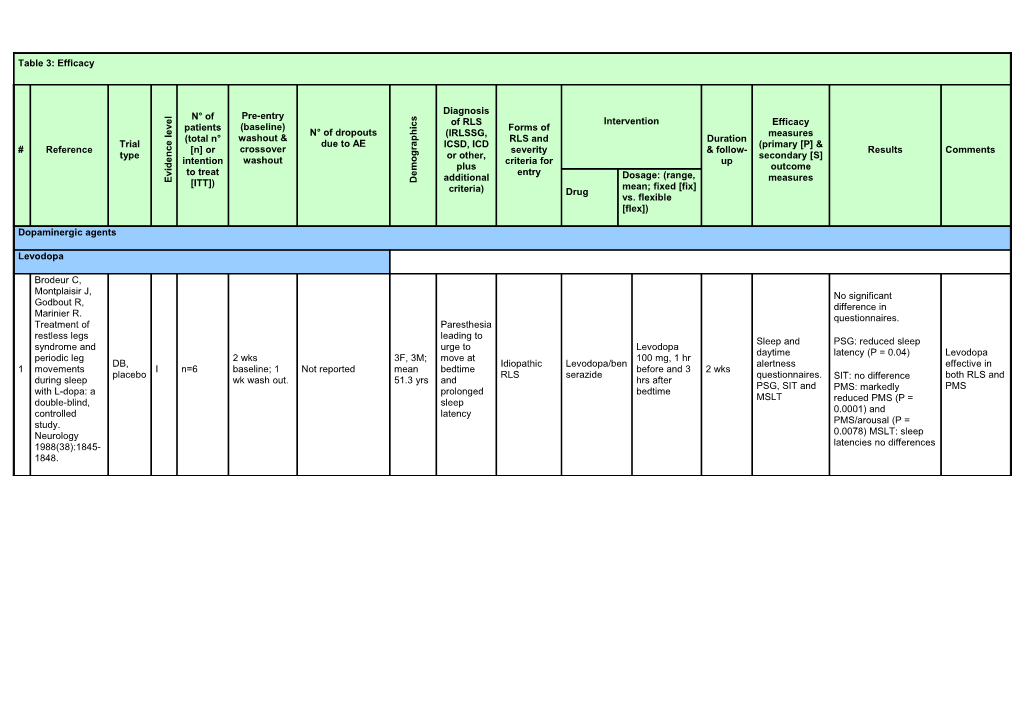
Table 3: Efficacy
Diagnosis
l Pre-entry N° of s
e Intervention c of RLS Efficacy i v patients (baseline) Forms of e h
l N° of dropouts (IRLSSG, measures
(total n° washout & p RLS and Duration e Trial due to AE a ICSD, ICD (primary [P] & r # Reference c [n] or crossover severity & follow- Results Comments g type n or other, secondary [S] o e intention washout criteria for up d m i plus outcome e v to treat entry additional Dosage: (range, measures E [ITT]) D mean; fixed [fix] criteria) Drug vs. flexible [flex])
Dopaminergic agents
Levodopa
Brodeur C, Montplaisir J, No significant Godbout R, difference in Marinier R. questionnaires. Treatment of Paresthesia restless legs leading to Sleep and PSG: reduced sleep syndrome and urge to Levodopa daytime latency (P = 0.04) Levodopa periodic leg 2 wks 3F, 3M; move at 100 mg, 1 hr DB, Idiopathic Levodopa/ben alertness effective in 1 movements I n=6 baseline; 1 Not reported mean bedtime before and 3 2 wks placebo RLS serazide questionnaires. both RLS and during sleep wk wash out. 51.3 yrs and hrs after SIT: no difference PSG, SIT and PMS with L-dopa: a prolonged bedtime PMS: markedly MSLT double-blind, sleep reduced PMS (P = controlled latency 0.0001) and study. PMS/arousal (P = Neurology 0.0078) MSLT: sleep 1988(38):1845- latencies no differences 1848. Idiopathic RLS: PLMI reduced with levodopa vs. placebo by 27% mean, P = 0.005;longer sleep time P = 0.045; better subjective sleep quality by 36% P = 0.002. Uremic RLS: PLMI reduced with levodopa vs. placebo by 29% Idiopathi mean P = 0.005;longer Trenkwalder C, c RLS: Authors: sleep time; better Stiasny K, 5F, [P]: 3 primary significant subjective sleep quality Pollmacher T, 12M; endpoints: PLM reduction of Levodopa/be by 42%, P = 0.002. et al. L-dopa 37-73 index, sleep PLMS during nserazide PSG effect of therapy of yrs; time, subjective the first 4 100/25 mg, levodopa on PLMI uremic and 33 AEs, 8/33 on mean 53 Personal quality of sleep. sleep hrs, Idiopathic Levodopa/ben increasing to only significant in the idiopathic RCT, 2 wk baseline placebo; only 1 yrs; criteria, but [S]: PSG improved 2 I n=28 and uremic serazide, 200/50 mg if 4 wks first 4 sleep hrs. restless legs DB, CO period severe AE on Uremic similar to measures, sleep quality RLS placebo needed. Actigraphy similar to syndrome: a levodopa RLS: IRLSSG actigraphy, and better Mean PSG. double-blind, 5F, subjective daytime life levodopa For both idiopathic crossover trial. 6M; patient and quality, used: 146 mg and uremic RLS: Sleep 29-66 physician without Patients' evaluation of 1995;18(8):681- yrs; reports severe side life quality (by VAS): 688. mean 49 effects. better life satisfaction yrs (P = 0.01) and negative feelings and complaints (P = 0.024). Physicians' evaluation by CGI: improved severity (P = 0.045) and global assessment of change (P = 0.025). (No difference between idiopathic and uremic RLS).
Levodopa reduced Walker SL, Fine PLMI by 40%, P = A, Kryger MH. 0.006. Also PLMA [P]: Leg Authors: no L- reduced by 61% P = movements, clinically DOPA/carbidop RCT, 4F, 1M; 0.05. No subjective 100/25 mg improved sleep. significant a for nocturnal DB, 1 wk wash mean Levodopa/car improvement in RLS 3 I n=5 No AE ICSD-1 Uremic RLS CR 1 h before 1 wk [S]: PSG subjective movement placebo out age 68 bidopa symptoms or sleep. bedtime measures improvement disorders in , CO yrs Other PSG measures: of RLS or uremia. Sleep no improvement in sleep! 1996;19(3):214- sleep latency, SE, 218. increased SWS P = 0.01. Staedt J, Wassmuth F, Ziemann U, Levodopa/carbidopa Hajak G, complete relief 1/11 pts, Ruther E, partial in 0/11, mean Stoppe G. dose 363 mg. Pergolide: Pergolide complete treatment of relief in 9/11, partial in choice in 2/11 patients, mean restless legs dose 0.159 mg. syndrome Pergolide Authors: 5F Pergolide at 18 days PSG: levodopa reduced ( RLS) and Nausea in 1/11 0.125mg at PSG and pergolide RCT, 1 day wash 6M Not Idiopathic bedtime vs. for each "nocturnal myoclonus 4 nocturnal I n=11 levodopa, 9/11 bedtime vs. clinical more DB, CO out age 50- specified RLS levodopa/carb active time" by 45%, P < myoclonus pergolide. levodopa/carb interviews effective than 69 yrs idopa drug 0.025; Pergolide syndrome idopa 250mg. levodopa. reduced NMT by 79%, (NMS). A P < 0.001. double -blind No change in sleep randomized parameters. Pergolide crossover trial significantly increased of pergolide time in bed and sleep versus L-Dopa. time compared to J Neural levodopa, P <0.05. Transm 1997;104(4- 5):461-468.
