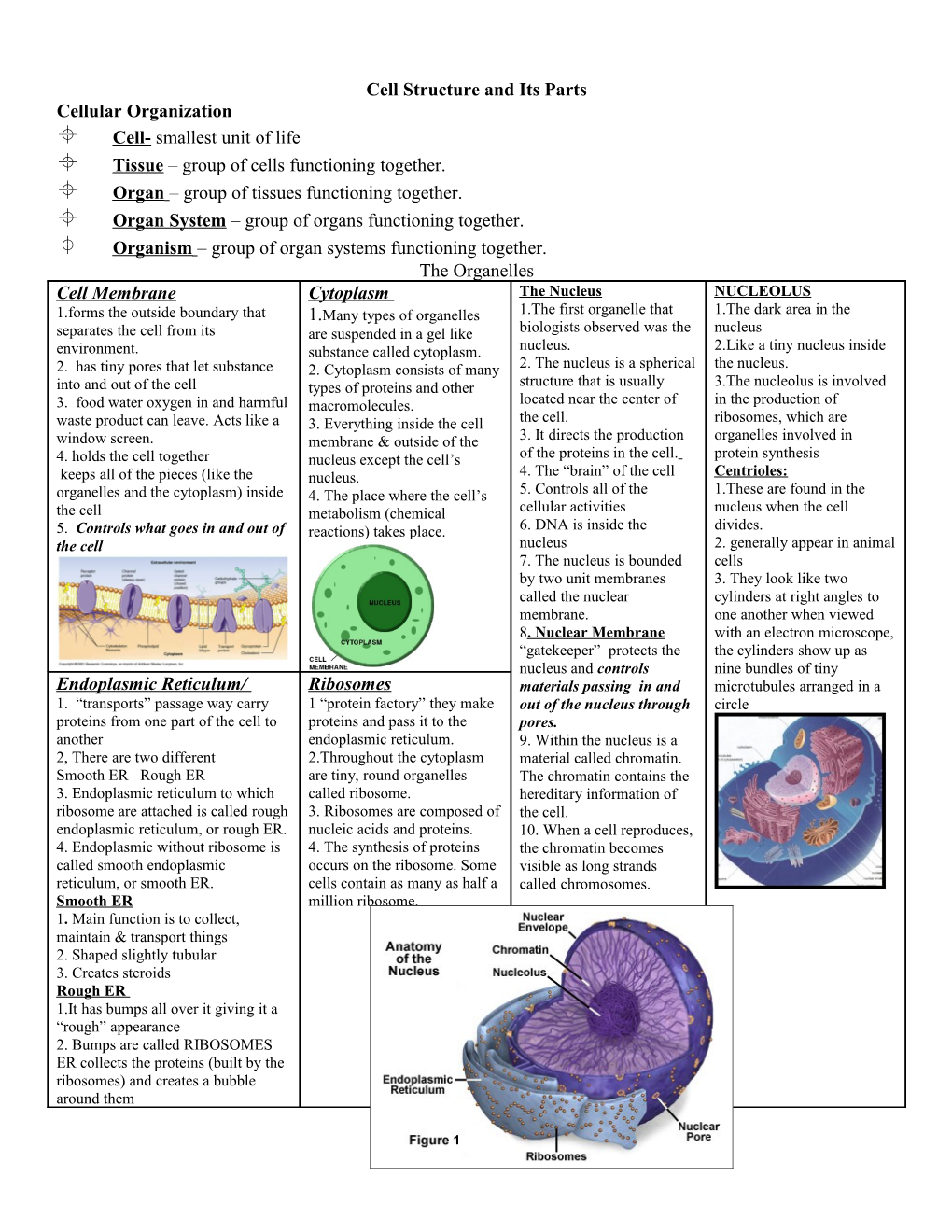
Cell Structure and Its Parts Cellular Organization Cell- smallest unit of life Tissue – group of cells functioning together. Organ – group of tissues functioning together. Organ System – group of organs functioning together. Organism – group of organ systems functioning together. The Organelles Cell Membrane Cytoplasm The Nucleus NUCLEOLUS 1.forms the outside boundary that 1.Many types of organelles 1.The first organelle that 1.The dark area in the separates the cell from its are suspended in a gel like biologists observed was the nucleus environment. substance called cytoplasm. nucleus. 2.Like a tiny nucleus inside 2. has tiny pores that let substance 2. Cytoplasm consists of many 2. The nucleus is a spherical the nucleus. into and out of the cell types of proteins and other structure that is usually 3.The nucleolus is involved 3. food water oxygen in and harmful macromolecules. located near the center of in the production of waste product can leave. Acts like a 3. Everything inside the cell the cell. ribosomes, which are window screen. membrane & outside of the 3. It directs the production organelles involved in 4. holds the cell together nucleus except the cell’s of the proteins in the cell. protein synthesis keeps all of the pieces (like the nucleus. 4. The “brain” of the cell Centrioles: organelles and the cytoplasm) inside 4. The place where the cell’s 5. Controls all of the 1.These are found in the the cell metabolism (chemical cellular activities nucleus when the cell 5. Controls what goes in and out of reactions) takes place. 6. DNA is inside the divides. the cell nucleus 2. generally appear in animal 7. The nucleus is bounded cells by two unit membranes 3. They look like two called the nuclear cylinders at right angles to membrane. one another when viewed 8. Nuclear Membrane with an electron microscope, “gatekeeper” protects the the cylinders show up as nucleus and controls nine bundles of tiny Endoplasmic Reticulum/ Ribosomes materials passing in and microtubules arranged in a 1. “transports” passage way carry 1 “protein factory” they make out of the nucleus through circle proteins from one part of the cell to proteins and pass it to the pores. another endoplasmic reticulum. 9. Within the nucleus is a 2, There are two different 2.Throughout the cytoplasm material called chromatin. Smooth ER Rough ER are tiny, round organelles The chromatin contains the 3. Endoplasmic reticulum to which called ribosome. hereditary information of ribosome are attached is called rough 3. Ribosomes are composed of the cell. endoplasmic reticulum, or rough ER. nucleic acids and proteins. 10. When a cell reproduces, 4. Endoplasmic without ribosome is 4. The synthesis of proteins the chromatin becomes called smooth endoplasmic occurs on the ribosome. Some visible as long strands reticulum, or smooth ER. cells contain as many as half a called chromosomes. Smooth ER million ribosome. 1. Main function is to collect, maintain & transport things 2. Shaped slightly tubular 3. Creates steroids Rough ER 1.It has bumps all over it giving it a “rough” appearance 2. Bumps are called RIBOSOMES ER collects the proteins (built by the ribosomes) and creates a bubble around them GOLGI APPARATUS LYSOSOMES Mitochondria Matrix in Mitochondria 1.Also called the Golgi (primarily animal cells) Mito = Mighty / Power Complex 1. When an organelle no longer 1. The Power-House of the 2.It is made up of a stack of works, the lysosome will attach cell flattened out sacs …like a itself to it and break it down like 2. They break down food loose stack of pancakes food (kind of like a cannibal) molecules so the cell has