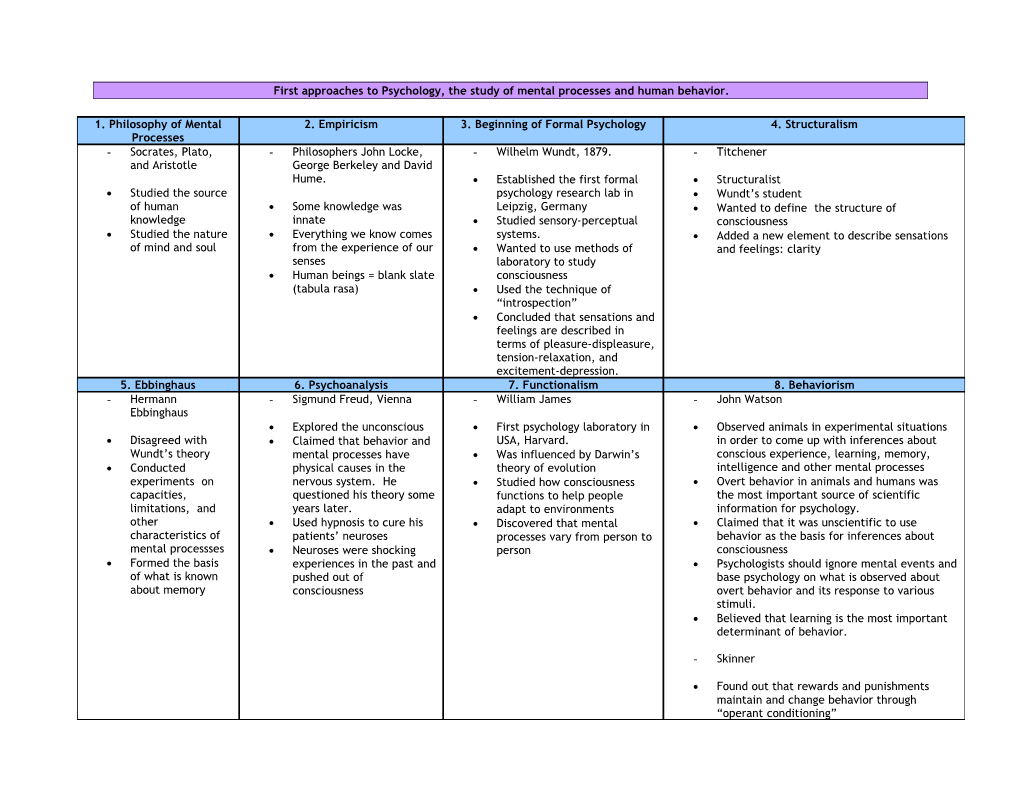
First approaches to Psychology, the study of mental processes and human behavior.
1. Philosophy of Mental 2. Empiricism 3. Beginning of Formal Psychology 4. Structuralism Processes - Socrates, Plato, - Philosophers John Locke, - Wilhelm Wundt, 1879. - Titchener and Aristotle George Berkeley and David Hume. Established the first formal Structuralist Studied the source psychology research lab in Wundt’s student of human Some knowledge was Leipzig, Germany Wanted to define the structure of knowledge innate Studied sensory-perceptual consciousness Studied the nature Everything we know comes systems. Added a new element to describe sensations of mind and soul from the experience of our Wanted to use methods of and feelings: clarity senses laboratory to study Human beings = blank slate consciousness (tabula rasa) Used the technique of “introspection” Concluded that sensations and feelings are described in terms of pleasure-displeasure, tension-relaxation, and excitement-depression. 5. Ebbinghaus 6. Psychoanalysis 7. Functionalism 8. Behaviorism - Hermann - Sigmund Freud, Vienna - William James - John Watson Ebbinghaus Explored the unconscious First psychology laboratory in Observed animals in experimental situations Disagreed with Claimed that behavior and USA, Harvard. in order to come up with inferences about Wundt’s theory mental processes have Was influenced by Darwin’s conscious experience, learning, memory, Conducted physical causes in the theory of evolution intelligence and other mental processes experiments on nervous system. He Studied how consciousness Overt behavior in animals and humans was capacities, questioned his theory some functions to help people the most important source of scientific limitations, and years later. adapt to environments information for psychology. other Used hypnosis to cure his Discovered that mental Claimed that it was unscientific to use characteristics of patients’ neuroses processes vary from person to behavior as the basis for inferences about mental processses Neuroses were shocking person consciousness Formed the basis experiences in the past and Psychologists should ignore mental events and of what is known pushed out of base psychology on what is observed about about memory consciousness overt behavior and its response to various stimuli. Believed that learning is the most important determinant of behavior.
- Skinner
Found out that rewards and punishments maintain and change behavior through “operant conditioning” Modern Psychology
- Psychologists are dissatisfied with limitations imposed by behaviorism - Uncomfortable with ignoring mental processes that might be important to fully understand behavior - Computers enabled psychologists to measure mental activity and to study the biological bases of mental processes. - Cognitive and biological factors are influential - Commitment to empiricism and scientific research - Evolution of psychology into subfields - Your approach to psychology –that is, the set of assumptions, questions, and methods that you believe will be most helpful for understanding the behavior and mental processes you wish to explore. - Some psychologists have adopted an eclectic approach, combining features of two or more approaches because they believe that no one perspective can fully account for all aspects of psychological phenomena.
Biological approach Evolutionary approach Psychodynamic approach Behavior and mental processes are shaped The foundation for this approach was Rooted in Freud’s psychoanalysis by biological processes. English naturalist Charles Darwin’s book, All behavior and mental processes reflect the Study of the psychological effects of The Origin of Species. constant and mostly unconscious psychological hormones, genes, and the activity of the The behavior of animals and humans struggles that rage silently within each person. nervous system, especially the brain. today is the result of evolution through Conflict to satisfy instincts or wishes and the Patterns of brain activity natural selection. need to put up with the social restrictions. Psychologists who take an evolutionary approach try to understand: a) the adaptive value of behavior b) the anatomical and biological mechanisms that make behavior possible c) the environmental conditions that encourage or discourage behavior Behavioral approach Cognitive approach Humanistic approach Behavior and mental processes are the Focuses on how people take in, mentally Also called phenomenological approach primary results of learning. represent, and store information Behavior is determined primarily by each Behaviorists try to understand behavior in Studies how cognitive processes are person’s capacity to choose how to think and terms of an individual’s learning history, related to the integrated patterns of act. These choices are dictated by each especially the patterns of reward and behavior we can see individual’s perceptions. punishment experienced. Attempts to discover the building blocks Celebrates immediate, individual experience. People can change problematic behaviors of cognition and to determine how these Behavior and mental processes can be by unlearning old habits and developing components produce complex behaviors understood by appreciating the perceptions and new ones. feelings experienced by each individual. People are essentially good, in control of themselves, and their main innate tendency is to grow toward their highest potential.