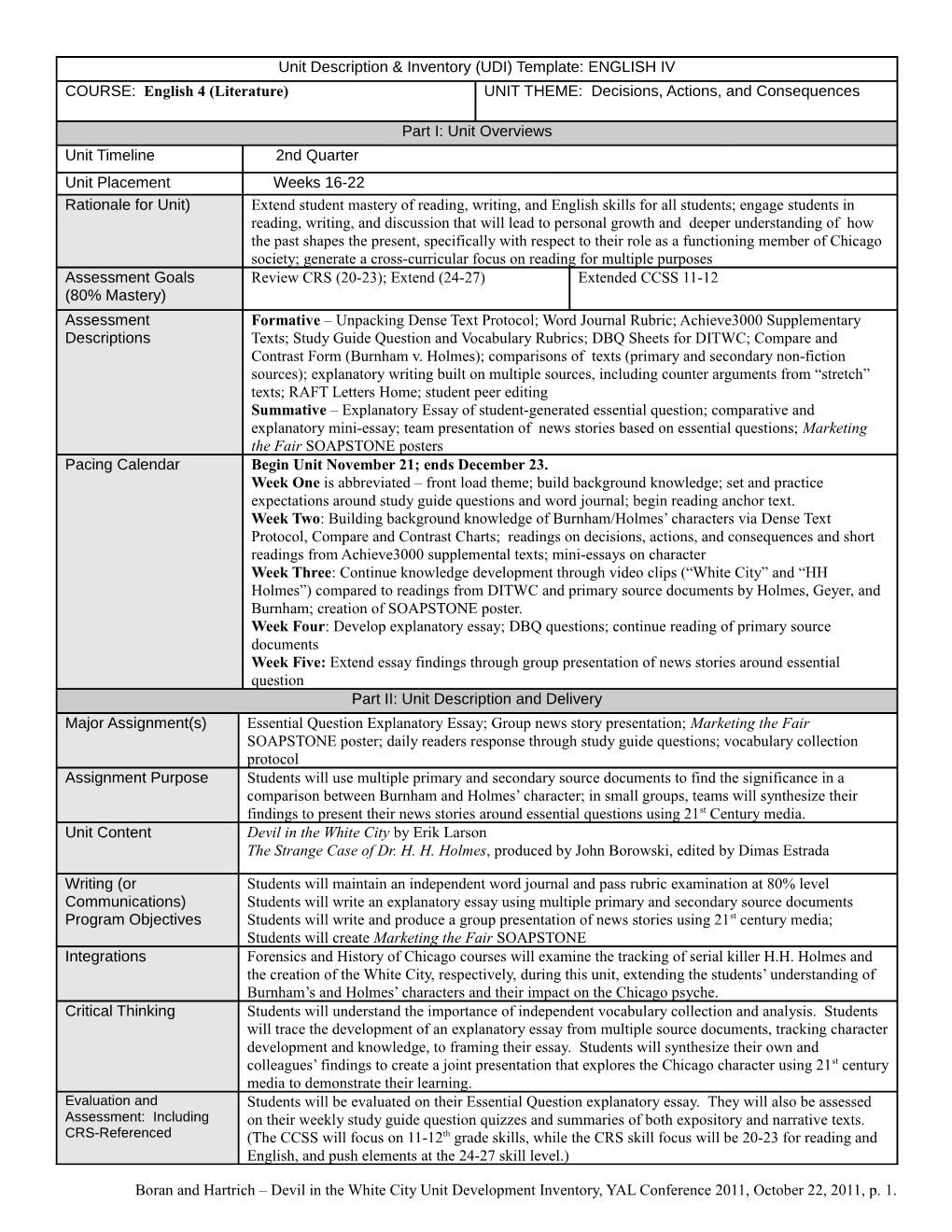
Unit Description & Inventory (UDI) Template: ENGLISH IV COURSE: English 4 (Literature) UNIT THEME: Decisions, Actions, and Consequences
Part I: Unit Overviews Unit Timeline 2nd Quarter Unit Placement Weeks 16-22 Rationale for Unit) Extend student mastery of reading, writing, and English skills for all students; engage students in reading, writing, and discussion that will lead to personal growth and deeper understanding of how the past shapes the present, specifically with respect to their role as a functioning member of Chicago society; generate a cross-curricular focus on reading for multiple purposes Assessment Goals Review CRS (20-23); Extend (24-27) Extended CCSS 11-12 (80% Mastery) Assessment Formative – Unpacking Dense Text Protocol; Word Journal Rubric; Achieve3000 Supplementary Descriptions Texts; Study Guide Question and Vocabulary Rubrics; DBQ Sheets for DITWC; Compare and Contrast Form (Burnham v. Holmes); comparisons of texts (primary and secondary non-fiction sources); explanatory writing built on multiple sources, including counter arguments from “stretch” texts; RAFT Letters Home; student peer editing Summative – Explanatory Essay of student-generated essential question; comparative and explanatory mini-essay; team presentation of news stories based on essential questions; Marketing the Fair SOAPSTONE posters Pacing Calendar Begin Unit November 21; ends December 23. Week One is abbreviated – front load theme; build background knowledge; set and practice expectations around study guide questions and word journal; begin reading anchor text. Week Two: Building background knowledge of Burnham/Holmes’ characters via Dense Text Protocol, Compare and Contrast Charts; readings on decisions, actions, and consequences and short readings from Achieve3000 supplemental texts; mini-essays on character Week Three: Continue knowledge development through video clips (“White City” and “HH Holmes”) compared to readings from DITWC and primary source documents by Holmes, Geyer, and Burnham; creation of SOAPSTONE poster. Week Four: Develop explanatory essay; DBQ questions; continue reading of primary source documents Week Five: Extend essay findings through group presentation of news