RR- Levodopa/benserazide Collado-Seidel 110/25mg marked V, Kazenwadel improvement in RLS J, Wetter TC, et Minor AE: dry first half night in 77%; al. A controlled mouth (n = 3), superior efficacy of study of nightmares (n = 2), 100 or 200 combination therapy additional sr-L- dizziness, 19F, PLMSI; %TIB IRLSSG + RR-levodopa mg RR-levodopa & CR- dopa in L-dopa- 2 wks nervousness, 11M; Idiopathic & without LM; RCT, PLMSI > 5 CR-levodopa/ 100/25 mg or levodopa compared 5 responsive I n=30 baseline. No dyspepsia, mean secondary 4 wks subjective DB, CO + SL > 25m benserazide 200/50 mg 1h with RR-levodopa alone restless legs wash out. epigastric pain, age 58 RLS quality of sleep +SE ≤85% placebo before for PLMSI (P < syndrome with cardiac rhythm yrs during last wk. bedtime 0.0001), %TIB without late-night disorder, and LM (P < 0.0001), symptoms. abnormal visus (n subjective quality of Neurology = 1) sleep during last wk (P 1999;52(2):285- < 0.001). 290. Quality of life not improved Levodopa/benserazide superior to placebo in reducing Benes H, PLMSI (P < 0.0001), Karalla B, in increasing %TIB Kummer J, without LM (P < Kazenwadel J, 0.0001), and in Selzer R, improving quality of Authors: Kohnen R. sleep (P = 0.0004) but onset of Rapid onset of IRLSSG + only during first half of RCT, 19F, Levodopa/ben action rapid action of SL > 30m Levodopa/be PLMSI; %TIB night not during the DB, 2 wks 28 pts with 98 AE 13M; serazide and full levodopa in and/or SE ≤ Idiopathic & nserazide without LM; second half. 6 placebo I 32 pts baseline. No vs. 4 pts with 16 mean 100/25mg 1h 4 wks efficacy restless legs 85% and uremic RLS 100/25mg 1 subjective Sleep quality , CO, wash out. AE on placebo. age 56 before achieved syndrome: a PLMA-I or 2 cps quality of sleep. significantly improved, MC yrs bedtime within the first double-blind, > 5/h SL shorter (P < few days of randomized, 0.0001), sleep duration therapy. multicenter, longer crossover trial. (P = 0.0002), and less Sleep getting up during the 1999;22(8):107 night (P = 0.0261) with 3-1081. levodopa. RLS severity reduced, at sleep onset (P = 0.0061) and during the night (P = 0.0011).
Eisensehr I, Ehrenberg BL, Rogge Solti S, VPA start at Noachtar S. 300 mg, go to Authors: Treatment of 600 mg PO one day hourly 12F, VPA significantly superior idiopathic after 2 days; diary with 8M; idiopathic decreased RLS efficacy of restless legs RCT, slow release levodopa 200 minutes of mean RLS, symptoms per diary combination syndrome DB valproic acid, mg with symptoms; 0- age 58.9 IRLSSG PLMI>10 by 3 wks per and overall intensity of rr-levodopa 7 (RLS) with drug & I n=20 5 days 0 slow release benserazide 10 VAS of yrs; (1995) PSG; daily phase score; overall, LD did and sr- slow-release placebo levodopa- 50 mg; all overall severity; range symptoms not. LD significantly levodopa vs. valproic acid , CO benserazide drugs & PSG measures 41-74 for 6 months decreased PLMI, monotherapy compared with placebo taken from 2 nights yrs neither decreased SE of rr- slow-release 90 minutes per phase levodopa. levodopa/bense before razide. J Neurol bedtime 2004;251:579- 583. Micozkadioglu H, Ozdemir FN, Significantly improved Kut A, Sezer S, on IRLS-abbreviated Saatci U, compared to baseline Haberal M. and to levodopa scores; Fixed dose, Gabapentin significantly improved 5F, gabapentin versus SF36 domains of RCT, 10M, 200 mg after levodopa for 2 wks Abbreviated general health, body No statement CO mean IRLSSG Dialysis Gabapentin, each 8 the treatment of I n=15 between 1 4 wks IRLS, PSQI, pain and social in paper on compar age 45.8 1995 patients ropinirole hemodialysis Restless Legs phases SF36 functions (P < 0.001); blinding ison (15.3) session or Syndrome in superior to baseline years 125 mg hemodialysis and levodopa in sleep levodopa. patients: an parameters on PSQI open-label sleep quality, sleep study. Ren Fail latency, and sleep 2004;26:393- disturbance 397.
Trenkwalder C, Side effects Benes H, Grote for 9 subjects L, et al. in placebo, Cabergoline valproic acid compared to phase; 13 in levodopa in the levodopa, [P]: IRLS treatment of - 16.1 (cabergoline), including 4 RCT, 38 (cabergoline), [S]: sleep patients with -9.6 (levodopa) P< reported with DB, 26 (levodopa), 2 IRLS > 10, 200 - 300 mg quality (SF-A), severe restless idiopathi Levodopa vs. 0.0001; discontinuation augmentation 9 prosp., I n=361 1 wk drug related IRLSSG RLS-6 at fixed 30 wks RLS-QoL, legs syndrome: c RLS cabergoline due to augmentation; 7 ; open label parallel, severe AE in each night >= 4 2 - 3 mg ASRS, 4-item Results from a (cabergoline), 18 follow-up at 6 MC group version, CGI, multi-center, (levodopa). to 18 months: RLS-6 randomized, 9 of 12 on active valproic acid controlled trial. remained on Mov Disord effective 2007;22:696- therapy; 2 of 703. 7 on levodopa
Ergot-derived dopamine agonists
Bromocriptine
1 Walters AS, Hening RCT, DB, I n=6 Preentry not 0 4F, 2M History of Not Bromocri 7.5 mg, 1 or 2 30 days [P] and [S] not 5 patients subjectively WA, Kavey N, prosp., specified; 2 wks restlessness specified ptine divided doses specified responded to treatment; Chokroverty S, CO, in between and significant decrease of Gidro-Frank S. A placebo, paresthesias PLMS index (P < 0.025) double-blind that were randomized worse at night crossover trial of bromocriptine and placebo in restless legs syndrome. Ann Neurol 1988;24:455- 458.
Pergolide
Levodopa/carbidopa Staedt J, Wassmuth complete relief 1/11 pts, F, Ziemann U, Hajak partial in 0/11, mean dose G, Ruther E, Stoppe 363 mg. G. Pergolide: Pergolide complete relief treatment of choice Nause in 9/11, partial in 2/11 pts, in restless legs a in Pergolide mean dose 0.159 mg. syndrome ( RLS) Pergolide 1/11 at 18 days PSG: levodopa reduced and nocturnal 0.125mg at PSG and RCT, DB, levodo 5F, 6M; Idiopathic bedtime for each "nocturnal myoclonus 1 myoclonus I n=11 1 day wash out Not specified bedtime vs. clinical CO pa, 50-69 yrs RLS vs. active time" by 45%, P < 0.025; syndrome (NMS). A levodopa/carb interviews 9/11 levodopa/ drug Pergolide reduced NMT double -blind idopa 250mg. pergoli carbidopa by 79%, P < 0.001. randomized de. No change in sleep crossover trial of parameters. Pergolide pergolide versus L- significantly increased Dopa. J Neural time in bed and sleep Transm 1997;104(4- time compared to 5):461-468. levodopa, P < 0.05.
