233/1 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1
MARKING SCHEME
1. i) Luminous 1mk ii) Flame is sooty; less hot and takes long 1mk iii) Open air hole fully to allow adequate mixing of laboratory gas with air for complete combustion
2. Z is more reactive than y ½ it is easier to remove an electron from Z than from( 1mk) because less energy is required ½ mk 3. a) H H CH3 H – C – C - C – C C– H 1mk H H CH3
b) i) Propyl ethanoate 1mk ii) 3 – Bromo 2methy pent -1-ene 1mk 3- bromo 2- methyl pent – l – ene OR 3, 2 – bromomethylpent – l- ene 4.
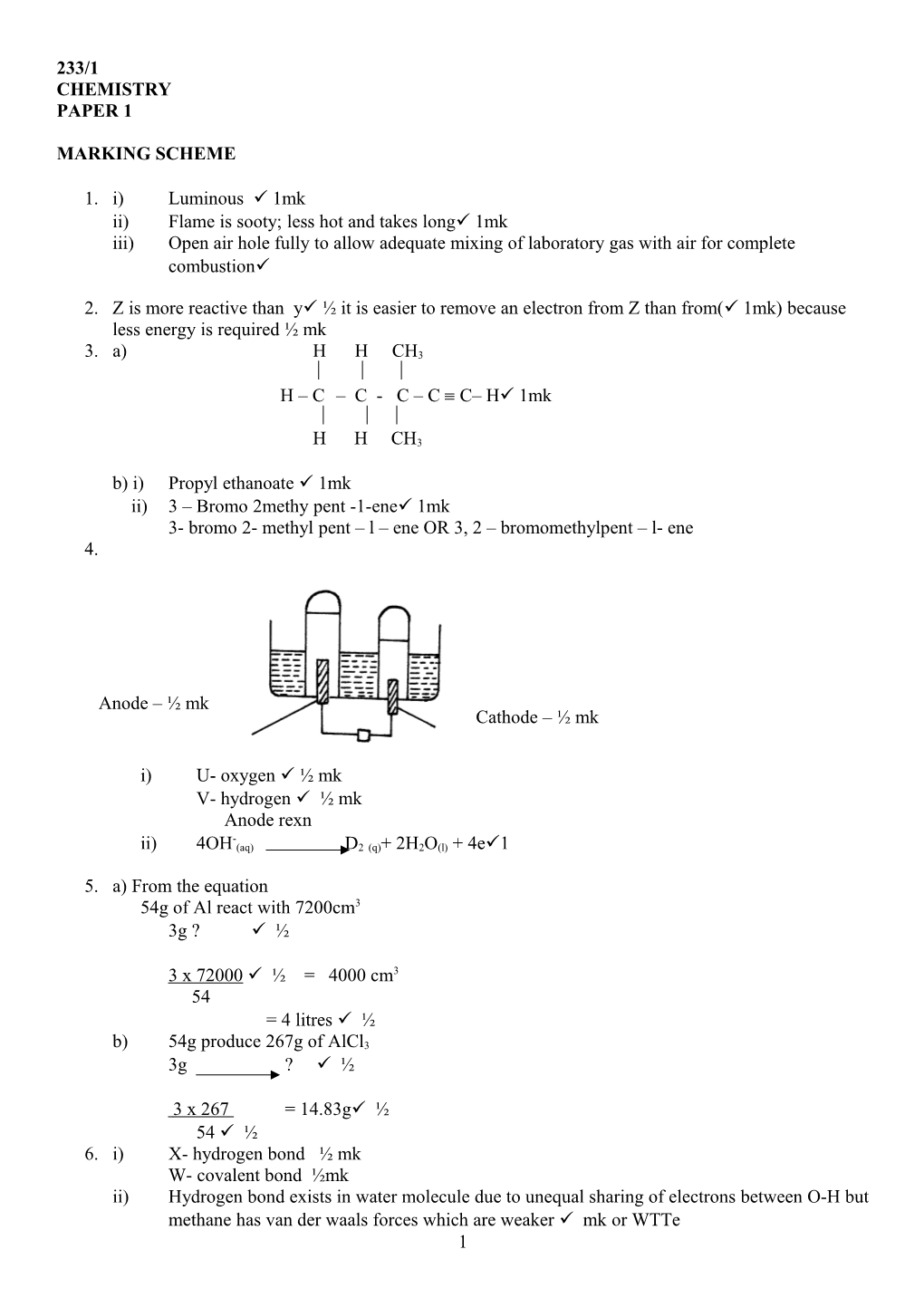
Anode – ½ mk Cathode – ½ mk
i) U- oxygen ½ mk V- hydrogen ½ mk Anode rexn - ii) 4OH (aq) D2 (q)+ 2H2O(l) + 4e1
5. a) From the equation 54g of Al react with 7200cm3 3g ? ½
3 x 72000 ½ = 4000 cm3 54 = 4 litres ½ b) 54g produce 267g of AlCl3 3g ? ½
3 x 267 = 14.83g ½ 54 ½ 6. i) X- hydrogen bond ½ mk W- covalent bond ½mk ii) Hydrogen bond exists in water molecule due to unequal sharing of electrons between O-H but methane has van der waals forces which are weaker mk or WTTe 1 7. Copper metal :- increases ½ because it absorbs / combines with oxygen to form copper ½ (II) oxide Sulphur powder :- Reduces ½ because it combines with oxygen to form sulphur (iv) oxide ½ which escapes ½ reducing mess
8. a) Ammonium chloride / NH4Cl(s) 1
b) Rate NH3 = 60 40 ½ Rate Hcl t t
3 = 60 x t = /2 ½ t 40 c) Graham law constant pressure and temperature the rate of diffusion of a gas is inversely proportional 9. a) sulphur (iv) oxide 1 b) Removes ammonia gas by reacting with it 1
10. Half- life is the time taken for a radio active isotope substance to decay into half its original mass 1mk
1 b) 1 ½ ¼ /8 t1 = 3 half – lifes 1 2 2 x 3 = 6 hours
11. C H O 26.7 2:2 71.1 RAM 12 1 16 No. of moles 26.7 = 2.23 2.2 = 2.2 71.1 = 4.44 12 1 16 All 3 correct ½ mk
Mole ratio 2.23 = 1 2.2 = 1 4.44 = 2 2.2 2.2 2 All 3 correct ½ mk
Mole ration 1: 1: 2
EF CHO2 ½ b) (CHO2)n = 90 45n = 90 n = 2 ½
MF = C2H2O4 ½
12. i) A hydrolysis mk ii) B Bromopropanolmk
iii) C Acidified KMnO4 or K2 Cr2 O7mk
13. a) - Purple colour is deposited at the bottom of the crucible due to iodine subliming - White solid of NaCl remains in the beaker b) To cool iodingevapour to iodine solid.