stories around essential question Part II: Unit Description and Delivery Major Assignment(s) Essential Question Explanatory Essay; Group news story presentation; Marketing the Fair SOAPSTONE poster; daily readers response through study guide questions; vocabulary collection protocol Assignment Purpose Students will use multiple primary and secondary source documents to find the significance in a comparison between Burnham and Holmes’ character; in small groups, teams will synthesize their findings to present their news stories around essential questions using 21st Century media. Unit Content Devil in the White City by Erik Larson The Strange Case of Dr. H. H. Holmes, produced by John Borowski, edited by Dimas Estrada
Writing (or Students will maintain an independent word journal and pass rubric examination at 80% level Communications) Students will write an explanatory essay using multiple primary and secondary source documents Program Objectives Students will write and produce a group presentation of news stories using 21st century media; Students will create Marketing the Fair SOAPSTONE Integrations Forensics and History of Chicago courses will examine the tracking of serial killer H.H. Holmes and the creation of the White City, respectively, during this unit, extending the students’ understanding of Burnham’s and Holmes’ characters and their impact on the Chicago psyche. Critical Thinking Students will understand the importance of independent vocabulary collection and analysis. Students will trace the development of an explanatory essay from multiple source documents, tracking character development and knowledge, to framing their essay. Students will synthesize their own and colleagues’ findings to create a joint presentation that explores the Chicago character using 21st century media to demonstrate their learning. Evaluation and Students will be evaluated on their Essential Question explanatory essay. They will also be assessed Assessment: Including on their weekly study guide question quizzes and summaries of both expository and narrative texts. CRS-Referenced (The CCSS will focus on 11-12th grade skills, while the CRS skill focus will be 20-23 for reading and English, and push elements at the 24-27 skill level.)