Earley CJ, Yaffee JB, Allen RP. Flexible Randomized, titration, twice PLMSI 48.9 to 14.5 (P < RCT, DB, [P]: PLMSI, SE, double-blind, 8 F, 8 M; a day (dinner, 0.05); SE 61% to 79% (P prosp., hrs per day with placebo-controlled 43-80 yrs; IRLSSG + Not 2 hrs. Before < 0.05); hrs RLS 7.0 to 2 parallel, I n=16 4 days 0 Pergolide 18 days RLS, global trial of pergolide in mean age PLMS > 15/hr specified bedtime), 1.8 hrs/day; improvement MC, improvement restless legs 59.5 yrs median 0.35 61% pergolide, 19% placebo score (in %) syndrome. mg (0.1 - placebo Neurology. 1998 0.65) Dec;51(6):1599-602. [P]: PLMI, TST, subjective Wetter TC, Stiasny sleep quality K, Winkelmann J, et (QoS). PLMI = 6 (Plc. 55) p> al. A randomized RCT, DB, PLMI > 5; Flexible [S]: PLMS, 0.001; PLMSI = n.a.; 4 wks controlled study of prosp., 2 wks pre Sleep titration 0.25 PLMSAI, sleep PLMSAI = 2 (Plc. 32); SE idiopathic crossover 3 pergolide in patients CO, I n=28 baseline; 1 wk 0 IRLSSG latency > Pergolide up to 0.75 latency, n° of = 78% (Plc. 55%); TST = RLS + 1 year with restless legs placebo, in-between 25 min; SE mg; mean awakenings, % 373.6 (Plc. 261.9) P = follow-up syndrome. MC < 75% 0.51 mg sleep stages, 0.0001; QoS = 3.0 (Plc. Neurology CGI, QoL 2.2) P = 0.0001 1999;52(5):944-950. (modified VAS Kramer et al.) sleep diary
Trenkwalder C, Hundemer HP, Lledo A, et al. Sleep [P]: PLMSAI, PLMI = -12 (Plc -2); Many Flexible Efficacy of pergolide RCT, DB, disturbanc SE. PLMSI = n.a.; PLMSAI = results in e- titration 0.25 in treatment of prosp., idiopathic es for 3 [S]: TST, PLMI, -13 (Plc -4) P = 0.004; SE tables that 4 I n=100 10 days 5 IRLSSG Pergolide up to 0.75 6 wks restless legs MC, RLS months, IRLS, CGI, = 11.3% (Plc 6.1%) P = the task mg, mean syndrome: the placebo PLMSAI > PGI, sleep 0.196; TST P = 0.145; force did 0.40 mg PEARLS Study. 5, IRLSSG diary IRLS P < 0.001 not find Neurology 2004;62:1391-1397.
Cabergoline
RLS-6 during the night p< Stiasny-Kolster K, 0.0001 for all dosages, [P]: RLS-6 RLS Benes H, Peglau I, IRLS -13.1 (0.5 mg; P < severity during et al. Effective RCT, DB, 0.01), -13.5 (1.0; P < Idiopathic the night. cabergoline prosp., 5 wks, 47 0.01), -15.7 (2.0 mg, P < 1 wk, 2 wks for Idiopathic RLS, RLS Cabergoli Fixed 0.5, 1, [S]: RLS-6, 1 treatment in parallel, I n=85 11 IRLSSG wks 0.001); RLS-6 severity at levodopa RLS at night >= ne 2 mg or Plc IRLS, Remitters idiopathic restless MC, follow-up bedtime and during the 4 (0 - 10) (0 points in legs syndrome. placebo day and RLS-6 sleep RLS-6 severity Neurology satisfaction improved scales or IRLS) 2004;63:2272-2279. particularly with > 1mg (P < 0.05)
Idiopathic Oertel et al. Efficacy RLS, of cabergoline in gender and Idiopathic restless legs RCT, DB, mean age RLS, IRLS [P]: PLMSAI, syndrome: a prosp., not possible > 10, RLS- SE, -18 (plc - 5) P = 0.0014, Cabergoli 2 placebo-controlled parallel, I n=40 5 half-lives 3 since given IRLSSG 6 at night Fixed 2 mg 5 wks [S]: IRLS, RLS- +6.2% (plc + 3.3) P = ne study with MC, separately > 4, 6, SF-A, QoL- 0.0443, 23.7 (-7.9) polysomnography placebo for PLMSAI > RLS, CGI (CATOR). Neurology cabergoline 5 2006;67:1040-1046 and placebo Trenkwalder C, Benes H, Grote L, et 38 al. Cabergoline (caber compared to goline), [P]: IRLS - 16.1 (cabergoline), -9.6 levodopa in the 26 [S]: sleep RCT, DB, Levodopa (levodopa) P< 0.0001; treatment of patients (levodo IRLS > 10, 200 - 300 mg quality (SF-A), prosp., Idiopathic , discontinuation due to 3 with severe restless I n=361 1 wk pa), 2 IRLSSG RLS-6 at fixed 6 wks RLS-QoL, parallel, RLS cabergoli augmentation; 7 legs syndrome: drug night >= 4 2 - 3 mg ASRS, 4-item MC ne (cabergoline), 18 Results from a multi- related version, CGI, (levodopa). center, randomized, SAE in RLS-6 active controlled each trial. Mov Disord group 2007;22:696-703.
Dihydroergocriptine (DHEC)
Tergau F, Wischer S, Wolf C, Paulus W. Treatment of Flexible, up to Improvement from 55.7 ± restless legs Idiopathic 60 mg per [P]: RLS during 27.3 to 20.1 ± 17.5 (P< syndrome with the Open, and III n=16 1 wk 1 10F, 6M IRLSSG DHEC day, divided 4 wks the night (VAS 0.003) at night; dopamine agonist prosp., MC secondary in 1 or 2 0 to 100) improvement by 63.9 ± alpha- RLS dosages 38.1% dihydroergocryptine. Mov Disord. 2001 Jul;16(4):731-5.
Lisuride
10 IRLS; [P]: IRLS 3 RLS-6 [S]: RLS-6 Benes H OL: Pretreatme severity of (severity at Transdermal 1 patch: IRLS - 23.3 ± nt: 2 wks RLS bedtime, during lisuride: short-term OL flexible 11.6 (n=3) OL, during the the night, efficacy and 3F, 4M; 18- lisuride 3 to 6 2wks OL 2 patch: IRLS - 22.0 ± followed day; during the day, tolerability study in n=9 75 yrs; mg, fixed run-in, 1 12.5 (n=7) 1 by 1 wk I 3 days 1 IRLSSG previous Lisuride when the patients with severe ITT=10 mean 58± 6 dose 3 or 6 wk DB all together IRLS - 22.1 ± RCT, DB, positive patients were at restless legs yrs mg in DB placebo 11.6 (n=10) DB: final prosp., levodopa rest or active, syndrome. Sleep period IRLS lisuride: 6.8 +/- placebo, response; quality of sleep, Med. 2006 12.0; placebo: 18.5 +/- parallel response daytime Jan;7(1):31-5. 7.5 to lisuride tiredness, PLM in OL (actigraphy)
Non-ergot derived dopamine agonists
Ropinirole Happe S, Sauter C, Klosch G, Saletu B, Gabapentin Zeitlhofer J. titrated to Gabapentin versus 5F, 11M; Compared to baseline, RCT, OL, Gabapenti max of 1200 ropinirole in the 47-74 yrs; IRLSSG IRLS, PSG, decreased IRLS, PLM, Low levels 1 head-to- I n=16 4 wks 0 Idiopathic n, mg in divided 4 wks treatment of mean 56 (1995) ESS unchanged ESS; SE of AEs head ropinirole doses; mean idiopathic restless yrs better vs. ropinirole 800 (397) mg legs syndrome. (300-1200mg) Neuropsychobiology 2003;48 (2):82-86.