What does it do? 2. Chemicals can then be the energy to live 1. “mailroom” they receive reabsorbed or excreted 3.If a cell needs a lot of proteins, package them, 3. Lysosomes can also destroy the energy…it will have more distribute them to others cell if it breaks open accidentally mitochondria parts of the cell and release 4. The enzymes inside the 4. Mitochondria contain materials to the outside of lysosome spread throughout the enzymes that release the the cell. cell and digest it energy stored in food in the 2. It takes simple molecules 5. Next…smaller molecules are process of cellular and combines them to make released which are absorbed by the respiration. larger molecules. mitochondria The Mitochondria 3. Takes those larger structure has three main molecules and puts them parts: into packs called GOLGI 1.OUTER MEMBRANE: VESICLES covers the mitochondria 2. INNER MEMBRANE: folds many times to Cellular Respiration: increase the surface area food+O2 -----> is changed into because chemical reactions CO2+H2O+ Energy (glycolysis) occur here So…the more space it has this is the process in which food the more energy it can and oxygen combine in the create mitochondria to make carbon 3. MATRIX dioxide and water and release a fluid that has water and energy to do all of the cell’s work. proteins all mixed together VACUOLE Turgor Pressure- force exerted (like a solution) Chloroplasts 1.Vacuoles are “bubbles” that by the water entering (osmosis) the The proteins take the food 1.the site of photosynthesis in float in the cell vacuole, which then swells eukaryotic cells 2.Vacuoles are more important molecules in and combine exerting internal force on the cell 2. disk-like structures to the survival of plant cells them with Oxygen to than they are to animal cells wall release the energy 3.composed of a single membrane 3. Storage In Plant Cells Causes “rigidity” so the plant may CELL WALL 4.surrounding a fluid containing 4. Vacuoles in plants support increase by stacking cells 1.is a rigid layer of stacks of membranous disks SOLAR energy radiated from the sun structure You will know that a plant's nonliving material that is captured by plants chloroplast 5.Vacuoles hold onto things vacuoles are shrinking when you surrounds the cells of that the cell might need…like a see the plant begin to droop over 5.Then it is instantaneously changed backpack plants and some other into ELECTRICAL energy 6.There are some vacuoles that organisms. 6. Then packaged as CHEMICAL hold onto waste products, 2. It protects and supports energy similar to having a big septic the cellIt adds strength 7.are green organelles that trap energy tank 3. Material like water and from sunlight and turn it into food. 7. Storing waste products oxygen can pass through This food is needed by the plant to protects the cell from easily stay alive. As the plant needs energy, contamination 4. It is made from a tough the mitochondria release the food’s 8. So, when there is no water… flexible material called energy the vacuole shrinks and the cell wall is the only thing holding cellulose - fiber we can't the plant together. digest this but it helps keep you regular. Photosynthesis: takes place inside the chloroplast. the process in which plant use water, carbon dioxide, and energy form the sun to make food. No energy transformation is 100% efficient. Not all the solar energy captured is converted to electrical and then chemical energy. Some of it gets lost as heat or other forms of energy (light) sun’s energy + water + carbon dioxide --is changed into--> food and oxygen
Cell Structure and Its Parts
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Recommended publications