Boran and Hartrich – Devil in the White City Unit Development Inventory, YAL Conference 2011, October 22, 2011, p. 1. Part III: Inventory MATERIALS WE HAVE MATERIALS WE NEED Word Journal Samples, Word Journal Rubric Sample journal for model; Protocols Modified Frayer Model Tutorials and exercises for 24-27 Visual idioms Tracing Reference Words Study Guide Questions Scoring and Annotation Instructions Study Guide Question Rubric Compare and Contrast Charts (T, Y, Venn) Plot Synopsis Chess Save the Last Word For Me Storyboards Choral Montage instructions Hotseat instructions, rubric Wordsplash instructions
CRS Reading Skills Devil in the White City by Erik Larson Two essays on Chicago then and now Materials Achieve3000 articles The Strange Case of Dr. H. H. Holmes, produced Images for Picture into Words by John Borowski, edited by Dimas Estrada What makes a good essential question article
(Explanatory) Writing SOAPSTONE instructions SOAPSTONE rubric Program Materials RAFT Letters Home instructions Peer editing rubric, protocol RAFT rubric Essential Question Essay rubric Mini Essay (character, explanatory) rubric News story model, rubric, protocol
CCSS Emphasis Reading: Key Ideas and Details: RI 11-12.2 – Determine two or more central ideas of a text and analyze their development over the course of the text, including how they interact and build on one another to provide a complex analysis; provide an objective summary of the text. Craft and Structure: RI 11-12.4 – Determine the meaning of words and phrases as they are used in text, including figurative, connotative, and technical meanings; analyze how an author uses and refines the meaning of a key term or terms over the course of a text Range of Reading and Level of Text Complexity: RI 11-12.10 – By the end of grate 11, read and comprehend literary nonfiction in the grades 11-CCR text complexity band proficiently, with scaffolding as needed at the high end of the range. Writing: Text Types and Purposes: W 11-12.2b – Develop the topic thoroughly by selecting the most significant and relevant facts, extended definitions, concrete details, quotations, or other information and examples appropriate to the audience’s knowledge of the topic. Production and Distribution of Writing: W 11-12.4 – Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. Production and Distribution of Writing: W 11-12.5 – Develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach, focusing on addressing what is more significant for a specific purpose and audience. Research to Build and Present Knowledge: W 11-12.7 – Conduct short as well as more sustained research projects to answer a question (including a self-generated question) or solve a problem; narrow or broaden the inquiry when appropriate; synthesize multiple sources on the subject, demonstrating understanding of the subject under investigation. Range of Writing: W 11-12.10 – Write routinely over extended time frames (time for research, reflection, and revision) and shorter time frames (a single sitting or a day or two) for a range of tasks, purposes, and audiences.
Boran and Hartrich – Devil in the White City Unit Development Inventory, YAL Conference 2011, October 22, 2011, p. 2. CCSS Emphasis, Speaking and Listening: continued Comprehension and Collaboration: SL 11-12.1.a – Come to discussions prepared, having red and researched material under study; explicitly draw on that preparation by referring to evidence from texts and other research on the topic or issue to stimulate a thoughtful, well- reasoned exchange of ideas. Comprehension and Collaboration: SL 11-12.1.b– Work with peers to promote civil, democratic discussions and decision-making, set clear goals and deadlines, and establish individual roles as needed. Comprehension and Collaboration: SL 11-12.2 – Integrate multiple sources of information presented in diverse formats and media (e.g., visually, quantitatively, orally) in order to make informed decisions and solve problems, evaluating the credibility and accuracy of each source and noting any discrepancies among the data. Presentation of Knowledge and Ideas SL 11-12.4 – Present information, findings, and supporting evidence, conveying a clear and distinct perspective, such that listeners can follow the line of reasoning, alternative or opposing perspectives are addressed, and the organization, development, substance, and style are appropriate to purpose, audience, and a range of formal and informal tasks. Presentation of Knowledge and Ideas SL 11-12.5 – Make use of digital media (e.g., textual, graphic, audio, visual, and interactive elements) in presentations to enhance understanding of findings, reasoning, and to add interest. Language: Conventions of Standard English SL 11-12.2 – Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing Vocabulary Acquisition and Use L 11-12.4a – Use context (e.g., the overall meaning of a sentence, paragraph, or text; a word’s position or function in a sentence) as a clue to the meaning of a word or phrase. Vocabulary Acquisition and Use L 11-12.4c -- Consult general and specialized reference materials (e.g., dictionaries, glossaries, thesauruses), both print and digital, to find the pronunciation of a word or determine or clarify its precise meaning, its part of speech, its etymology, or its standard usage. Vocabulary Acquisition and Use L 11-12.5a – Interpret figures of speech (e.g., hyperbole, paradox) in context and analyze their role in text. Vocabulary Acquisition and Use L 11-12.5.b – Analyze nuances in the meanings of words with similar denotations. Vocabulary Acquisition and Use L 11-12.6 – Acquire and use general academic and domain- specific words and phrases, sufficient for reading, writing, speaking and listening at the college and career readiness level; demonstrate independence in gathering vocabulary knowledge when considering a word or phrase important to comprehension or expression.
Boran and Hartrich – Devil in the White City Unit Development Inventory, YAL Conference 2011, October 22, 2011, p. 3.