Idiopathic RLS >20 yrs old not allowed to be on RLS medication for at least IRLS improved (p<0.001) 2 wks prior from a mean (SD) of 25 to the Adler CH, Hauser (7) during placebo baseline Mean 4.6 RA, Sethi K, et al. 4 wks treatment to 13 (12) 2 visit. (2.0) mg/day Ropinirole for with a 1- [P]: IRLS during ropinirole treat. No RLS (ropinirol 16F; 6M; Exclusions range 1-6 restless legs DB, Ropinirole wk wash- ESS ESS score did not differ n=22 medication 2 e) 40-83 yrs; IRLSSG included mg/day 2 syndrome: a placebo, I , out RLS diary sign. ITT=18 wks prior to the 1 mean 60 IRLS >10 previous with 14 placebo-controlled CO placebo between sheet 2 Diary sheet (19 pat.) baseline visit (placebo yrs use of patients crossover trial treatment days/wk mean rate of RLS during ) ropinirole taking the full Neurology 2004;62 s placebo treat. was 23%, secondary 6 mg/day (8):1405-1407. during ropinirole treat. RLS, was about 50% reduced significant to 12% (p=0.008) medical disease that would not allow use of ropinirole, pregnancy or lactation PLMSI: ropinirole (48.5- 11.8); placebo (35.7- Idiopathic Allen R, Becker PM, 34.2), P < 0.0001. RLS Bogan R, et al. PLMA ropinirole (7.0 5 PLMS/hr Ropinirole Any medications -2.5); placebo (4.2 -6.0), IRLS >15 decreases periodic affecting RLS or P=0.0096. minimum [P]: PLMS; leg movements and DB, sleep entered a Ropinirole TST (P=0.1068) n=65 of 15 0.25-4.0 IRLSSG 3 improves sleep parallel, I washout phase 0 18-79 yrs IRLSSG , 12 wks Sleep efficiency ITT=59 nights with mg/day [S]: MOS sleep parameters in placebo for a minimum of placebo (P=0.0106) RLS scale patients with restless 7 days or 5 half- IRLS not significant symptoms legs syndrome. lives MOS Sdisturbance in the Sleep 2004;27 (P=0.4172), Sadequancy month (5):907-914. (P=0.0316), Squantity prior (P=0.2411), Ssomnolence (P=0.3028)
Idiopathic. score of at IRLS: significant greater least 15 on for ropinirole (-11.04 IRLS (0.719) p.) than for Trenkwalder C, had either placebo (-8.03 (0.738) P.; Garcia-Borreguero 7 consecutive experience adjusted treatment D, Montagna P, et nights or 5 half- d at least difference= -3.01 (95% [P]: al. Ropinirole in the lives (any 18-79 yrs; 15 nights confidence interval (CI), IRLS treatment of restless medications 16 10 with -5.03 to -0.99)) legs syndrome: affecting RLS or (ropinirol European symptoms 0.25–4.0 (P=0.0036); RCT, Ropinirole [S]: results from a 12-wk, sleep, or to e.) countries; IRLSSG of RLS in mg/day 3 hrs CGI: ropinirole 53.4% vs. 4 Prosp, DB, I 284 (ITT) , 12 wks CGI-I randomised, cause 6 (146 IRLS >15 the before placebo 40.9% placebo placebo MOS sleep placebo-controlled drowsiness) (placebo ropinirole, previous bedtime (p=0.0416); scale study in 10 small proportion ) 138 month or, sleep adequacy RLS QoL European countries. of pat. may have placebo) reported P=0.0015; WPAI J Neurol Neurosurg had a washout they had sleep quantity p=0.0331; Psychiatry period shorter had daytime somnolence 2004;75(1):92-97. symptoms P=0.0064; of this RLSQoL P=0.0314 frequency no difference SF-36; before WPAI treatment Primary diagnosis of RLS, only Walters AS, Ondo idiopathic WG, Dreykluft T, score of at Grunstein R, Lee D, least 15 on IRLS score: -11.2 (0.76) Sethi K. Ropinirole is IRLS vs. -8.7 (0.75) (P= "ropinirole effective in the at least 15 [P]: IRLS 0.0197)(ropinirole to effectively treatment of restless 5 half-lives or 7 9 18-79 yrs; nights of [S]: CGI-I RCT, DB, 0.25-4.0 placebo) treats the legs syndrome. nights (any (ropinirol Australian RLS Ropinirole MOS sleep MC, n=267 mg/day 1 to 3 CGI-I scale: 59.5% vs. symptoms 5 TREAT RLS 2: a 12- I medications e) , Europe, IRLSSG symptoms , 12 wks scale, Restless parallel, ITT=266 hrs before 39.6% (P<0.001) of wk, double-blind, affecting RLS or 11 N during the placebo Legs Syndrome placebo bedtime MOS Sdisturbance, moderate- randomized, sleep) (plac.) America previous Quality of Life Sadequancy, Squantity to-severe parallel-group, month questionnaire (P=0.0001), RLS" placebo-controlled pat. who Ssomnolence (P=0.0043) study. Mov Disord would 2004;19(12):1414- have 1423. required daytime treatment was excluded
Bliwise DL, Freeman A, Ingram CD, Rye Mean dose of 1.4mg HS DB, Chakravorty S, sign. decreased PLMS Watts RL. and RLS Symptoms Only [P]: PLMS Randomized, 13F, 9M 0.25 mg at sleep macroarchitecture DB, RCT, patients Ropinirole [S]: IRLSSG double-blind, n=33 A drug-free mean age bedtime; up did not change 6 parallel, I 0 IRLSSG with , 4 wks sleep placebo-controlled, ITT=22 baseline 50.8 to 1.5 mg; NREM/PLMS placebo idiopathic placebo macroarchitect short-term trial of years max. 6.0 mg placebo.19.2 (4.6–33.9) RLS ure ropinirole in restless to 76.4 (37.3–115.5) legs syndrome. ropinirole 19.7 (0–45.6) to Sleep Med 19.8 (0–44.4) 2005;6(2):141-147.
