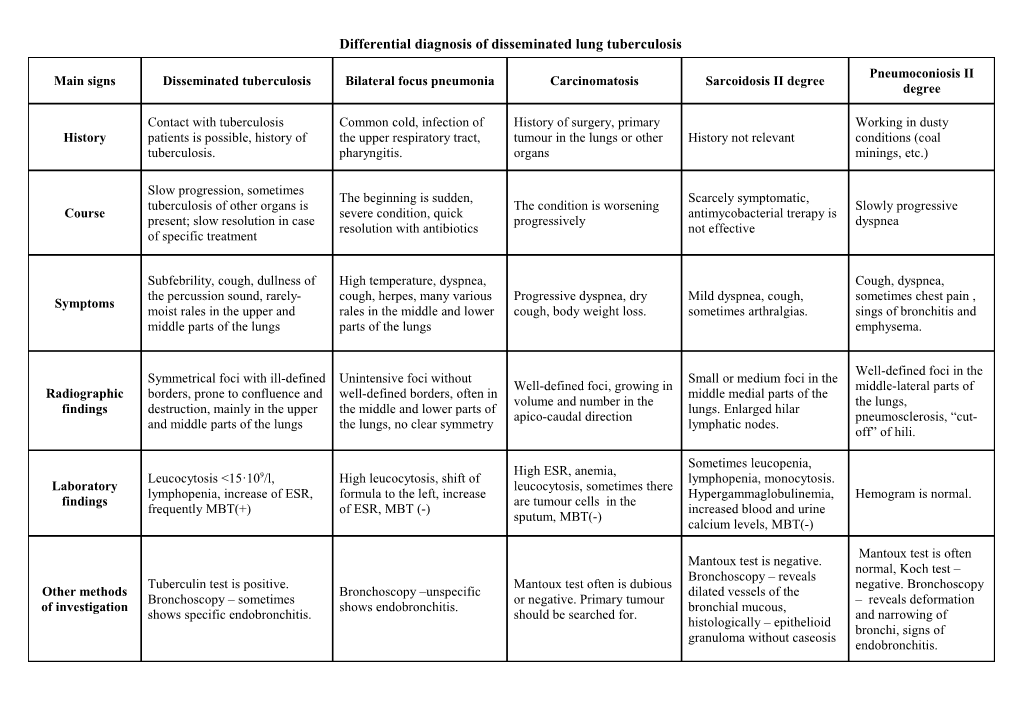
Differential diagnosis of disseminated lung tuberculosis
Pneumoconiosis II Main signs Disseminated tuberculosis Bilateral focus pneumonia Carcinomatosis Sarcoidosis II degree degree
Contact with tuberculosis Common cold, infection of History of surgery, primary Working in dusty History patients is possible, history of the upper respiratory tract, tumour in the lungs or other History not relevant conditions (coal tuberculosis. pharyngitis. organs minings, etc.)
Slow progression, sometimes The beginning is sudden, Scarcely symptomatic, tuberculosis of other organs is The condition is worsening Slowly progressive Course severe condition, quick antimycobacterial trerapy is present; slow resolution in case progressively dyspnea resolution with antibiotics not effective of specific treatment
Subfebrility, cough, dullness of High temperature, dyspnea, Cough, dyspnea, the percussion sound, rarely- cough, herpes, many various Progressive dyspnea, dry Mild dyspnea, cough, sometimes chest pain , Symptoms moist rales in the upper and rales in the middle and lower cough, body weight loss. sometimes arthralgias. sings of bronchitis and middle parts of the lungs parts of the lungs emphysema.
Well-defined foci in the Symmetrical foci with ill-defined Unintensive foci without Small or medium foci in the Well-defined foci, growing in middle-lateral parts of Radiographic borders, prone to confluence and well-defined borders, often in middle medial parts of the volume and number in the the lungs, findings destruction, mainly in the upper the middle and lower parts of lungs. Enlarged hilar apico-caudal direction pneumosclerosis, “cut- and middle parts of the lungs the lungs, no clear symmetry lymphatic nodes. off” of hili.
Sometimes leucopenia, High ESR, anemia, Leucocytosis <15·109/l, High leucocytosis, shift of lymphopenia, monocytosis. Laboratory leucocytosis, sometimes there lymphopenia, increase of ESR, formula to the left, increase Hypergammaglobulinemia, Hemogram is normal. findings are tumour cells in the frequently MBT(+) of ESR, MBT (-) increased blood and urine sputum, MBT(-) calcium levels, MBT(-)
Mantoux test is often Mantoux test is negative. normal, Koch test – Bronchoscopy – reveals Tuberculin test is positive. Mantoux test often is dubious negative. Bronchoscopy Other methods Bronchoscopy –unspecific dilated vessels of the Bronchoscopy – sometimes or negative. Primary tumour – reveals deformation of investigation shows endobronchitis. bronchial mucous, shows specific endobronchitis. should be searched for. and narrowing of histologically – epithelioid bronchi, signs of granuloma without caseosis endobronchitis.