2 14. H H H H H – C – C - H + Cl – Cl H - C – C - C– Cl + HCl 1mk H H H H
Broken Formed
6(H- C) = 416 x 6 5(H- C) = 414 x 5 = 2070 = 2484 CL- Cl = 432 x 1 = 4320 H – Cl = 340 x 1 = 340 Cl- Cl = 243 x 1 = 243 C - C = 348 = 348 - 3190 C - C = 348 mk + 3075 mk
H = +3075 – 3190 = - 115 Kjmol -1mk
15. Q i) Potassium1/ sodium 1/ cal calcium1 / magnesium1
R – copper (ii) oxide / Cuo 1
ii) Redox (Reduction & oxidation)1
Because Cuo is reduced to copper metal while H2 is oxidized to H2O1
16. Mass of the solute = 142 – 23 = 119g ½
Mass of water 192 - 142 = 50 g ½
Solubility = 119 x 100 = 238g/ 100g of water1 501 + 17. a) i) NH 4 1 ii) OH- 1
b) H2S in a weak acid while H2SO4 is a strong acid
18. i) C ii) A 19. Protons : 301 Neutrons = 65 – 30 = 321
3 20. - Hot platinum wire continues to glow - Brown fames / gas given out in the flask 1 - Platinum is a catalyst for oxidation of ammonia1 the reaction is exothermic and takes place on its surface. Hence , the heat produced keeps the wire glowing 4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) NO(g) + 6H2O
NO is immediately oxidised by air to from nitrogen (iv) oxide, a brown gas 1
2NO(g) + O2(g) 2NO2 (g)
- -1 21. ClO 3 = x- 6 = x = +51
- ClO 4 = x – 8 x = +7 1
22. LJK2 or KJL 1
23. Zn(s) + 2HNO3(aq Zn (NO3)2(aq) + H2O(l) 1
Na2CO3(s) Na2CO3(aq) 1
Na2CO3(aq) + Zn(NO3)2(aq) Zn CO3(s) + 2NaNO3(aq) 1
2- 2+ CO (aq) + Zn (aq) ZnCO3(s) 1 Max 3 3 24. a) wet / moisture 1
b) Yellow solid1 colourless liquid1 formed in the lower jar Explanation Max 1
H2S is oxidized to sulphur (yellow solid )while SO2 is reduced1 to sulphur OR 1 reduced
2H2S(g) + SO2(g) 3S(s) + 2H2O
Oxidised 1 25. In the experiment magnesium reacts with both oxygen1 and nitrogen1 while zinc reacts with oxygen only1. 26. P1 = 760mmHg 3 V1 = 600cm
T1 = 273 + 25 = 298 K ½
T2 = 273 + 50 = 323K ½ P2 = 780 mmHg
P1V1 = P2V2 T1 T2 4
V2 = P1V1 T2 T1 P2
V2 = 760mmHg x 600cm3 x 323K ½ 298k x 780mmHg
= 633.7cm3 ½ (- ½ if units not given) 27 .a) When it does not lather with soap easily 1
b) Boiling 1 c) - Permit any one 1 - distillation - addition Na2CO3 28. a) They prevent air and water from coming in contact with the metals since theycoat the metal 1 b) Because the material used for galvanizing e.g. Zinc is more reactive than iron. Once scratched they form oxides which prevent rusting1
29. a) NH4Cl is soluble; NaHCO3 is insoluble ½ Hence separated by filtration ½
b) By ½ heating NaHCO3 which decomposes to Na2CO3 NaHCO3(s) Na2CO3(s) + H2O(l) + CO2
c) Ammonium chloride is reacted with slaked lime / calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2(aq) + NH4Cl(aq) Cacl2(aq) + H2O(l) + NH3(g) 30. - Increasing pressure - Lowering temperature - Increasing concentration of reactants
5 6