7 Bogan RK, Fry JM, MC, DB, I n=381 Minimum of 7 7 ropinirole: IRLSSG Idiopathic Ropinirole 0.25-4.0 12 wks [P]: IRLS Mean (SD) IRLS score Schmidt MH, Carson placebo, ITT=321 consecutive (ropinirol 109F; RLS; , mg/day [S]: Clinical ropinirole 22.0 (4.99) to SW, Ritchie SY. flexible- nights or 5 half- e) placebo: excluded if placebo global 8.4 (7.32) Ropinirole in the dose lives (any 9 123F; 18- signs of impression placebo 21.6 (4.79) to treatment of patients medication that (placebo 79 yrs secondary (CGI), 11.9 (9.20) with restless legs might affect RLS ) forms, Medical wk 12: LOCF was sign. syndrome: a US- or sleep) augmentati Outcomes greater for ropinirole (- based randomized, on Study sleep 13.5 [1.2] compared with double-blind, scale (MOS) placebo (-9.8 [1.2]) placebo-controlled IRLS adjusted mean clinical trial. Mayo treatment difference -3.7 Clin Proc *<0.001 2006;81(1):17-27. wk 1: ropinirole (-8.9 [1.04] placebo -4.8 [1.04], -4.1; 95%CI,-5.6 to -2.7;P<0.001) MOS Sdisturbance, Sadequancy, Sproblems (P<0.001), Squantity (P=0.005), daytime somnolence not stat. sign (P=0.10)
Sign. fewer pat. relapsed on ropinirole than on Mean and [P] proportion placebo (32.6% vs. 51F, 41M; Montplaisir J, median dose of pat. 57.8%, P=0.0156) Study was 18-79 yrs; Karrasch J, Haan J, at wk 20, after single relapsing CGI-I score much, or very not Volc D. Ropinirole is Single Idiopathic which no blind during double- much improved: ropinirole specifically n=202 pat. from effective in the long- blind RLS more phase: blind treatment vs. placebo (68.9% vs. designed to (single blind 18 term management of phase: 15 nights changes in 24 wks [S] time to 46.7%, P=0.0298) assess the RCT, phase) centers in restless legs 5 half-lives or 7 n=37 IRLSSG of RLS Ropinirole dose were double relapse IRLS increased by 4.1 augmentati 8 placebo, I ITT=n=92 Australia, syndrome: a nights double IRLS >15 symptoms , placebo allowed: 2.05 blind withdrawals points (ropinirole) vs. 8.2 on rate (3 MC (double Austria, randomized blind during the and 2.00 phase: due to lack of points placebo pat. blind Canada, controlled trial. Mov phase: previous mg/day for a efficacy (P=0.0246) possible, phase) Germany, Disord n=1 month at wk 24: further 12 CGI-I MOS sleep disturbance one with and 2006;21(10):1627- 15.8% of pat. wks IRLS (P=0.0003), somnolence this AE was South 1635. max. dose of MOS (P=0.0136) withdrawn) Africa 4.0 mg/day QoL QoL 17.0 points vs. 5.2 (placebo vs. ropinirole) (P=0.004)
Pramipexole
Idiopathic RLS, PLMSI Montplaisir J, 2 wks before IRLSSG >10, [P]: Nicolas A, Denesle baseline (drugs, presence of presence PLMS R, Gomez-Mancilla which influence RLS 5F, 5M; of RLS PLMW B. Restless legs sleep symptoms PLMS (Wilcoxon RCT, DB, 30-61 yrs; symptoms Pramipex home syndrome improved architecture or interfering with 0.75- P=0.005) 1 placebo, I ITT=10 0 mean age interfering ole, 10 wks questionnaires by pramipexole: a motor sleep onset or 1.5mg/day PLMW (Wilcoxon CO 49.3 ± with sleep placebo about leg double-blind manifestations) with the P=0.007) 11.5 yrs onset / the restlessness randomized trial. 2 wks washout continuity > 3 continuity during daytime Neurology period between nights/wk for at of sleep > and nighttime 1999;52(5):938-943. treatments least 1 yr 3 nights / wk for at least 1 yr Idiopathic Partinen M, RLS [P]: PLMI At all doses Hirvonen K, Jama L, IRLS > 15 [S]: PLMI (P<0.0001) et al. Efficacy and PLMS at additional PSG IRLS (P=0.0274 for 0.125 safety of DB, least 5 Fix. measures mg) (P<0.0001 for all pramipexole in placebo, times/hr Washout period 0.125 mg/day IRLS other active treatments) idiopathic restless parallel, 79F, 28M; IRLSSG wkly RLS Pramipex 2 I n=109 of 1 wk for any 1 0.25 mg/day 3 wks CGI CGI ´much improved` or legs syndrome: a dose- 27-76 yrs IRLS >15 symptoms ole drug 0.50 mg/day patient global ´very much improved` polysomnographic finding that had 0.75 mg/day impression 61.9-86.4% pramipexole dose-finding study-- study disrupted (PGI) vs. 42.9% placebo the PRELUDE sleep quality of life (P<0.05 for 0.25, 0.50, study. Sleep Med within the (QOL) 0.75 group) 2006;7(5):407-417. previous 3 months
IRLS: SE change from baseline to wk 12 was -9.3 (1.0) for placebo, -12.8 (1.0) for 0.25 Winkelman JW, IRLSSG [P]: IRLS mg/day, -13.8 (1.0) for Sethi KD, Kushida IRLS >15 CGI-I 0.50 mg/day, and -14.0 CA, et al. Efficacy 62.2% F; No Were up-titrated symptoms at Fix. [S]: RLS QoL (1.0) for 0.75 mg/day (all and safety of 18-80 yrs; information RCT, DB, to their 38 least 2 to 3 Idiopathic Pramipex 0.25 mg/day PGI P<0.01) 3 pramipexole in I ITT=339 mean 12 wks about placebo randomized (11%) days per wk RLS ole 0.50 mg/day VAS CGI-I: 51.2% for placebo restless legs 51.4±13.0 augmentati dose over 3 wks for at least the 0.75 mg/day Epworth and 74.7%, 67.9%, and syndrome. yrs on previous 3 Sleepiness 72.9% for pramipexole; Neurology months Scale all P < 0.05). 2006;67:1034-1039. RLS QoL: P = 0.0041 for 0.25 mg/d P = 0.0002 for 0.50 mg/d P = 0.0029 for 0.75 mg/d
4 Trenkwalder C, RCT, DB, I n=150 Open treatment 0 72.8%F; IRLSSG Idiopathic Pramipex Mean 0.50 (6- [P]: Patients switched to Over the Stiasny-Kolster K, parallel, with pramipexole 18-80 yrs RLS ole, mg months increase of the placebo reached the total 9 Kupsch A, Oertel placebo, for 24 wks mean age IRLS total placebo run-in IRLS to a score primary endpoint sign months, WH, Koester J, MC, before 59.6±10.3 score at individually period) > 15 and earlier and more often clinician Reess J. Controlled withdrawal randomization yrs baseline > optimized (for a CGI score of than patients who and patient withdrawal of 15; dose of 0.125 further 3 "minimally", continued to receive ratings of pramipexole after 6 before to 0.75 month) "much", or pramipexole symptoms, months of open- randomizat mg/day "very much" 85.5% vs. 20.5%; sleep, and label treatment in ion < 15 worse (P<0.0001) (a predefined QoL patients with restless (compared with worsening) identified no legs syndrome. Mov the score at the reached the primary decline in Disord start of Period endpoint faster, in 5 vs. pramipexole 2006;21(9):1404- 2) 42 days ´s benefit or 1410. tolerability. Augmentati on was considered an AE, but in this population of responders it did not occur.
5 Oertel WH, Stiasny- RCT, DB, I n=345 All 1 222F, IRLSSG Idiopathic Starting dose 6 wks [P]: IRLS IRLS 24.9 to 5.7 (+0.9) Kolster K, Bergtholdt placebo, ITT=338 pharmacological 116M; IRLS >15 RLS of 0.125 mg/d CGI-I. for placebo (median dose B, et al. Pramipexole MC treatment for 18-80 yrs RLS max. of 0.75 [S]: PGI 0.47mg/d); RLS Study Group. RLS was patients. symptoms mg/d IRLS responder 24.7 to 12.3 (+0.6) for Efficacy of discontinued from 37 present for dose was rates pramipexole (P < 0.0001) pramipexole in within 14 days centers in at least 2 individually (median dose 0.35 mg/d) restless legs before study 5 to 3 Pramipex optimized CGI ´much improved` or syndrome: a six-wk, start European days/wk in ole, according to ´very much improved` multicenter, countries the 3 placebo PGI 62.9% pramipexole vs. randomized, double- month 32.5% placebo (P < blind study (effect- before 0.0001) RLS study). Mov study entry PGI responder rates Disord 2007;22:213- 31.6% (placebo) 61.6% 9. (pramipexole) (P < 0.0001)
Rotigotine
Washout at least Stiasny-Kolster K, 3 days or at Kohnen R, least five half- Schollmayer E, lives if longer (at Moller JC, Oertel Idiopathic baseline) WH. Patch RLS (neuroleptics, RLS severity improved application of the minimum RCT, DB, hypnotics, [P]: IRLS related to dose by 10.5 CGI dopamine agonist score of 3 MC, antidepressants, 3 fixed doses (additionally:) (1.125 mg/die; P=0.41), supported rotigotine to patients 64% F; in RLS-6 Rotigotine parallel, n=68 anxiolytic drugs, 1.125 mg, [S]: RLS-6 12.3 (2.25 mg/d; P=0.18), favorable 1 with moderate to I 1 mean IRLSSG scale 1 wk placebo, ITT=63 anticonvulsive 2.25 mg, 4.5 scale and 15.7 points (4.5 efficacy of advanced stages of 58±9 yrs excluded: placebo proof-of- therapy, mg CGI mg/d; P<0.01) on the 4.5 mg restless legs any form principal psychostimulator sleep diary IRLS compared to dose syndrome: a double- of y drugs., placebo (8 points) blind, placebo- secondary levodopa or controlled pilot RLS opiods) study. Mov Disord run-in period of 2004;19(12):1432- 7+3 days without 1438. patch application
Sumanirole Idiopathic RLS PLMS IRLSSG index >11 Garcia-Borreguero PLMSI >11 per IRLS >20 D, Winkelman J, hr of total IRLS mean change presence Adams A, et al. sleep time showed no statistical of RLS Efficacy and IRLS score of significance symptoms "The dose tolerability of Other >20 at although mean change RCT, DB, that range of sumanirole in medications had baseline [P]: IRLS. with 4.0 mg dose was placebo, interfered Sumanirol sumanirole restless legs to be 60% F; presence of 0.5, 1.0, 2.0 numerically greater 1 parallel, I ITT=270 5 with sleep e, 9 wks selected syndrome: a phase discontinued 18-75 yrs RLS or 4.0 mg [S]: PLMSI, PLMS (2.0, 4.0 mg dose- onset or placebo here may II, randomized, prior to the symptoms that CGI p<0.0001) (1.0 mg response maintenan have been double-blind, baseline interfered with p=0.0631) (0.5 mg ce on >4 too low" placebo-controlled, sleep onset or p=0.1748) nights per dose-response maintenance results CGI-R = results wk for <12 study. Sleep Med on >4 nights IRLS wks 2007;8(2):119-127. per wk for <12 exclusion wks included secondary RLS
Opioids
Oxycodone
Walters AS, Wagner Sleep ML, Hening WA, et Oxycodone superior to apnea al. Successful PB in improving sensory Non-validated noted in 4 treatment of the Idiopathic oxycodone discomfort, subjective subject scale subjects did idiopathic restless RCT, DB, RLS, Oxycodon titrated from motor restlessness, and 5F, 6M; IRLSSG 2 wks per for RLS not worsen; 1 legs syndrome in a placebo, I n=11 2 wks 0 needed to e, 2.5 to max of daytime alertness; PSG 36-74 yrs (1995) phase features; PSG 10 of 11 randomized double- CO have placebo 25 mg, mean showed decreased measures of subjects blind trial of PLM>5/h dose 15.9 mg arousals and improved sleep and PLM preferred oxycodone versus sleep efficiency; reduced oxycodone placebo. Sleep PLM by 65% to placebo 1993;16:327-332.
Methadone
1 Ondo WG. CS III n=27 Added 5 14F, 13M, IRLSSG Idiopathic Methadon Titrated to 22.9 CGI (0-5) 17/27 remain on No Methadone for medication mean (2003) and e effect, initial month methadone at last f/u; all augmentati refractory restless 54.8±14.4 secondary dose 13.0 FU (4-44 score 3 or higher on CGI on on legs syndrome. Mov yrs RLS; failed (5.9) mg (5- months) (3:75 to 99% improved; 4: methadone; Disord at least 2 30 mg), final only residual sleep 8 previously 2005;20(3):345-348. dopaminer dose 15.5 problems; 5: no had gic (7.7) mg (5- symptoms or sleep augmentati medication 40 mg) problems) on; 12/19 s (including 2 dialysis who died) were able to stop all other medications
Tramadol
Lauerma H, Not 10 felt more effective than AEs Markkula J. specified other drugs, 1 had included: Treatment of for all, 8 mean 8F, 6M; IRLSSG 50-150 General modest improvement, 1 abdominal restless legs were 22.8 29-78 yrs; (1995) plus mg/day, only satisfaction, 0- had no benefit; pain (1), 1 syndrome with Open III n=12 Not specified 0 familial, all Tramadol months mean 57 Gibbs & Lee 1 over 100 100 symptom improvement on scale dizziness tramadol: an open had (5 to 26 yrs 1986 mg/day severity scale from median 90 to (1), tremor study. J Clin complaint months) median 5 (P=.0039, (2), pruritis Psychiatry of Mann-Whitney) (1) 1999;60:241-244 insomnia
Sedative hypnotics: Benzodiazepines
Clonazepam
Boghen D, Lamothe L, Elie R, Godbout R, Montplaisir J. The treatment of the restless legs Subjects Clonazepam syndrome with RCT, DB, Clonazep No benefit compared to reported 3F, 3M; Not 0.5 mg 1/2 hr 4 wks per 1 clonazepam: a placebo, I n=6 Not specified 0 Clinical criteria am, CGI, PGI placebo on either CGI or sleepiness 31-61 yrs specified before phase prospective CO, prosp placebo PGI on bedtime controlled study. clonazepam Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences 1986;13:245-247.
Montagna P, de Clonazepam fixed Bianchi LS, Zucconi 1 mg 1/2 hr protocol: Subjective Clonazepam improved M, Cirignotta F, before 3M, 3F; 1 wk assessment of subjective reports of 5 of 6 Lugaresi E. RCT, CO, Clonazep bedtime; 44-61 yrs; Not clonazep sleep, sensory sensory discomfort, preferred 2 Clonazepam and DB, I n=6 Not specified 0 Clinical criteria am, vibration 15 mean specified am, 1 wk discomfort, and sleep, not leg jerking; clonazepam vibration in restless placebo vibration min with 54.3 yrs placebo, nocturnal leg superior to vibration in to vibration leg syndrome. Acta mechanical 1 wk jerking sensory discomfort Neurol Scand vibrator at vibration 1984;69:428-430. 120 hertz
Sedative hypnotics: Benzodiazepine-receptor agonists
Zolpidem Subjects had RLS without remission for a mean of 2.3 yrs before receiving Bezerra MLS, zolpidem; Martinez J-VL. 5F, 3M; All patients had a total no adverse Zolpidem in Restless 32-75 yrs; IRLSSG 1 yr to 30 Patient 1 OL, CS III n=8 Not specified 0 Idiopathic Zolpidem Fixed, 10 mg remission within 5 days effects Legs Syndrome. Eur mean (1995) months symptom report (mean 4) reported; Neurol 2002;48:180- 50.9 yrs after 1 yr of 181. complete relief, 2 stopped zolpidem and had recurrence of RLS symptoms
Anticonvulsants
Gabapentin
Thorp ML, Morris CD, Bagby SP. A IRLSSG crossover study of (1995); Summed score (0-8) Non-validated gabapentin in needed to gabapentin significantly lower after RCT, DB, 1F, 15M; Secondary Gabapenti 0-2 subjective treatment of restless have a score 300 mg 3 6 wks per gabapentin than placebo; Veteran 1 placebo, I n=16 2 mean 64 RLS, on n, scale for 4 RLS legs syndrome of 6 on 4 times a wk phase 11 of 13 completers rated population CO yrs dialysis placebo features among hemodialysis features (scale after dialysis gabapentin as only (IRLSSG 2005) patients. Am J 0=never to 2- effective agent Kidney Dis constantly) 2001;38:104-108.
2 Garcia-Borreguero RCT, DB I n=24 2 wks 0 16F, 8M; Dual clinical Idiopathic, Gabapenti titrated dose, 6 wks per [P]: IRLS; Drug superior on all Low level of D, Larrosa O, de la 33-75 yrs; exam based low iron n start 600 mg, phase [S]: CGI, PGI, measures, statistically AEs and no Llave Y, Verger K, mean on IRLSSG- stores max 2400 with 1 wk PSQI, and PSG significant favor in IRLS serious AEs Masramon X, 55±11.6 1995 plus (ferritin, mg, given 1/3 washout measures (8.3 pts); CGI-C; PGI-C Hernandez G. yrs screen PSG 20 Happe S, Sauter C, Klosch G, Saletu B, Gabapentin Zeitlhofer J. titrated to Gabapentin versus 5F, 11M; max of 1200 Compared to baseline, RCT, OL, Gabapenti ropinirole in the 47-74 yrs; IRLSSG mg in divided IRLS, PSG, decreased IRLS, PLM, Low levels 3 head-to- II n=16 4 wks 0 Idiopathic n, 4 wks treatment of mean 56 (1995) doses; mean ESS unchanged ESS; SE of AEs head ropinirole idiopathic restless yrs 800 (397) mg better vs. ropinirole legs syndrome. (300 to Neuropsychobiology 1200mg) 2003;48 (2):82-86. Significantly improved on Micozkadioglu H, IRLS-abbreviated Ozdemir FN, Kut A, compared to baseline and Sezer S, Saatci U, Fixed dose, to levodopa scores; Haberal M. gabapentin significantly improved Gabapentin versus 5F, 10M, 200 mg after SF36 domains of general No levodopa for the RCT, CO mean age Gabapenti Abbreviated 2 wks between Dialysis each health, body pain and statement in 4 treatment of compariso II n=15 1 45.8 IRLSSG 1995 n, 4 wks IRLS, PSQI. phases patients hemodialysis social functions (P < paper on Restless Legs n (15.3) ropinirole SF36 session or 0.001); superior to blinding Syndrome in years 125 mg baseline and levodopa in hemodialysis levodopa. sleep parameters on patients: an open- PSQI sleep quality, sleep label study. Ren Fail latency, and sleep 2004;26:393-397. disturbance Carbamazepine Inconclusiv Lundvall O, Abom e due to PE, Holm R. lack of Carbamazepine in 2F, 4M; RCT, DB, Ad hoc statistics, restless legs. A 37-71 yrs; Clinical: not Not Carbamaz 200 mg BID Carbamazepine superior 1 placebo, I n=6 4 wk 0 4 wks subjective scale one pt with controlled pilot mean 53 specified specified epine or TID in diary ratings CO in diary format carbamaze study. Eur J Clin yrs pine Pharmacol dizziness, 1983;25(3):323-324. vomiting 2 Telstad W, RCT, DB, I n=181 Not specified Unspecif 122F, Clinical: Not Carbamaz Titrated from 5 wks VAS scale, Significant decrease in Nonvalidate Sørensen O, Larsen parallel ITT=174 ied 52M; 17- unpleasant leg specified epine 100 mg to number of attacks per wk in both d scale S, Lillevold PE, 86 yrs sensations at max of 300 attacks per wk groups, significantly Stensrud P, Nyberg- rest, worst at mg at greater in carbamazepine Hansen R. night bedtime, Treatment of the average dose restless legs 239 mg syndrome with carbamazepine: a double blind study. Br. Med J. 1984;288:444-446. Valproic Acid Side effects for 9 subjects in Eisensehr I, PB, VPA VPA start at Ehrenberg BL, phase; 13 300 mg, go to Rogge Solti S, in LD, 600 mg PO One day hourly Noachtar S. Idiopathic Slow VPA significantly including 4 after 2 days; diary with Treatment of RLS, release decreased RLS reported 12F, 8M; levodopa 200 minutes of idiopathic restless PLMI>10 valproic symptoms per diary and with RCT, DB, 41-74 yrs; mg with symptoms; 0- legs syndrome IRLSSG by PSG; acid, slow 3 wks per overall intensity score; augmentati 1 placebo, I n=20 5 days 0 mean benserazide 10 VAS of (RLS) with slow- (1995) daily release phase overall, levodopa did not. on; open CO 58.9±6.9 50 mg; all overall severity; release valproic acid symptoms levodopa- Levodopa significantly label follow- yrs drugs & PSG measures compared with slow- for 6 benserazi decreased PLMI, neither up at 6 to placebo taken from 2 nights release months de decreased SE 18 months: 90 minutes per phase levodopa/benserazid 9 of 12 on before e. J Neurol VPA bedtime 2004;251:579-583. remained on effective therapy; 2 of 7 on LD Topiramate Additional AEs: CGI: reduced from 79% sleepiness Reduction in to 37% moderate severe; (1), tremor Pérez Bravo, A. 12 CGI & PGI PGI, reduced from 73% 3 4F, 15M; (1); none of Topiramate use as idiopathic, values of to 37% moderate to (sleepin 51-76 yrs; 42.1 mg (+/- the patients treatment in restless 7 Topiramat moderately or severe; 11/17 had 1 Prosp., CS III n=19 1 wk ess -2; mean ICSD (1997) 18.7 mg)/day, 90 days reported a legs syndrome. unspecifie e severely ill; sensory symptoms and paresthe 62.05±6.2 flexible dose family Actas Esp Psiquiatr d symptom 11/17 had motor sias - 1) 2 yrs history; 2004;32(3):132-137 secondary report; sleep symptoms resolved; most hrs reported. sleep improved, but not symptoms statistically significant. were in the feet N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA) antagonists Amantadine This was an add-on trial; AEs (drowsiness - 3, fatigue - 2, insomnia None, allowed to - 2, dry Idiopathic stay on other mouth - 1, Evidente VGH, Adler and meds, 17 leg edema - CH, Caviness, JN, 2 (leg secondary 100 to 300 up to 13 Response to (levodopa 10, 11/21 responded (mean 1, weight Hentz JG, Gwinn- edema; RLS, 8/21 mg/day, months meds (25+% or pergolide 1, 13F, 8 M; response 69%); overall, loss - 1); Hardy K. fatigue, with signs Oral flexible dose (mean greater Prosp., benzodiazepine 46 to 84 summary scale score this was 1 Amantadine is III n=21 drowsin Not specified of amantadi and response improvement); OL, CS 4, opioid 2, yrs; 70 went from 9.8 to 6.6 (P = largely a beneficial in restless ess, peripheral ne scheduling to s for 3.6 10 point scale gabapentin 1, (±9) yrs 0.001 by Wilcoxon pre-treated legs syndrome. Mov weight neuropath match (+/- 4.5) from O'Keefe non-opioid signed-rank test) population Disord loss) y; 10 with symptoms months) 1994 analgesics 1, -- 7 had 2000;15(2):32-237. family multiple drug augmentati history types 4) on on levodopa; 12 had previously failed 2 or more medications Clonidine Benefit restricted to waking period and sleep onset; Wagner ML, Walters Subject scales many minor AS, Coleman RG, (0-4) for AEs in Hening WA, Grasing sensory and Advantage to placebo on clonidine K, Chokroverty S. Clinical - 3F, 8M; Titrated to 01. motor 0-4 scales: sensory 1.6, group Randomized, sensory and 2-3 wks RCT, DB, 29-61 yrs; To 1.0 mg symptoms; motor restlessness 1.7; including: 1 double-blind, I n=11 motor Idiopathic Clonidine each CO mean (mean 0.5) PSG measures PSG: reduced sleep dry mouth placebo-controlled symptoms phase 44.5 yrs over 2 wks of sleep latency (35.5 mins), (8), study of clonidine in worse at night latency, sleep PLMI, SE unchanged lightheaded restless legs efficiency, ness (6), syndrome. Sleep PLMS decreased 1996;19(1):52-58. thinking (6), somnolence (5), constipation (4) Minerals and vitamins Iron preparations: oral iron 4 subjects did not meet IRLSSG criteria; 28/36 screened entered study. 6/8 failed criteria, 2 declined; AEs noted Davis BJ, Rajput A, in 9 in iron Rajput ML, Aul EA, Two wk daily arm, none 325 mg Eichhorn GR. A measures of No significant difference in placebo ferrous randomized double- No washout, 19F, 9M; Idiopathic sleep, percent in any measures between (nausea sulfate twice blind placebo- RCT, DB, continued on 33-80 yrs; IRLSSG and Oral iron of days with iron and placebo groups; and/or 1 I n=28 3 on iron a day as 16 wks controlled trial of iron placebo prior mean (1995) secondary sulfate RLS symptoms, RLS impact reduced constipation liquid with in restless legs medications 59.2 yrs RLS VAS summary (p=0.11) in 8 who , 5; dark similar tasting syndrome. Eur on effect of completed 14 wks on iron stools, 3); 3 placebo Neurol 2000;43:70- RLS of 14 75. continued on iron after study ended; iron group as a whole did not show significant gain in iron measures -- mean ferritin 117 (range 9- 680 mg/L). O'Keeffe ST, Gavin Idiopathic K, Lavan JN. Iron variable RLS, but Symptoms reduced for status and restless 13F, 5M; Oral iron fixed dose, treatment 2 CS III n=18 None 0 Clinical low iron 0-10 PGI those with ferritin levels No statistics legs syndrome in the 70-87 yrs sulfate 200 mg, TID , 8-20 stores in <45 microgram/liter elderly. Age Ageing wks some 1994;23(3):200-203. Iron preparations: intravenous iron dextran Drug Sloand JA, Shelly group: 5 Mark A, feigin A, F, 6 M; Bernstein P, Monk 39-74 yrs; Significant improvement Only study RD. A double-blind, mean 58 1000 mg 10 point scale over baseline at 1 and 2 to include a placebo-controlled yrs; 55% (given 30 mg (0-4 for wks for drug, but not None, 4 subjects Intraveno significant trial of intravenous RCT, DB, white; IRLSSG Patients test, then frequency of placebo group; in drug 1 I ITT=25 were on current 1 us iron 4 wks number of iron dextran therapy placebo Placebo (1995) on dialysis after 1 hr, the symptoms; 0-3 group, scores were still RLS meds dextran African- in patients with group: rest infused for distress; 0-3 lower at 4 wks, but American ESRD and restless 4F, 10M; over 3 hrs) for duration) increasing toward subjects legs syndrome. Am 36-73 yrs; baseline J Kidney Dis mean 53 2004;43(4):663-670. yrs; 78% white Clinical All patients except 1 Nordlander NB. 12F, 9M; description -- one to several Some Mixed Intraveno achieved a complete Therapy in restless 19-75 yrs; deep doses of 100 patients idiopathic us sustained relief after legs syndrome. mean discomfort, to 200 mg of 3 days to with 2 OL, CS III n=21 Not specified 0 and colloidal Symptom relief variable dosing (17 Acta Med Scand 46.7 provoked by elemental iron 1 year response secondary iron required 1 to 3 injections, 1953;145(6):453- (±15.6) rest, relieved given every 1 had normal RLS (Intrafer) 3 required more 457 yrs by activity, to 4 days iron indices injections) worst at night One subject had a possible allergic first 25 reaction to mg, then beginning 3 -5 of infusion; mg/min 10 received after 6 patients "responded" full infusion; pause; PLM/hr by and needed no other none of Earley CJ, Heckler 10 follow-up actigraphy; 5 therapy at 2 wks; overall subjects D, Allen RP. The Idiopathic, completer at 2 wks, day paper at 2 wks there was 54 had anemia treatment of restless with Intraveno 1 during s, 4F, 6 IRLSSG 1000 mg responde sleep diary for (41)% decrease PGI-S; or elevated 3 legs syndrome with OL, CS III n=11 5 days PLM/hr by us iron infusion M; 51-74 (2003) infused rs go on hrs of 28 (32)% decrease iron indices; intravenous iron actigraphy dextran yrs; mean while symptoms and PLM/hr; 57 (37)% MRI dextran. Sleep Med >20 62.4 yrs respondi hrs of sleep; decrease in diary hrs with showed 2004:5:231-235 ng for 3- PGI-S (0-6) symptoms; 18 (25)% increased 30 increase TST from diary iron in months substantia (mean nigra, 11.3 prefrontal months) cortex; subjects showed rapid drop in ferritin Folic acid Botez MI, Fontaine F, Botez T, Clinical criteria Folate Bachevalier J. -- bilateral leg deficiency Folate-responsive discomfort at Either 3 mg Assessment of 12F, 4M; by 6-12 15 of 16 achieved 1 neurological and CS III n=16 Not specified 0 night with urge Folic acid IM/wk or 30 global 26-76 yrs laboratory months remission with folate mental disorders: to move legs, mg PO qD symptoms assessme Report of 16 cases. relieved by nt Eur Neurol movement 1977;15:230-246. Magnesium No AEs reported; Hornyak M, subjects Voderholzer U, PLMAI reduced by more showed Hohagen F, Berger than 50% in 4/6 RLS pts, only a M, Riemann D. PLMI, PLMAI, 5/6 reported improvement modest, not Magnesium therapy n=10 (of 4F, 6M; PSQI, morning on PGI-change; in all 10 IRLSSG Oral 12.4 mmoles mean 5.1 statistically for periodic leg which 4 mean sleep subjects, PLMI, PLMAI 1 OT CS III Not specified 0 (1995) & Idiopathic magnesiu per day taken wks (4 to significant movements-related with PLMD 57.4±9.4 questionnaire, decreased, SE increased PLMAI <30 m oxide in evening 6 wks) increase in insomnia and alone) yrs PGI-change for significantly; no magnesium; restless legs response significant change in all 6 RLS syndrome: an open PSQI, sleep subjects pilot study. Sleep questionnaire had normal 1998;21(5):501-505 magnesium values Other Exercise 2 controls on Aukerman MM, pramipexole Aukerman D, Bayard Exercise: decrease of 3/wk lower ; 2 exercise M, Tudiver F, Thorp IRLS form 20.6 to 12.6 at body strength subjects on L, Bailey B. Exercise exercise: Idiopathic 12 wks 6 wks, to 12.1 at 12; max & half hour gabapentin; and restless legs 4F, 7M; IRLSSG RLS, no with f/u IRLS total control change of 1.7 (6 1 RCT I n=28 No 0 Exercise treadmill relatively syndrome: a control: (1995) severity every 3 score, 0-8 PGI wks); exercise decrease titrated to mild randomized 13F, 4M criteria wks PGI to 1.7 (6 wks), 2.0 effort level subjects; controlled trial. J Am (12 wks); control no and heart rate control Board Fam Med decrease at 12 wks group did 2006;19(5):487-493. not receive placebo External Counter-pulsation No significant difference Rajaram S-S, in decreased IRLS total Rudzinskiy P, External score (-10 in active; -9 in Walters AS. counterpu Testing placebo); no change from Very small Enhanced external lsation to at end of IRLS, PSG 6F, 6M; baseline in active group study with counter pulsation Not maximum 7 wks measures, RCT, DB, 45-70 yrs; 1 hr 5 in amounts of REM and only 4 in (EECP) for restless IRLSSG specified; pressure plus clinical follow 1 placebo, II n=6 Not applicable 0 mean days/wk for 7 SWS or SE; decreased active group legs syndrome (2003) average (active) clinical up and parallel 58.7±8.2 wks PLMI but increased and 2 in the (RLS): Preliminary IRLS = 34 vs. sub- follow-up reduction of yrs PLMAI; clinical follow-up placebo negative results in a maximal at 6 meds at 6 months showed no group parallel double-blind peak in months improvement in study. Sleep Med placebo symptoms or reduction in 2006;7:390-391 medications Abbreviations of trial type: Randomized controlled trial (RCT) Nonrandomized controlled trial (Non-RCT) Open label (open) Double-blind (DB) Single-blind (SB) Prospective (prosp) Retrospective (retro) Crossover (CO) Parallel group (parallel) Placebo controlled (placebo) Single center (SC) Multicenter (MC) Case series (CS)